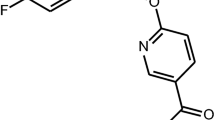
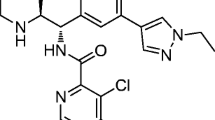
Abstract
Rationale and objectives
The reported inconsistent effects of negative allosteric modulators of α5-containing GABAA receptors on learning and memory may be attributed to receptor selectivity, effective plasma concentration maintenance, and administration time. This study aimed to compare the effects of L-655,708 administered by single-dosing regimen versus multi-dosing regimen on spatial memory, signaling molecules, and brain functional connectivity.
Methods
After comparing the maintenance time of the effective plasma concentration of L-655,708 between multi-dosing and single-dosing regimens, we further compared the effects of the administration of the two regimens at different phases (before-learning, during-learning, and before-probe) of the Morris water maze (MWM) test on the performance of learning and memory and the levels of signaling molecules related to learning and memory in hippocampal tissues. Functional connectivity analyses between hippocampal and cortical regions were performed to further clarify the effects of the multi-dosing regimen.
Results
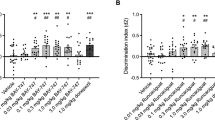
The multi-dosing regimen could maintain the effective plasma concentration of L-655,708 much longer than the single-dosing regimen. Only the multi-dosing regimen for L-655,708 administration during the learning period led to significant improvement in spatial memory in the MWM test and increases in levels of glutamate receptors and phosphorylated signaling molecules (p-PKAα, p-CaMKII, and p-CREB-1). Compared with the vehicle control, the multi-dosing regimen increased the functional connectivity of the left hippocampal CA1 with cingulate and motor cortices.
Conclusions
A multi-dosing regimen for L-655,708 administered during the learning period is an effective strategy to improve spatial memory, increase signaling molecule levels, and enhance the functional connectivity of the hippocampus.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel T, Lattal KM (2001) Molecular mechanisms of memory acquisition, consolidation and retrieval. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11(2):180–187
Abel T, Nguyen PV, Barad M, Deuel TA, Kandel ER, Bourtchouladze R (1997) Genetic demonstration of a role for PKA in the late phase of LTP and in hippocampus-based long-term memory. Cell 88(5):615–626
Angenstein F, Krautwald K, Wetzel W, Scheich H (2013) Perforant pathway stimulation as a conditioned stimulus for active avoidance learning triggers BOLD responses in various target regions of the hippocampus: a combined fMRI and electrophysiological study. Neuroimage 15(75):213–227
Ash JA, Lu H, Taxier LR, Long JM, Yang Y, Stein EA, Rapp PR (2016) Functional connectivity with the retrosplenial cortex predicts cognitive aging in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(43):12286–12291
Atack JR (2010) Preclinical and clinical pharmacology of the GABAA receptor α5 subtype-selective inverse agonist α5IA. Pharmacol Ther 125(1):11–26
Atack JR, Bayley PJ, Seabrook GR, Wafford KA, McKernan RM, Dawson GR (2006a) L-655,708 enhances cognition in rats but is not proconvulsant at a dose selective for α5-containing GABAA receptors. Neuropharmacology 51(6):1023–1029
Atack JR, Hutson PH, Collinson N, Marshall G, Bentley G, Moyes C, Cook SM, Collins I, Wafford K, McKernan RM, Dawson GR (2005) Anxiogenic properties of an inverse agonist selective for α3 subunit-containing GABAA receptors. Br J Pharmacol 144(3):357–366
Atack JR, Maubach KA, Wafford KA, O’Connor D, Rodrigues AD, Evans DC, Tattersall FD, Chambers MS, MacLeod AM, Eng WS, Ryan C, Hostetler E, Sanabria SM, Gibson RE, Krause S, Burns HD, Hargreaves RJ, Agrawal NG, McKernan RM, Murphy MG, Gingrich K, Dawson GR, Musson DG, Petty KJ (2009) In vitro and in vivo properties of 3-tert-butyl-7-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)-2-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-ylmethoxy)- pyrazolo[1,5-d]-[1,2,4]triazine (MRK-016), a GABAA receptor α5 subtype-selective inverse agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 331(2):470–484
Atack JR, Pike A, Clarke A, Cook SM, Sohal B, McKernan RM, Dawson GR (2006b) Rat pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a sustained release formulation of the GABAA α5-selective compound L-655,708. Drug Metab Dispos 34(5):887–893
