Abstract
In this paper, we use a quantitative structure–retention relationship (QSRR) method to predict the retention times of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography (GC×GC). We analyse the GC×GC retention data taken from the literature by comparing predictive capability of different regression methods. The various models are generated using 70 out of 209 PCB congeners in the calibration stage, while their predictive performance is evaluated on the remaining 139 compounds. The two-dimensional chromatogram is initially estimated by separately modelling retention times of PCBs in the first and in the second column (1 t R and 2 t R, respectively). In particular, multilinear regression (MLR) combined with genetic algorithm (GA) variable selection is performed to extract two small subsets of predictors for 1 t R and 2 t R from a large set of theoretical molecular descriptors provided by the popular software Dragon, which after removal of highly correlated or almost constant variables consists of 237 structure-related quantities. Based on GA-MLR analysis, a four-dimensional and a five-dimensional relationship modelling 1 t R and 2 t R, respectively, are identified. Single-response partial least square (PLS-1) regression is alternatively applied to independently model 1 t R and 2 t R without the need for preliminary GA variable selection. Further, we explore the possibility of predicting the two-dimensional chromatogram of PCBs in a single calibration procedure by using a two-response PLS (PLS-2) model or a feed-forward artificial neural network (ANN) with two output neurons. In the first case, regression is carried out on the full set of 237 descriptors, while the variables previously selected by GA-MLR are initially considered as ANN inputs and subjected to a sensitivity analysis to remove the redundant ones. Results show PLS-1 regression exhibits a noticeably better descriptive and predictive performance than the other investigated approaches. The observed values of determination coefficients for 1 t R and 2 t R in calibration (0.9999 and 0.9993, respectively) and prediction (0.9987 and 0.9793, respectively) provided by PLS-1 demonstrate that GC×GC behaviour of PCBs is properly modelled. In particular, the predicted two-dimensional GC×GC chromatogram of 139 PCBs not involved in the calibration stage closely resembles the experimental one. Based on the above lines of evidence, the proposed approach ensures accurate simulation of the whole GC×GC chromatogram of PCBs using experimental determination of only 1/3 retention data of representative congeners.

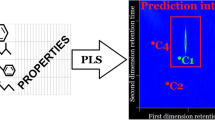
Agreement between experimental two-dimensional GCxGC chromatogram of 139 polychlorinated biphenyls and the one predicted by PLS-1 regression based on 237 molecular descriptors








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gdaniec-Pietryka M, Wolska L, Namieśnik J (2007) Trends Anal Chem 26:1005–1012
Sun P, Basu I, Hites RA (2006) Environ Sci Technol 40:1178–1183
Riget F, Dietz R, Vorkamp K, Johansen P, Muir D (2004) Sci Total Environ 331:29–52
Thomas GO, Wilkinson M, Hodson S, Jones KC (2006) Environ Pollut 141:30–41
Donato F, Magoni M, Bergonzi R, Scarcella C, Indelicato A, Carasi S, Apostoli P (2006) Chemosphere 64:1562–1572
Cochran JW, Frame GM (1999) J Chromatogr A 843:323–368
Mydlová-Memersheimerová J, Tienpont B, David F, Krupčík J, Sandra P (2009) J Chromatogr A 1216:6043–6062
Focant JF, Sjödin A, Patterson DG Jr (2004) J Chromatogr A 1040:227–238
Korytár P, Leonards PEG, de Boer J, Brinkman UATH (2002) J Chromatogr A 958:203–218
Harju M, Danielsson C, Haglund P (2003) J Chromatogr A 1019:111–126
Dallüge J, Beens J, Brinkman UATH (2003) J Chromatogr A 1000:69–108
Beens J, Tijssen R, Blomberg J (1998) J Chromatogr A 822:233–251
Vendeuvre C, Bertoncini F, Thiébaut D, Martin M, Hennion MC (2005) J Sep Sci 28:1129–1136
Lu X, Kong H, Li H, Ma C, Tian J, Xu G (2005) J Chromatogr A 1086:175–184
Seeley JV, Seeley SK (2007) J Chromatogr A 1172:72–83
Seeley JV, Libby EM, Hill Edwards KA, Seeley SK (2009) J Chromatogr A 1216:1650–1657
Héberger K (2007) J Chromatogr A 1158:273–305
Kaliszan R (2007) Chem Rev 107:3212–3246
Vitha M, Carr PW (2006) J Chromatogr A 1126:143–194
Arey JS, Nelson RK, Xu L, Reddy CM (2005) Anal Chem 77:7172–7182
Poole SK, Poole CF (2008) J Sep Sci 31:1118–1123
Abraham MH (2000) Database of general solvation model molecular descriptors. University College, London
Krawczuk A, Voelkel A, Lulek J, Urbaniak R, Szyrwińska K (2003) J Chromatogr A 1018:63–71
Gramatica P, Navas N, Todeschini R (1998) Chemom Intell Lab Syst 40:53–63
Liu SS, Liu Y, Yin DQ, Wang XD, Wang LS (2006) J Sep Sci 29:296–301
Ghavami R, Sadeghi F (2009) Chromatographia 70:851–868
Jäntschi L, Bolboacă SD, Diudea MV (2007) Int J Mol Sci 8:1125–1157
Hasan MN, Jurs PC (1988) Anal Chem 60:978–982
Robbat A Jr, Xyrafas G, Marshall D (1988) Anal Chem 60:982–985
Ren Y, Liu H, Yao X, Liu M (2007) Anal Bioanal Chem 388:165–172
Talete SRL (2006) DRAGON version 5.4 for windows (Software for molecular descriptor calculations) http://www.talete.mi.it/
Kennard RW, Stone LA (1969) Technometrics 11:137–148
Dorofeeva OV, Novikov VP, Moiseeva NF, Yungman VS (2005) J Struct Chem 46:237–242
Todeschini R, Consonni V (2000) Handbook of molecular descriptors. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Leardi R (ed) (2003) Nature-Inspired methods in chemometrics: genetic algorithms and artificial neural networks (data handling in science and technology, vol 23). Elsevier, Amsterdam
Wehrens R, Buydens LMC (1998) Trends Anal Chem 17:193–203
Forina M, Lanteri S, Armanino C, Casolino C, Casale M, Oliver P, V-PARVUS (2008) Dip chimica e tecnologie farmaceutiche ed alimentari, University of Genova http://www.parvus.unige.it
Zupan J, Gasteiger J (1999) Neural networks in chemistry and drug design. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim
Derks EPPA, Buydens LMC (1998) Chemom Intell Lab Syst 41:171–184
Copyright ©1996–2001 JavaNNS Group, Wilhelm-Schickard-Institute for Computer Science (WSI), University of Tübingen, Germany
Wold S, Sjöström M, Eriksson L (2001) Chemom Intell Lab Syst 58:109–130
Martens H, Naes T (1993) Multivariate calibration. Wiley, Chichester
Nord LI, Jacobsson SP (1998) Chemom Intell Lab Syst 44:153–160
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D’Archivio, A.A., Incani, A. & Ruggieri, F. Retention modelling of polychlorinated biphenyls in comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography. Anal Bioanal Chem 399, 903–913 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4326-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4326-z