Abstract
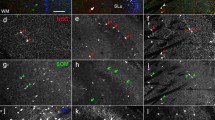
The ventral part of the cat oral pontine reticular nucleus (vRPO) is the site in which microinjections of small dose and volume of cholinergic agonists produce long-lasting rapid eye movement sleep with short latency. The present study determined the precise location and proportions of the cholinergic brainstem neuronal population that projects to the vRPO using a double-labeling method that combines the neuronal tracer horseradish peroxidase–wheat germ agglutinin with choline acetyltransferase immunocytochemistry in cats. Our results show that 88.9% of the double-labeled neurons in the brainstem were located, noticeably bilaterally, in the cholinergic structures of the pontine tegmentum. These neurons occupied not only the pedunculopontine and laterodorsal tegmental nuclei, which have been described to project to other pontine tegmentum structures, but also the locus ceruleus complex principally the locus ceruleus α and peri-α, and the parabrachial nuclei. Most double-labeled neurons were found in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus and locus ceruleus complex and, much less abundantly, in the laterodorsal tegmental nucleus and the parabrachial nuclei. The proportions of these neurons among all choline acetyltransferase positive neurons within each structure were highest in the locus ceruleus complex, followed in descending order by the pedunculopontine and laterodorsal tegmental nuclei and then, the parabrachial nuclei. The remaining 11.1% of double-labeled neurons were found bilaterally in other cholinergic brainstem structures: around the oculomotor, facial and masticatory nuclei, the caudal pontine tegmentum and the praepositus hypoglossi nucleus. The disperse origins of the cholinergic neurons projecting to the vRPO, in addition to the abundant noncholinergic afferents to this nucleus may indicate that cholinergic stimulation is not the only or even the most decisive event in the generation of REM sleep.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 10M :
-
Motor nucleus of the vagus nerve
- 3 :
-
Nucleus of the oculomotor nerve
- 3N :
-
Oculomotor nerve
- 4 :
-
Nucleus of the trochlear nerve
- 4N :
-
Trochlear nerve
- 5M :
-
Motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve
- 5N :
-
Trigeminal nerve
- 5P :
-
Principal trigeminal nucleus
- 5SN :
-
Spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve
- 5ST :
-
Spinal trigeminal tract
- 6 :
-
Nucleus of the abducens nerve
- 6N :
-
Abducens nerve
- 7 :
-
Nucleus of the facial nerve
- 7N :
-
Facial nerve
- A :
-
Nucleus ambiguous
- BC :
-
Brachium conjunctivum
- BP :
-
Brachium pontis
- Cnf :
-
Cuneiform nucleus
- CS :
-
Central superior raphe nucleus
- CtF :
-
Centrotegmental fascicle
- DR :
-
Dorsal raphe nucleus
- GR :
-
Gigantocellular reticular formation
- IC :
-
Inferior colliculus
- IO :
-
Inferior olive
- Ip :
-
Interpeduncular nucleus
- LC :
-
Locus coeruleus principal
- LCC :
-
Locus coeruleus complex
- LCα :
-
Locus coeruleus alpha
- LdT :
-
Laterodorsal tegmental nucleus
- Li :
-
Linearis centralis raphe nucleus
- LL :
-
Lateral lemniscus
- M5 :
-
Mesencephalic trigeminal tract
- ML :
-
Medial lemniscus
- MLF :
-
Medial longitudinal fascicle
- MR :
-
Raphe magnus nucleus
- MRF :
-
Mesencephalic reticular formation
- P :
-
Pyramidal tract
- PaG :
-
Central grey matter
- PbD :
-
Dorsal parabrachial nucleus
- Pbg :
-
Parabigeminal nucleus
- PbV :
-
Ventral parabrachial nucleus
- PH :
-
Praepositus hypoglossi nucleus
- PoR :
-
Raphe pontis nucleus
- PpT :
-
Pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus
- Pα :
-
Perilocus coeruleus alpha
- RB :
-
Restiform body
- RM :
-
Raphe magnus nucleus
- RN :
-
Red nucleus
- RP :
-
Raphe pontis nucleus
- RPC :
-
Caudal pontine reticular nucleus
- RPO :
-
Oral pontine reticular nucleus
- SC :
-
Superior colliculus
- SCoe :
-
Nucleus subcoeruleus
- SF :
-
Solitary fascicle
- SN :
-
Substancia nigra
- SO :
-
Superior olive
- TD :
-
Dorsal tegmental nucleus of Gudden
- Tp :
-
Tegmental pontine nucleus
- Tr :
-
Trapezoid body
- TV :
-
Ventral tegmental nucleus of Gudden
- vRPO :
-
Ventral part of the RPO
References
Baghdoyan HA, Rodrigo-Angulo ML, McCarley RW, Hobson JA (1984) Site specific enhancement and suppression of desynchronized signs following cholinergic stimulation of three brainstem regions. Brain Res 306:39–52
Baghdoyan HA, Rodrigo-Angulo ML, McCarley RW, Hobson JA (1987) A neuroanatomical gradient in the pontine tegmentum for the cholinoceptive induction of desynchronized sleep signs. Brain Res 414:245–261
Baghdoyan HA, Spotts JL, Snyder SG (1993) Simultaneous pontine and basal forebrain microinjections of carbachol suppress REM sleep. J Neurosci 13:229–242
Bier MJ, McCarley RW (1994) REM-enhancing effects of the adrenergic antagonist idazoxan infused into the medial pontine reticular formation of the freely moving cat. Brain Res 634:333–338
De Andrés I, Manquillo A, Garzón M, Reinoso-Suárez F (1998) Polygraphic and behavioural effects of small-volume and low-dose carbachol microinjections in the caudal perilocus coeruleus α. J Sleep Res 7 [Suppl 2]:58
Deurveilher S, Hars B, Hennevin E (1997) Pontine microinjections of carbachol does not reliably enhance paradoxical sleep in rats. Sleep 20:593–607
Garzón M (1996) Estudio morfofuncional de los núcleos reticular oral y reticular caudal del tegmento pontino como regiones generadoras de sueño paradójico. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid
Garzón M, De Andrés I, Reinoso-Suárez F (1996) Sleep patterning after cholinergic and glutamatergic stimulation in the ventral oral pontine tegmentum. J Sleep Res 5 [Suppl 1]:72
Garzón M, De Andrés I, Reinoso-Suárez F (1997) Neocortical and hippocampal electrical activities are similar in spontaneous and cholinergic-induced REM sleep. Brain Res 766:266–270
Garzón M, De Andrés I, Reinoso-Suárez F (1998) Sleep patterns after carbachol delivery in the ventral oral pontine tegmentum of the cat. Neuroscience 83:1137–1144
Henderson Z, Sherrif FE (1991) Distribution of choline acetyltransferase immunoreactive axons and terminals in the rat and ferret brainstem. J Comp Neurol 314:147–163
Holmes CJ, Mainville LS, Jones BE (1994) Distribution of cholinergic, GABAergic and serotonergic neurons in the medial medullary reticular formation and their projections studied by cytotoxic lesions in the cat. Neuroscience 62:1155–1178
Horner RL, Kubin L (1999) Pontine carbachol elicits multiple rapid eye movement sleep-like neural events in urethane-anaesthetized rats. Neuroscience 93:215–226
Ito K, McCarley RW (1987) Physiological studies of brainstem reticular connectivity. I. Responses of mPRF neurons to stimulation of bulbar reticular formation. Brain Res 409:97–110
Iwakiri H, Matsuyama K, Mori S (1993) Extracellular levels of serotonin in the medial pontine reticular formation in relation to sleep-wake cycle in cats: a microdialysis study. Neurosci Res 18:157–170
Jones BE (1990) Immunohistochemical study of choline acetyltransferase-immunoreactive processes and cells innervating the pontomedullary reticular formation in the rat. J Comp Neurol 295:485–514
Jones BE (1991) Paradoxical sleep and its chemical/structural substrates in the brain. Neuroscience 40:637–656
Jones BE, Beaudet A (1987) Distribution of acetylcholine and catecholamine neurons in the cat brainstem: A choline acetyltransferase and tyrosine hydroxylase immunohistochemical study. J Comp Neurol 261:15–32
Kimura H, McGeer P, Peng JH, McGeer EG (1981) The central cholinergic system studied by choline acetyltransferase immunohistochemistry in the cat. J Comp Neurol 200:151–201
Kohlmeier KA, Burns J, Reiner PB, Semba K (2002) Substance P in the descending cholinergic projection to REM sleep-induction regions of the rat pontine reticular formation: Anatomical and electrophysiological analyses. Eur J Neurosci 15:176–196
Kshatri AM, Baghdoyan HA, Lydic R (1998) Cholinomimetics, but not morphine, increase antinociceptive behavior from pontine reticular regions regulating rapid-eye-movement sleep. Sleep 21:677–685
Lai YY, Clements JR, Siegel JM (1993) Glutamatergic and cholinergic projections to the pontine inhibitory area identified with horseradish peroxidase retrograde transport and immunohistochemistry. J Comp Neurol 336:321–330
Leonard TO, Lydic R (1997) Pontine nitric oxide modulates acetylcholine release, rapid eye movement sleep generation, and respiratory rate. J Neurosci 17:774–875
Manquillo A (2000) Estudio de los mecanismos colinérgicos y gabaérgicos mediados por el tegmento pontino rostral en las fases del ciclo vigilia-sueño. Thesis, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid
Mesulam MM (1982) Tracing neural connections with horseradish peroxidase. Wiley, Chichester
Mitani A, Ito K, Mitani Y, McCarley RW (1988a) Descending projections from the gigantocellular tegmental field in the cat: cells of origin and their brainstem and spinal cord trajectories. J Comp Neurol 268:546–566
Mitani A, Ito K, Hallanger AE, Wainer BH, Kataoka K, McCarley RW (1988b) Cholinergic projections from the laterodorsal and pedunculopontine tegmental nuclei to the pontine gigantocellular tegmental field in the cat. Brain Res 451:397–402
Núñez A, de la Roza C, Rodrigo-Angulo ML, Buño W, Reinoso-Suárez F (1997) Electrophysiological properties and cholinergic responses to rat ventral oral pontine reticular neurons in vitro. Brain Res 754:1–11
Núñez A, Rodrigo-Angulo ML, De Andrés I, Reinoso-Suárez F (2002) Firing activity and postsynaptic properties of morphologically identified neurons of ventral oral pontine reticular nucleus. Neuroscience 115:1165–1175
Pace-Schott EF, Hobson JA (2002) The neurobiology of sleep: genetics, cellular physiology and subcortical networks. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:591–605
Reinoso-Suárez F (1961) Topographischer Hirnatlas der Katze. Merck, Darmstad
Reinoso-Suárez F, Rodrigo-Angulo ML, Rodríguez-Veiga E, De Andrés I (1990) Thalamic connections of the oral pontine tegmentum sites whose cholinergic stimulation produces enhancement of paradoxical sleep signs. In: Mancia M, Marini G (eds) The diencephalon and sleep. Raven, New York, pp 49–63
Reinoso-Suárez F, De Andrés I, Rodrigo-Angulo ML, Rodríguez-Veiga E (1994) Location and anatomical connections of a paradoxical sleep induction site in the cat ventral pontine tegmentum. Eur J Neurosci 6:1829–1836
Reinoso-Suárez F, De Andrés I, Rodrigo-Angulo ML, De la Roza C, Núñez A, Garzón M (1999) The anatomy of dreaming and REM sleep. Eur J Anat 3:163–175
Reinoso-Suárez F, De Andrés I, Rodrigo-Angulo ML, Garzón M (2001) Brain structures and mechanisms involved in the generation of REM sleep. Sleep Med Rev 5:63–77
Rodrigo-Angulo ML, Rodríguez-Veiga E, Reinoso-Suárez F (2000) Serotonergic connections to the ventral oral pontine reticular nucleus: Implication in paradoxical sleep modulation. J Comp Neurol 418:93–105
Roza C de la, Reinoso-Suárez F (2000) Ultrastructural synaptic organization of axon terminals in the ventral part of the cat oral pontine reticular nucleus. J Comp Neurol 427:31–53
Saper CB, Chou TC, Scammell TE (2001) The sleep switch: hypothalamic control of sleep and wakefulness. Trends Neurosci 24:726–731
Semba K (1993) Aminergic and cholinergic afferents to REM sleep induction regions of the pontine reticular formation in the rat. J Comp Neurol 330:543–556
Semba K (1999) The mesopontine cholinergic system: A dual role in REM sleep and wakefulness. In: Lydic R, Baghdoyan HA (eds) Handbook of behavioral state control: cellular and molecular mechanisms. CRC, pp 161–180
Shiromani PJ, Armstrong DM, Berkowitz A, Jeste DV, Gillin JC (1988a) Distribution of choline acetyltransferase immunoreactive somata in the feline brainstem: Implications for REM sleep generation. Sleep 11:1–16
Shiromani PJ, Armstrong DM, Gillin JC (1988b) Cholinergic neurons from the dorsolateral pons project to the medial pons: a WGA-HRP and choline acetyltransferase immunohistochemical study. Neurosci Lett 95:19–23
Steriade M, Paré D, Datta S, Oakson G, Curró-Dossi R (1990) Different cellular types in mesopontine cholinergic nuclei related to ponto-geniculo-occipital waves. J Neurosci 10:2560–2579
Vanni-Mercier G, Sakai K, Lin JS, Jouvet M (1989) Mapping of cholinoceptive brainstem structures responsible for the generation of paradoxical sleep in the cat. Arch Ital Biol 127:133–164
Vincent SR, Reiner PB (1987) The immunohistochemical localization of choline acetyltransferase in the cat brain. Brain Res Bull 18:371–415
Wiklund L, Léger L, Persson M (1981) Monoamine cell distribution in the cat brain stem. A fluorecensce histochemical study with quantification of indolaminergic and locus coeruleus cell groups. J Comp Neurol 203:613–647
Yamamoto K, Mamelak AN, Quattrochi JJ, Hobson JA (1990) A cholinoceptive desynchronized sleep induction zone in the anterodorsal pontine tegmentum: locus of the sensitive region. Neuroscience 39:279–293
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. I. De Andrés for critical reading and valuable suggestions of the manuscript and C. Warren for revising the English. The technical assistance of G. de la Fuente, P. Romero and R.M. Sánchez-Lozano is gratefully acknowledged. Supported by Grants DGESIC PB98-0097 and BFI2002–01314
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigo-Angulo, M.L., Rodríguez-Veiga, E. & Reinoso-Suárez, F. A quantitative study of the brainstem cholinergic projections to the ventral part of the oral pontine reticular nucleus (REM sleep induction site) in the cat. Exp Brain Res 160, 334–343 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-004-2015-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-004-2015-x