Abstract
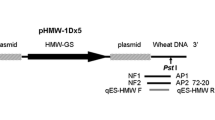
In this study, 3′-flanking sequence between the host plant DNA and the integrated gene construct of pHMW1Dx5 vector in transgenic wheat B73-6-1 was revealed by means of adaptor PCR; thus, the fragment with the length of 3.1 kb was obtained, including a 190-bp wheat genomic DNA, which demonstrates that this HMW-GS gene was located on the wheat chromosome 3B. And the event-specific PCR primers were designed based upon the revealed 3′-flanking sequence; the conventional qualitative PCR and quantitative SYBR real-time PCR detection methods employing these primers were successfully developed. In conventional qualitative PCR assay, the limit of detection was 0.1 % for B73-6-1 wheat genomic DNA for one reaction. In the quantitative SYBR real-time PCR assay, the limit of detection and limit of quantification were 10 and 100 haploid genome copies, respectively. In addition, three mixed blind wheat samples with known B73-6-1 contents were detected using the established real-time PCR systems, and the ideal results indicated that the established event-specific real-time PCR detection systems were reliable, sensitive and accurate.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
James C. (2011) Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops: 2011. ISAAA brief no. 43. ISAAA, Ithaca
Liu J, Guo JC, Zhang HB, Li N, Yang LT, Zhang DB (2009) Development and in-house validation of the event specific polymerase chain reaction detection methods for genetically modified soybean MON89788 based on the cloned integration flanking sequence. J Agric Food Chem 57:10524–10530
Windels P, Taverniers I, Depicker A, Bockstaele EV, Loose MD (2001) Characterisation of the Roundup Ready soybean insert. Eur Food Res Technol 213:107–112
Alvarez ML, Guelman S, Halford NG, Lustig S, Reggiardo MI, Ryabushkina N, Shewry P, Stein J, Vallejos RH (2000) Silencing of HMW glutenins in transgenic wheat expressing extra HMW subunits. Theor Appl Genet 100:319–327
Barro F, Rooke L, Bekes F, Gras P, Tatham AS, Fido R (1997) Transformation of wheat with high-molecular-weight subunit genes results in improved functional properties. Nature Biotechnol 15:1295–1299
Shewry PR, Halford NG, Tatham AS, Popineau Y, Lafiandra D, Belton PS (2003) The high molecular weight subunits of wheat glutenin and their role in determining wheat processing properties. Adv Food Nutr Res 45:221–302
Darlington H, Fido R, Tatham AS, Jones HD, Salmon SE, Shewry PR (2003) Milling and baking properties of field grown wheat expressing HMW subunit transgenes. J Cereal Sci 38:301–306
Anderson OD, Greene FC, Yip RE, Halford NG, Shewry PR, Malpica-Romero JM (1989) Nucleotide sequences of the two high-molecular-weight glutenin genes from the d-genome of a hexaploid bread wheat Triticum aestivum L. cv Cheyenne. Nucl Acids Res 17:461–462
Luan FX, Zhang HX, Bai Y (2007) Screening and detecting of genetically modified components in transgenic wheat by PCR. J Triticeae Crops 27:378–381 (In Chinese)
Bulletin No.869-8-2007 of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China (2007) Detection of genetically modified plants and derived products qualitative PCR method for insect-resistant maize MON810 and its derivates[S]. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Bulletin No.1485-6-2010 of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China (2010) Detection of genetically modified plants and derived products qualitative PCR method for herbicide-tolerant soybean MON89788 and its derivates[S]. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Bulletin No.1193-3-2009 of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China (2009) Detection of genetically modified plants and derived products qualitative PCR method for insect-resistant rice TT51-1 and its derivates[S]. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Bulletin No.1485-10-2010 of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China (2010) Detection of genetically modified plants and derived products qualitative PCR method for herbicide-tolerant cotton LLcotton25 and its derivates[S]. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Bulletin No.869-4-2007 of the Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China (2007) Detection of genetically modified plants and derived products qualitative PCR method for herbicide-tolerant rapeseed MS1, RF1 and their derivates[S]. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Luan FX, Zhang HX, Bai Y (2007) Protocol of polymerase chain reaction and real-time PCR for qualitative detecting genetically modified components in transgenic wheat[S]. SN/T 1943–2007 Standards Press of China, Beijing
