Abstract
Introduction
Gelsemine is a natural alkaloid extracted from Gelsemium elegans Benth., a traditional Chinese medicinal herb. Gelsemine has been shown to penetrate the brain, and could produce neurological activities, such as anxiolytic and neuralgia-alleviating effects, suggesting that this natural compound might be used for treating nervous system diseases.
Results
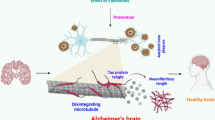
In this study, we have found, for the first time, that gelsemine at low concentrations (5–10 μg/kg) significantly alleviated cognitive impairments induced by β-amyloid (Aβ) oligomer, a main neurotoxin of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In addition, gelsemine substantially prevented Aβ oligomer-induced over-activation of microglia and astrocytes, indicating that gelsemine might reduce AD-related gliosis. Consistently, gelsemine inhibited the over-expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), in the brain of mice. Moreover, gelsemine largely increased the expression of pSer9-glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β), and decreased the hyper-phosphorylation of tau protein as evidenced by Western blotting analysis. Furthermore, gelsemine prevented Aβ oligomer-induced reduction of PSD-95, a representative post-synaptic protein.
Conclusion
All these results directly demonstrated the anti-Aβ oligomer neuroprotective properties of gelsemine, opening a novel perspective for the development of gelsemine-based therapeutics against Aβ-associated neurodegeneration disorders, including AD in particular.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aβ:
-
β-Amyloid
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl-sulfoxide
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein GSK3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3β
- HFIP:
-
1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoro-2-propanol
- ICR:
-
Institute of Cancer Research
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1β
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- MWM:
-
Morris water maze
- NFT:
-
Neurofibrillary tangles
- NIH:
-
National Institutes of Health
- OFT:
-
Open filed test
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- RAM:
-
Radial arm maze
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Betz H, Laube B (2006) Glycine receptors: recent insights into their structural organization and functional diversity. J Neurochem 97:1600–1610
Carol A, Grimes RSJ (2001) The multifaceted roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3 in cellular signaling. Prog Neurobiol 65:391–426
Chang L, Cui W, Yang Y, Xu S, Zhou W, Fu H, Hu S, Mak S, Hu J, Wang Q, Ma VP, Choi TC, Ma ED, Tao L, Pang Y, Rowan MJ, Anwyl R, Han Y, Wang Q (2015) Protection against beta-amyloid-induced synaptic and memory impairments via altering beta-amyloid assembly by bis(heptyl)-cognitin. Sci Rep 5:10256
Chen G, Liu C, Meng G, Zhang C, Chen F, Tang S, Hong H, Zhang C (2018) Neuroprotective effect of mogrol against Abeta1-42-induced memory impairment neuroinflammation and apoptosis in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol
Chunhui H, Dilin X, Ke Z, Jieyi S, Sicheng Y, Dapeng W, Qinwen W, Wei C (2018) A11-positive beta-amyloid oligomer preparation and assessment using dot blotting analysis. J Vis Exp.
DaRocha-Souto B, Coma M, Pérez-Nievas BG, Scotton TC, Siao M, Sánchez-Ferrer P, Hashimoto T, Fan Z, Hudry E, Barroeta I, Serenó L, Rodríguez M, Sánchez MB, Hyman BT, Gómez-Isla T (2012) Activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta mediates β-amyloid induced neuritic damage in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 45:425–437
De Strooper B, Karran E (2016) The cellular phase of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 164:603–615
Felix Hernandez JB, Carmen Guaza, Jesus Avila, Lucas JJ (2002) Spatial learning deficit in transgenic mice that conditionally over-express GSK-3b in the brain but do not form tau filaments. J Neurochem 83:1529–1533
Fu AKY, Hung KW, Huang HQ, Gu S, Shen Y, Cheng EYL, Ip FCF, Huang XH, Fu WY, Ip NY (2014) Blockade of EphA4 signaling ameliorates hippocampal synaptic dysfunctions in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:9959–9964
Han SD, Gruhl J, Beckett L, Dodge HH, Stricker NH, Farias S, Mungas D (2012) Beta amyloid, tau, neuroimaging, and cognition: sequence modeling of biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Imaging and Behavior 6:610–620
Huang L, Lin J, Xiang S, Zhao K, Yu J, Zheng J, Xu D, Mak S, Hu S, Nirasha S, Wang C, Chen X, Zhang J, Xu S, Wei X, Zhang Z, Zhou D, Zhou W, Cui W, Han Y, Hu Z, Wang Q (2016) Sunitinib, a clinically used anticancer drug, is a potent AChE inhibitor and attenuates cognitive impairments in mice. ACS Chem Neurosci 7:1047–1056
Jiao SS, Yao XQ, Liu YH, Wang QH, Zeng F, Lu JJ, Liu J, Zhu C, Shen LL, Liu CH, Wang YR, Zeng GH, Parikh A, Chen J, Liang CR, Xiang Y, Bu XL, Deng J, Li J, Xu J, Zeng YQ, Xu X, Xu HW, Zhong JH, Zhou HD, Zhou XF, Wang YJ (2015) Edaravone alleviates Alzheimer’s disease-type pathologies and cognitive deficits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:5225–5230
Jope RS, Yuskaitis CJ, Beurel E (2007) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): inflammation, diseases, and therapeutics. Neurochem Res 32:577–595
Kraeuter A-K, Guest PC, Sarnyai Z (2019) The open field test for measuring locomotor activity and anxiety-like behavior pre-clinical models (methods in molecular biology), pp 99-103
Lara CO, Murath P, Munoz B, Marileo AM, Martin LS, San Martin VP, Burgos CF, Mariqueo TA, Aguayo LG, Fuentealba J, Godoy P, Guzman L, Yevenes GE (2016) Functional modulation of glycine receptors by the alkaloid gelsemine. Br J Pharmacol 173:2263–2277
Li H-Q, Ip S-P, Zheng G-Q, Xian Y-F, Lin Z-X (2018a) Isorhynchophylline alleviates learning and memory impairments induced by aluminum chloride in mice Chinese Medicine 13
Li J, Ma X, Wang Y, Chen C, Hu M, Wang L, Fu J, Shi G, Zhang D, Zhang T (2018b) Methyl salicylate lactoside protects neurons ameliorating cognitive disorder through inhibiting amyloid beta-induced neuroinflammatory response in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 10: 85
Lin M-S, Xiong W-C, Li S-J, Gong Z, Cao X, Kuang X-J, Zhang Y, Gao T-M, Mechawar N, Liu C, Zhu X-H (2017) α2-glycine receptors modulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis and spatial memory. Developmental Neurobiology 77:1430–1441
Liu J, Chang L, Roselli F, Almeida OF, Gao X, Wang X, Yew DT, Wu Y (2010) Amyloid-beta induces caspase-dependent loss of PSD-95 and synaptophysin through NMDA receptors. J Alzheimers Dis 22:541–556
Liu M, Huang H-H, Yang J, Su Y-P, Lin H-W, Lin L-Q, Liao W-J, Yu C-X (2012) The active alkaloids of Gelsemium elegans Benth. are potent anxiolytics. Psychopharmacology 225:839–851
Liu XJ, Wei J, Shang YH, Huang HC, Lao FX (2017) Modulation of AbetaPP and GSK3beta by endoplasmic reticulum stress and involvement in Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 57:1157–1170
Marsh J, Bagol SH, Williams RSB, Dickson G, Alifragis P (2017) Synapsin I phosphorylation is dysregulated by beta-amyloid oligomers and restored by valproic acid. Neurobiol Dis 106:63–75
Medina M, Avila J (2014) New insights into the role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets 18:69–77
Meyer L, Boujedaini N, Patte-Mensah C, Mensah-Nyagan AG (2013) Pharmacological effect of gelsemine on anxiety-like behavior in rat. Behav Brain Res 253:90–94
Ochalek A, Mihalik B, Avci HX, Chandrasekaran A, Téglási A, Bock I, Giudice ML, Táncos Z, Molnár K, László L, Nielsen JE, Holst B, Freude K, Hyttel P, Kobolák J, Dinnyés A (2017) Neurons derived from sporadic Alzheimer’s disease iPSCs reveal elevated TAU hyperphosphorylation, increased amyloid levels, and GSK3B activation. Alzheimer’s Research & Therapy 9
Park D, Chang S (2018) Soluble Abeta1-42 increases the heterogeneity in synaptic vesicle pool size among synapses by suppressing intersynaptic vesicle sharing. Mol Brain 11:10
Philippens IH, Ormel PR, Baarends G, Johansson M, Remarque EJ, Doverskog M (2017) Acceleration of amyloidosis by inflammation in the amyloid-beta marmoset monkey model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 55:101–113
Ralay Ranaivo H, Craft JM, Hu W, Guo L, Wing LK, Van Eldik LJ, Watterson DM (2006) Glia as a therapeutic target: selective suppression of human amyloid-beta-induced upregulation of brain proinflammatory cytokine production attenuates neurodegeneration. J Neurosci 26:662–670
Rujjanawate C, Kanjanapothi D, Panthong A (2003) Pharmacological effect and toxicity of alkaloids from Gelsemium elegans Benth. J Ethnopharmacol 89:91–95
Scheltens P, Blennow K, Breteler MMB, de Strooper B, Frisoni GB, Salloway S, Van der Flier WM (2016) Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 388:505–517
Sharma S, Verma S, Kapoor M, Saini A, Nehru B (2016) Alzheimer’s disease like pathology induced six weeks after aggregated amyloid-beta injection in rats: increased oxidative stress and impaired long-term memory with anxiety-like behavior. Neurol Res 38:838–850
Shi Q, Chowdhury S, Ma R, