Abstract
Rationale
The attraction to alcohol can be greatly increased when it is consumed in a social context. While pro-social interactions can potentiate voluntary alcohol drinking under some conditions, aversive social experience (i.e., social stress) can similarly intensify alcohol consumption.
Objective
We sought to determine how exposure to different types of chronic social stress (i.e., intermittent episodes of social defeat or continuous social stress) influences alcohol consumption and the reinforcing effects of alcohol in mice with a history of drinking.
Methods
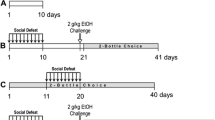
Separate cohorts of male C57BL/6J mice were exposed to either 10 days of continuous or intermittent social defeat stress. In experiment 1, mice were assigned to 20% w/v alcohol consumption in a two-bottle choice protocol both prior to and after exposure to social defeat stress. In a second experiment, mice engaged in an operant response sequence to gain access to alcohol wherein completion of a fixed interval (FI; 5 min) schedule was reinforced with continuous access to alcohol (fixed ratio; FR1) for up to 1.8 g/kg. Alcohol-reinforced responding and subsequent alcohol consumption were assessed daily for 4 weeks prior to the 10-day social stress exposure and for 6-week post-stress. Machine learning was implemented to standardize the analysis of defeat behaviors exhibited by the intruder mouse during confrontation with an attacking resident.
Results
In mice with a prior history of alcohol drinking, intermittent episodes of social defeat stress produced a significant increase in 20% EtOH consumption in preference over concurrently available water. This increased intake persisted for at least 6 weeks after the final social stress experience. Intermittently stressed mice also accelerated their anticipatory responding during the fixed interval component of the operant response chain that was reinforced by alcohol. Neither unstressed controls nor mice exposed to continuous social stress exhibited significant increases in alcohol consumption and alcohol reinforcement.
Discussion
Episodic social defeat stress promotes the seeking and consumption of alcohol, extending earlier work to alcohol-experienced mice. We hypothesize that intermittent access to alcohol and intermittent episodes of social stress are additive and share common sensitizing neural mechanisms that engender excessive alcohol consumption.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbey A, Smith MJ, Scott RO (1993) The relationship between reasons for drinking alcohol and alcohol consumption: an interactional approach. Addict Behav 18(6):659–670
Albrechet-Souza L, Viola TW, Grassi-Oliveira R, Miczek KA, de Almeida RMM (2017) Corticotropin releasing factor in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in socially defeated and non-stressed mice with a history of chronic alcohol intake. Front Pharmacol 8:762
Anacker AM, Ryabinin AE (2010) Biological contribution to social influences on alcohol drinking: evidence from animal models. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7(2):473–493
Arena DT, Covington HE, DeBold JF 3rd, Miczek KA (2019) Persistent increase of I.V cocaine self-administration in a subgroup of C57BL/6J male mice after social defeat stress. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 236(7):2027–2037
Akdilek N, Leonard MZ, Kenneally E, Newman EL, Covington HE, Miczek KA (in press) Stimulation of aggressive arousal by alcohol and suppression by CRF R1 antagonist in C57BL/6J mice: role of central amygdala and ventral tegmental area.
Barry H 3rd, Buckley JP (1966) Drug effects on animal performance and the stress syndrome. J Pharm Sci 55(11):1159–1183
Becker HC, Lopez MF, Doremus-Fitzwater TL (2011) Effects of stress on alcohol drinking: a review of animal studies. Psychopharmacology 218(1):131–156
Belknap JK, Crabbe JC, Young ER (1993) Voluntary consumption of ethanol in 15 inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology 112(4):503–510
Berton O, McClung CA, Dileone RJ, Krishnan V, Renthal W, Russo SJ, Graham D, Tsankova NM, Bolanos CA, Rios M, Monteggia LM, Self DW, Nestler EJ (2006) Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress. Science 311(5762):864–868
Berton O, Covington HE 3rd, Ebner K, Tsankova NM, Carle TL, Ulery P, Bhonsle A, Barrot M, Krishnan V, Singewald GM, Singewald N, Birnbaum S, Neve RL, Nestler EJ (2007) Induction of deltaFosB in the periaqueductal gray by stress promotes active coping responses. Neuron 55(2):289–300
Boyson CO, Holly EN, Shimamoto A, Albrechet-Souza L, Weiner LA, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2014) Social stress and CRF-dopamine interactions in the VTA: role in long-term escalation of cocaine self-administration. J Neurosci 34(19):6659–6667
Cooper ML, Frone MR, Russell M, Mudar P (1995) Drinking to regulate positive and negative emotions: a motivational model of alcohol use. J Pers Soc Psychol 69(5):990–1005
Covington HE 3rd, Miczek KA (2005) Intense cocaine self-administration after episodic social defeat stress, but not after aggressive behavior: dissociation from corticosterone activation. Psychopharmacol 183(3):331–340
Covington HE 3rd, Kikusui T, Goodhue J, Nikulina EM, Hammer RP Jr, Miczek KA (2005) Brief social defeat stress: long lasting effects on cocaine taking during a binge and zif268 mRNA expression in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 30(2):310–321
Covington HE 3rd, Maze I, Sun H, Bomze HM, DeMaio KD, Wu EY, Dietz DM, Lobo MK, Ghose S, Mouzon E, Neve RL, Tamminga CA, Nestler EJ (2011) A role for repressive histone methylation in cocaine-induced vulnerability to stress. Neuron 71(4):656–670
Covington HE 3rd, Newman EL, Tran S, Walton L, Hayek W, Leonard MZ, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2018) The urge to fight: persistent escalation by alcohol and role of NMDA receptors in mice. Front Behav Neurosci 12:206
Cui C, Koob GF (2017) Titrating tipsy targets: the neurobiology of low-dose alcohol. Trends Pharmacol Sci 38(6):556–568
Curran HV, Hildebrandt M (1999) Dissociative effects of alcohol on recollective experience. Conscious Cogn 8(4):497–509
Deal AL, Konstantopoulos JK, Weiner JL, Budygin EA (2018) Exploring the consequences of social defeat stress and intermittent ethanol drinking on dopamine dynamics in the rat nucleus accumbens. Sci Rep 8(1):332
Dews PB (1970) The theory of fixed-interval responding. In: Schoenfeld WN (ed) The Theory of Reinforcement Schedules. Appelton-Century-Crofts, New York, pp 43–61
Duka T, Weissenborn R, Dienes Z (2001) State-dependent effects of alcohol on recollective experience, familiarity and awareness of memories. Psychopharmacol 153(3):295–306
Falk JL, Samson HH, Winger G (1972) Behavioral maintenance of high concentrations of blood ethanol and physical dependence in the rat. Science 177(4051):811–813
Fish EW, De Bold JF, Miczek KA (2002) Aggressive behavior as a reinforcer in mice: activation by allopregnanolone. Psychopharmacol 163(3–4):459–466
Ferster CB, Skinner BF 1957 Schedules of Reinforecment. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York, NY
Gilpin NW, Weiner JL (2017) Neurobiology of comorbid post-traumatic stress disorder and alcohol-use disorder. Genes Brain Behav 16(1):15–43
Golden SA, Covington HE 3rd, Berton O, Russo SJ (2011) A standardized protocol for repeated social defeat stress in mice. Nat Protoc 6(8):1183–1191
Goodwin NL, Nilsson SRO, Golden SA (2020) Rage against the machine: advancing the study of aggression ethology via machine learning. Psychopharmacol 237(9):2569–2588
Grant EC, Mackintosh JH (1963) A comparison of the social postures of some common laboratory rodents. Behaviour 21(3–4):246–259
Han X, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2017) Prevention and reversal of social stress-escalated cocaine self-administration in mice by intra-VTA CRFR1 antagonism. Psychopharmacol 234(18):2813–2821
Holly EN, Boyson CO, Montagud-Romero S, Stein DJ, Gobrogge KL, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2016) Episodic social stress-escalated cocaine self-administration: role of phasic and tonic corticotropin releasing factor in the anterior and posterior ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci 36(14):4093–4105
Hunt GM, Azrin NH (1973) A community-reinforcement approach to alcoholism. Behav Res Ther 11(1):91–104
Hwa LS, Chu A, Levinson SA, Kayyali TM, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2011) Persistent escalation of alcohol drinking in C57BL/6J mice with intermittent access to 20% ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35(11):1938–1947
Hwa LS, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2013) Alcohol in excess: CRF(1) receptors in the rat and mouse VTA and DRN. Psychopharmacol 225(2):313–327
Hwa LS, Holly EN, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2016) Social stress-escalated intermittent alcohol drinking: modulation by CRF-R1 in the ventral tegmental area and accumbal dopamine in mice. Psychopharmacol 233(4):681–690
Hwa LS, Neira S, Flanigan ME, Stanhope CM, Pina MM, Pati D, Hon OJ, Yu W, Kokush E, Calloway R, Boyt K, Kash TL (2020) Alcohol drinking alters stress response to predator odor via BNST kappa opioid receptor signaling in male mice. Elife 9:e59709
Jimenez VA, Grant KA (2017) Studies using macaque monkeys to address excessive alcohol drinking and stress interactions. Neuropharmacol 122:127–135
Karkhanis AN, Rose JH, Huggins KN, Konstantopoulos JK, Jones SR (2015) Chronic intermittent ethanol exposure reduces presynaptic dopamine neurotransmission in the mouse nucleus accumbens. Drug Alcohol Depend 150:24–30
Kollack-Walker S, Watson SJ, Akil H (1997) Social stress in hamsters: defeat activates specific neurocircuits within the brain. J Neurosci 17(22):8842–8855
Koolhaas JM, de Boer SF, Coppens CM, Buwalda B (2010) Neuroendocrinology of coping styles: towards understanding the biology of individual variation. Front Neuroendocrinol 31(3):307–321
Kudryavtseva NN, Bakshtanovskaya IV, Koryakina LA (1991) Social model of depression in mice of C57BL/6J strain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 38(2):315–320
Kwiatkowski CC, Akaeze H, Ndlebe I, Goodwin N, Eagle AL, Moon K, Bender AR, Golden SA, Robison AJ (2021) Quantitative standardization of resident mouse behavior for studies of aggression and social defeat. Neuropsychopharmacol 46:1584–1593
Kudryavtseva NN (2022) Development of mixed anxiety/depression-like state as a consequence of chronic anxiety: review of experimental data. In: Miczek KA, Sinha R (eds) Neuroscience of Social Stress. Springer Verlag, Heidelberg 54:125–152
Leonard MZ (2022) Motivated Arousal in Anticipation of Cocaine Access: Maladaptive Actions of Corticotropin Releasing Factor on the Accumbens Dopamine Signal [dissertation]. Ann Arbor: Tufts University
Leonard MZ, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2017) Escalated cocaine “binges” in rats: enduring effects of social defeat stress or intra-VTA CRF. Psychopharmacol 234(18):2823–2836
Miczek KA, O’Donnell JM (1978) Intruder-evoked aggression in isolated and nonisolated mice: effects of psychomotor stimulants and L-dopa. Psychopharmacol 57(1):47–55
Miczek KA, Thompson ML, Shuster L (1982) Opioid-like analgesia in defeated mice. Science 215(4539):1520–1522
Miczek KA, Maxson SC, Fish EW, Faccidomo S (2001) Aggressive behavioral phenotypes in mice. Behav Brain Res 125(1–2):167–181
Miczek KA, Yap JJ, Covington HE 3rd (2008) Social stress, therapeutics and drug abuse: preclinical models of escalated and depressed intake. Pharmacol Ther 120(2):102–128
Miczek KA, Nikulina EM, Shimamoto A, Covington HE 3rd (2011) Escalated or suppressed cocaine reward, tegmental BDNF, and accumbal dopamine caused by episodic versus continuous social stress in rats. J Neurosci 31(27):9848–9857
Miczek KA, Akdilek N, Ferreira VMM, Leonard MZ, Covington HE, III (2022b) To fight or not to fight: activation of neural circuits in VTA-mPFC for aggressive motivation and decision making after ethanol consumption in a novel murine model. Psychopharmacol Epub ahead of print
Miczek KA, DiLeo A, Newman EL, Akdilek N, Covington HE (2022a) Neurobiological bases of urges for alcohol consumption after social stress. In: Miczek KA, Sinha R (eds) Neuroscience of Social Stress. Springer Verlag, Heidelberg 54:245-282
National Research Council (U.S.) (2011) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academies Press, Washington, D.C.