Ballard TM, Knoflach F, Prinssen E, Borroni E, Vivian JA, Basile J, Gasser R, Moreau JL, Wettstein JG, Buettelmann B, Knust H, Thomas AW, Trube G, Hernandez MC (2009) RO4938581, a novel cognitive enhancer acting at GABAA α5 subunit-containing receptors. Psychopharmacology 202(1–3):207–223
Barriere DA, Magalhaes R, Novais A, Marques P, Selingue E, Geffroy F, Marques F, Cerqueira J, Sousa JC, Boumezbeur F, Bottlaender M, Jay TM, Cachia A, Sousa N, Meriaux S (2019) The SIGMA rat brain templates and atlases for multimodal MRI data analysis and visualization. Nat Commun 10(1):5699
Battaglia FP, Benchenane K, Sirota A, Pennartz CM, Wiener SI (2011) The hippocampus: hub of brain network communication for memory. Trends Cogn Sci 15(7):310–318
Benchenane K, Castel H, Boulouard M, Bluthe R, Fernandez-Monreal M, Roussel BD, Lopez-Atalaya JP, Butt-Gueulle S, Agin V, Maubert E, Dantzer R, Touzani O, Dauphin F, Vivien D, Ali C (2007) Anti-NR1 N-terminal-domain vaccination unmasks the crucial action of tPA on NMDA-receptor-mediated toxicity and spatial memory. J Cell Sci 120(Pt 4):578–585
Braudeau J, Delatour B, Duchon A, Pereira PL, Dauphinot L, de Chaumont F, Olivo-Marin JC, Dodd RH, Herault Y, Potier MC (2011) Specific targeting of the GABA-A receptor α5 subtype by a selective inverse agonist restores cognitive deficits in Down syndrome mice. J Psychopharmacol 25(8):1030–1042
Cai S, Chong T, Peng Y, Shen W, Li J, von Deneen KM, Huang L, Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative, (2017) Altered functional brain networks in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a resting-state fMRI study. Brain Imaging Behav 11(3):619–631
Canals S, Beyerlein M, Merkle H, Logothetis NK (2009) Functional MRI evidence for LTP-induced neural network reorganization. Curr Biol 19(5):398–403
Chambers MS, Atack JR, Broughton HB, Collinson N, Cook S, Dawson GR, Hobbs SC, Marshall G, Maubach KA, Pillai GV, Reeve AJ, MacLeod AM (2003) Identification of a novel, selective GABAA α5 receptor inverse agonist which enhances cognition. J Med Chem 46(11):2227–2240
Cheng H, Sun G, Li M, Yin M, Chen H (2019) Neuron loss and dysfunctionality in hippocampus explain aircraft noise induced working memory impairment: a resting-state fMRI study on military pilots. Biosci Trends 13(5):430–440
Chersi F, Burgess N (2015) The cognitive architecture of spatial navigation: hippocampal and striatal contributions. Neuron 88(1):64–77
Clayton T, Poe MM, Rallapalli S, Biawat P, Savic MM, Rowlett JK, Gallos G, Emala CW, Kaczorowski CC, Stafford DC, Arnold LA, Cook JM (2015) A review of the updated pharmacophore for the alpha 5 GABA(A) benzodiazepine receptor model. Int J Med Chem 2015: 430248.
Cole BJ, Hillmann M, Seidelmann D, Klewer M, Jones GH (1995) Effects of benzodiazepine receptor partial inverse agonists in the elevated plus maze test of anxiety in the rat. Psychopharmacology 121(1):118–126
Collinson N, Atack JR, Laughton P, Dawson GR, Stephens DN (2006) An inverse agonist selective for α5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors improves encoding and recall but not consolidation in the Morris water maze. Psychopharmacology 188(4):619–628
Daw NW, Stein PSG, Fox K (1993) The role of NMDA receptors in information processing. Annu Rev Neurosci 16:207–222
Dawson GR, Maubach KA, Collinson N, Cobain M, Everitt BJ, MacLeod AM, Choudhury HI, McDonald LM, Pillai G, Rycroft W, Smith AJ, Sternfeld F, Tattersall FD, Wafford KA, Reynolds DS, Seabrook GR, Atack JR (2006) An inverse agonist selective for α5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors enhances cognition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316(3):1335–1345
Frankland PW, Bontempi B (2005) The organization of recent and remote memories. Nat Rev Neurosci 6(2):119–130
Gao T, Liu Y, Zhao Z, Luo Y, Wang L, Wang Y, Yin Y (2019) L-655,708 does not prevent isoflurane-induced memory deficits in old mice. Transl Neurosci 10:180–186
Hausrat TJ, Muhia M, Gerrow K, Thomas P, Hirdes W, Tsukita S, Heisler FF, Herich L, Dubroqua S, Breiden P, Feldon J, Schwarz JR, Yee BK, Smart TG, Triller A, Kneussel M (2015) Radixin regulates synaptic GABAA receptor density and is essential for reversal learning and short-term memory. Nat Commun 6:6872
Hsu LM, Liang X, Gu H, Brynildsen JK, Stark JA, Ash JA, Lin CP, Lu H, Rapp PR, Stein EA, Yang Y (2016) Constituents and functional implications of the rat default mode network. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(31):E4541–E4547
Jacob TC (2019) Neurobiology and therapeutic potential of α5-GABA type A receptors. Front Mol Neurosci 12:179
Kandel ER (2001) The molecular biology of memory storage: a dialogue between genes and synapses. Science 294(5544):1030–1038
Kandel ER (2012) The molecular biology of memory: cAMP, PKA, CRE, CREB-1, CREB-2, and CPEB. Mol Brain 5:14
Leech R, Sharp DJ (2014) The role of the posterior cingulate cortex in cognition and disease. Brain 137:12–32
Liang X, Hsu LM, Lu H, Ash JA, Rapp PR, Yang Y (2020) Functional connectivity of hippocampal CA3 predicts neurocognitive aging via CA1-frontal circuit. Cereb Cortex 30:4297–4305
Lisman J, Yasuda R, Raghavachari S (2012) Mechanisms of CaMKII action in long-term potentiation. Nat Rev Neurosci 13(3):169–182
Liu X, Zhu XH, Zhang Y, Chen W (2013) The change of functional connectivity specificity in rats under various anesthesia levels and its neural origin. Brain Topogr 26(3):363–377
Lu H, Zou Q, Gu H, Raichle ME, Stein EA, Yang Y (2012) Rat brains also have a default mode network. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(10):3979–3984
Makkar SR, Zhang SQ, Cranney J (2010) Behavioral and neural analysis of GABA in the acquisition, consolidation, reconsolidation, and extinction of fear memory. Neuropsychopharmacology 35(8):1625–1652
Martin LJ, Oh GH, Orser BA (2009) Etomidate targets α5 γ-aminobutyric acid subtype A receptors to regulate synaptic plasticity and memory blockade. Anesthesiology 111(5):1025–1035
Martinez-Cue C, Martinez P, Rueda N, Vidal R, Garcia S, Vidal V, Corrales A, Montero JA, Pazos A, Florez J, Gasser R, Thomas AW, Honer M, Knoflach F, Trejo JL, Wettstein JG, Hernandez MC (2013) Reducing GABAA α5 receptor-mediated inhibition rescues functional and neuromorphological deficits in a mouse model of down syndrome. J Neurosci 33(9):3953–3966
Mayford M, Abel T, Kandel ER (1995) Transgenic approaches to cognition. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5(2):141–148
Milic M, Timic T, Joksimovic S, Biawat P, Rallapalli S, Divljakovic J, Radulovic T, Cook JM, Savic MM (2013) PWZ-029, an inverse agonist selective for α5 GABAA receptors, improves object recognition, but not water-maze memory in normal and scopolamine-treated rats. Behav Brain Res 241:206–213
Mohamad FH, Has ATC (2019) The α5-containing GABAA receptors-a brief summary. J Mol Neurosci 67(2):343–351
Mohler H (2007) Molecular regulation of cognitive functions and developmental plasticity: impact of GABAA receptors. J Neurochem 102(1):1–12
Mohler H (2009) Role of GABAA receptors in cognition. Biochem Soc Trans 37(Pt 6):1328–1333
Nasrallah FA, Lew SK, Low AS, Chuang KH (2014a) Neural correlate of resting-state functional connectivity under α2 adrenergic receptor agonist, medetomidine. Neuroimage 84:27–34
Nasrallah FA, Low SA, Lew SK, Chen K, Chuang KH (2014b) Pharmacological insight into neurotransmission origins of resting-state functional connectivity: α2-adrenergic agonist vs antagonist. Neuroimage 103:364–373
Nasrallah FA, Singh KKDR, Yeow LY, Chuang KH (2017) GABAergic effect on resting-state functional connectivity: Dynamics under pharmacological antagonism. Neuroimage 149:53–62
Nasrallah FA, Tan J, Chuang KH (2012) Pharmacological modulation of functional connectivity: α2-adrenergic receptor agonist alters synchrony but not neural activation. Neuroimage 60:436–446
Nasrallah FA, To XV, Chen DY, Routtenberg A, Chuang KH (2016) Functional connectivity MRI tracks memory networks after maze learning in rodents. Neuroimage 127:196–202
Navarro JF, Buron E, Martin-Lopez M (2002) Anxiogenic-like activity of L-655,708, a selective ligand for the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors which contain the alpha-5 subunit, in the elevated plus-maze test. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 26(7–8):1389–1392
Paasonen J, Stenroos P, Salo RA, Kiviniemi V, Grohn O (2018) Functional connectivity under six anesthesia protocols and the awake condition in rat brain. Neuroimage 172:9–20
Pirker S, Schwarzer C, Wieselthaler A, Sieghart W, Sperk G (2000) GABAA receptors: immunocytochemical distribution of 13 subunits in the adult rat brain. Neuroscience 101(4):815–850
Quirk K, Blurton P, Fletcher S, Leeson P, Tang F, Mellilo D, Ragan CI, McKernan RM (1996) [3H]L-655,708, a novel ligand selective for the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors which contain the α5 subunit. Neuropharmacology 35(9–10):1331–1335
Riedel G, Platt B, Micheau J (2003) Glutamate receptor function in learning and memory. Behav Brain Res 140(1–2):1–47
Rudolph U, Mohler H (2004) Analysis of GABAA receptor function and dissection of the pharmacology of benzodiazepines and general anesthetics through mouse genetics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 44:475–498
Saab BJ, Maclean AJ, Kanisek M, Zurek AA, Martin LJ, Roder JC, Orser BA (2010) Short-term memory impairment after isoflurane in mice is prevented by the α5 γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor inverse agonist L-655,708. Anesthesiology 113(5):1061–1071
Shah D, Verhoye M, Van der Linden A, D’Hooge R (2019) Acquisition of spatial search strategies and reversal learning in the Morris water maze depend on disparate brain functional connectivity in mice. Cereb Cortex 29(11):4519–4529
Shimizu E, Tang YP, Rampon C, Tsien JZ (2000) NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic reinforcement as a crucial process for memory consolidation. Science 290(5494):1170–1174
Sieghart W, Savic MM (2018) International union of basic and blinical pharmacology. CVI: GABAA receptor subtype- and function-selective ligands: key issues in translation to humans. Pharmacol Rev 70(4):836–878
Soh MS, Lynch JW (2015) Selective modulators of α5-containing GABAA receptors and their therapeutic significance. Curr Drug Targets 16(7):735–746
Tang S, Xu S, Waddell J, Zhu W, Gullapalli RP, Mooney SM (2019) Functional connectivity and metabolic alterations in medial prefrontal cortex in a rat model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging and in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Dev Neurosci 41(1–2):67–78
Teixeira CM, Pomedli SR, Maei HR, Kee N, Frankland PW (2006) Involvement of the anterior cingulate cortex in the expression of remote spatial memory. J Neurosci 26:7555–7564
Tsien JZ, Huerta PT, Tonegawa S (1996) The essential role of hippocampal CA1 NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity in spatial memory. Cell 87(7):1327–1338
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc 1:848–858
Walker MC, Semyanov A (2008) Regulation of excitability by extrasynaptic GABAA receptors. Results Probl Cell Differ 44:29–48
Wen T, Zhang X, Liang S, Li Z, Xing X, Liu W, Tao J (2018) Electroacupuncture ameliorates cognitive impairment and spontaneous low-frequency brain activity in rats with ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 27(10):2596–2605
Williams KA, Magnuson M, Majeed W, LaConte SM, Peltier SJ, Hu X, Keilholz SD (2010) Comparison of α-chloralose, medetomidine and isoflurane anesthesia for functional connectivity mapping in the rat. Magn Reson Imaging 28(7):995–1003
Xi Q, Zhao X, Wang P, Guo Q, Jiang H, Cao X, He Y, Yan C (2012) Spontaneous brain activity in mild cognitive impairment revealed by amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation analysis: a resting-state fMRI study. Radiol Med 117(5):865–871
Yan CG, Wang XD, Zuo XN, Zang YF (2016) DPABI: data processing & analysis for (resting-state) brain imaging. Neuroinformatics 14(3):339–351
Zang YF, He Y, Zhu CZ, Cao QJ, Sui MQ, Liang M, Tian LX, Jiang TZ, Wang YF (2007) Altered baseline brain activity in children with ADHD revealed by resting-state functional MRI. Brain Dev 29(2):83–91
Zhao ZF, Du L, Gao T, Bao L, Luo Y, Yin YQ, Wang YA (2019) Inhibition of α5 GABAA receptors has preventive but not therapeutic effects on isoflurane-induced memory impairment in aged rats. Neural Regen Res 14(6):1029–1036
Zurek AA, Bridgwater EM, Orser BA (2012) Inhibition of α5 γ-Aminobutyric acid type A receptors restores recognition memory after general anesthesia. Anesth Analg 114(4):845–855
Zurek AA, Yu J, Wang DS, Haffey SC, Bridgwater EM, Penna A, Lecker I, Lei G, Chang T, Salter EW, Orser BA (2014) Sustained increase in α5GABAA receptor function impairs memory after anesthesia. J Clin Invest 124(12):5437–5441
Acknowledgements
Functional magnetic resonance imaging data acquisition was supported by the Center for Advanced Imaging, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81801828 and 82030053).
Animal experiments were performed in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the Tianjin Medical University Animal Care and Use Committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, C., Gao, A., Xu, Q. et al. A multi-dosing regimen to enhance the spatial memory of normal rats with α5-containing GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulator L-655,708. Psychopharmacology 238, 3375–3389 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05951-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05951-3