Definition of Minimum Performance Requirements for Analytical Methods of GMO Testing-ENGL, http://gmo-crl.jrc.ec.europa.eu/doc/Min_Perf_Requirements_Analytical_methods.pdf
Liu B, Su Q, Tang MQ, Yuan XD, An LJ (2006) Progress of the PCR amplification techniques for chromosome walking. Hereditas 28:587–595
Zhang Y, Liu DQ, Yang WX, Li YN, Yan HF (2011) A nonspecific primer anchored PCR technique for chromosome walking. Brazilian Arch Biol Andtechnol 54:99–106
Holst-Jensen A, Røning SB, Løseth A, Berdal KG (2003) PCR technology for screening and quantification of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Anal Bioanal Chem 375:985–993
Miraglia M, Berdal KG, Brera C, Corbisier P, Holst-Jensen A, Kok EJ et al (2004) Detection and traceability of genetically modified organisms in the food production chain Food Chem. Toxicology 42:1157–1180
Bai Y, Luan FX, Wang X (2009) Detection Limits of PCR and Real time PCR for Genetically Modified Components in Transgenic Wheat. J Triticeae Crop 29:199–205 (In Chinese)
Taverniers I, Windels P, Van BE, De M (2001) Use of cloned DNA fragments for event specific quantification of genetically modified organisms in pure and mixed food products. Eur Food Res Technol 213:417–424
Lau LT, Collins RA, Yiu S, Xing J, Yu AC (2004) Detection and characterization of recombinant DNA in the Roundup Ready soybean insert. Food Control 15:471–478
Terry CF, Harris N (2001) Event specific detection of roundup ready soya using two different real time PCR detection chemistries. Eur Food Res Technol 213:425–431
Hernández M, Pla M, Esteve T, Prat S, Puigdomènech P, Ferrando A (2003) A specific real-time quantitative PCR detection system for event MON810 in maize YieldGard® based on the 3′-transgene integration sequence. Transgenic Res 12:179–189
Yang LT, Pan AH, Zhang KW et al (2005) Qualitative and quantitative PCR methods for event specific detection of genetically modified cotton Mon1445 and Mon531. Transgenic Res 14:817–831
Pan AH, Yang LT, Xu SC, Yin CS, Zhang KW, Wang ZY et al (2006) Event specific qualitative and quantitative PCR detection of MON863 maize based upon the 3′-transgene integration sequence. J Cereal Sci 43:250–257
Yang LT, Jiang LX, Shen KL, Guo JC, Rao J, Seonghun L, Zhang DB (2009) Event specific qualitative and quantitative PCR detection methods for genetically modified cotton MON88913. Food Safety Qual Detect Technol 1:10–19
Nielsen CR, Berdal KG, Holst JA (2004) Characterisation of the 5′ integration site and development of an event specific real-time PCR assay for NK603 maize from a low starting copy number. Eur Food Res Technol 219:421–427
Yang R, Xu WT, Luo YB, Guo F, Lu Y, Huang KL (2007) Event specific qualitative and quantitative polymerase chain reaction detection of Roundup Ready event GT73 based on the 3′-transgene integration sequence. Plant Cell Repots 26:1821–1831
Hernández M, Esteve T, Prat S, Pla M (2004) Development of real-time PCR system based on SYBR Green I, Amplifluor and TaqMan technologies for specific quantitative detection of the transgenic maize event GA21. J Cereal Sci 39:99–107
Cécile C, Alexandra S, Georges B, Francine B, Géraldine C, Annick D et al (2005) Characterization and event specific-detection by quantitative real-time PCR of T25 maize insert. J AOAC Int 88:536–546
Li P, Pan AH, Jia Jun W, Jiang LX, Bai L, Tang XM (2010) Establishment of event specific qualitative PCR for detecting transgenic carnation moonlite. J Agric Sci Technol 12:109–113
Xu WT, Yang R, Lu J, Zhang N, Luo YB, He J et al (2011) Event specific transgenic detection of genetically modified maize 59122 with flanking sequence. Food Sci 32:139–142 (In Chinese)
Wang WX, Zhu TH, Lai FX, Fu Q (2011) Event-specific qualitative and quantitative detection of transgenic rice Kefeng-6 by characterization of the transgene flanking sequence. Eur Food Res Technol 232:297–305
Nan Huo, Minghui Zhang, Ying Liu et al (2011) Establishment of even specific qualitative PCR for detecting genetically modified wheat B73–6-1. China Biotechnol 10:100–105 (In Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the foundation of Educational Committee of Heilongjiang Province of China (No.12521018). This is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Huo, N., Liu, Y. et al. Event-specific detection of genetically modified wheat B73-6-1 based on the 3′-flanking sequence. Eur Food Res Technol 235, 1149–1159 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-012-1848-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-012-1848-y