Newman SW (1999) The medial extended amygdala in male reproductive behavior. A node in the mammalian social behavior network. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:242–257
Newman EL, Albrechet-Souza L, Andrew PM, Auld JG, Burk KC, Hwa LS, Zhang EY, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2018a) Persistent escalation of alcohol consumption by mice exposed to brief episodes of social defeat stress: suppression by CRF-R1 antagonism. Psychopharmacol 235(6):1807–1820
Newman EL, Leonard MZ, Arena DT, de Almeida RMM, Miczek KA (2018b) Social defeat stress and escalation of cocaine and alcohol consumption: focus on CRF. Neurobiol Stress 9:151–165
Newman EL, Terunuma M, Wang TL, Hewage N, Bicakci MB, Moss SJ, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2018c) A role for prefrontal cortical NMDA receptors in murine alcohol-heightened aggression. Neuropsychopharmacol 43(6):1224–1234
Newman EL, Covington HE 3rd, Suh J, Bicakci MB, Ressler KJ, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2019) Fighting females: neural and behavioral consequences of social defeat stress in female mice. Biol Psychiatry 86(9):657–668
Nikulina EM, Covington HE 3rd, Ganschow L, Hammer RP Jr, Miczek KA (2004) Long-term behavioral and neuronal cross-sensitization to amphetamine induced by repeated brief social defeat stress: Fos in the ventral tegmental area and amygdala. Neuroscience 123(4):857–865
Noori HR, Helinski S, Spanagel R (2014) Cluster and meta-analyses on factors influencing stress-induced alcohol drinking and relapse in rodents. Addict Biol 19(2):225–232
Norman KJ, Seiden JA, Klickstein JA, Han X, Hwa LS, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2015) Social stress and escalated drug self-administration in mice I. Alcohol Corticosterone Psychopharmacol (berl) 232(6):991–1001
Newman EL, Covington HE, III, Leonard MZ, Burk K, Miczek KA (2021) Hypoactive thalamic Crh+ cells in a female mouse model of alcohol drinking after social trauma. Biol Psychiatry 90(8):563–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.05.022
Pacak K, Palkovits M (2001) Stressor specificity of central neuroendocrine responses: implications for stress-related disorders. Endocr Rev 22(4):502–548
Parrott DJ, Gallagher KE, Zeichner A (2012) Liquid courage or liquid fear: alcohol intoxication and anxiety facilitate physical aggression. Subst Use Misuse 47(7):774–786
Pohorecky LA (1981) The interaction of alcohol and stress. A Rev Neurosci Biobehav Rev 5(2):209–229
Pohorecky LA (1991) Stress and alcohol interaction: an update of human research. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 15(3):438–459
Rhodes JS, Best K, Belknap JK, Finn DA, Crabbe JC (2005) Evaluation of a simple model of ethanol drinking to intoxication in C57BL/6J mice. Physiol Behav 84(1):53–63
Scott JP (1966) Agonistic behavior of mice and rats: a review. Am Zool 6(4):683–701
Siciliano CA, Noamany H, Chang CJ, Brown AR, Chen X, Leible D, Lee JJ, Wang J, Vernon AN, Vander Weele CM, Kimchi EY, Heiman M, Tye KM (2019) A cortical-brainstem circuit predicts and governs compulsive alcohol drinking. Science 366(6468):1008–1012
Sillaber I, Rammes G, Zimmermann S, Mahal B, Zieglgansberger W, Wurst W, Holsboer F, Spanagel R (2002) Enhanced and delayed stress-induced alcohol drinking in mice lacking functional CRH1 receptors. Science 296(5569):931–933
Simms JA, Steensland P, Medina B, Abernathy KE, Chandler LJ, Wise R, Bartlett SE (2008) Intermittent access to 20% ethanol induces high ethanol consumption in Long-Evans and Wistar rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32(10):1816–1823
Sinha R (2001) How does stress increase risk of drug abuse and relapse? Psychopharmacol 158(4):343–359
Sinha R, Wemm S, Fogelman N, Milivojevic V, Morgan PM, Angarita GA, Hermes G, Fox HC (2021) Moderation of prazosin’s efficacy by alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Am J Psychiatry 178(5):447–458
Spanagel R, Holter SM (1999) Long-term alcohol self-administration with repeated alcohol deprivation phases: an animal model of alcoholism? Alcohol Alcohol 34(2):231–243
Spruijt BM, van Hooff JA, Gispen WH (1992) Ethology and neurobiology of grooming behavior. Physiol Rev 72(3):825–852
Vengeliene V, Siegmund S, Singer MV, Sinclair JD, Li TK, Spanagel R (2003) A comparative study on alcohol-preferring rat lines: effects of deprivation and stress phases on voluntary alcohol intake. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27(7):1048–1054
Vivian JA, Green HL, Young JE, Majerksy LS, Thomas BW, Shively CA, Tobin JR, Nader MA, Grant KA (2001) Induction and maintenance of ethanol self-administration in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis): long-term characterization of sex and individual differences. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25(8):1087–1097
Wise RA (1973) Voluntary ethanol intake in rats following exposure to ethanol on various schedules. Psychopharmacologia 29(3):203–210
Yap JJ, Chartoff EH, Holly EN, Potter DN, Carlezon WA Jr, Miczek KA (2015) Social defeat stress-induced sensitization and escalated cocaine self-administration: the role of ERK signaling in the rat ventral tegmental area. Psychopharmacol 232(9):1555–1569
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank J. Thomas Sopko, Rebecca Atherton, Kathryn Hazzard, William Hsu, Samar Shaqour, and Annika Witt for their assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by NIH grants AA013983 and DA031734 (KAM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Miczek, K.A., Akdilek, N., Ferreira, V.M.M. et al. Excessive alcohol consumption after exposure to two types of chronic social stress: intermittent episodes vs. continuous exposure in C57BL/6J mice with a history of drinking. Psychopharmacology 239, 3287–3296 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-022-06211-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-022-06211-8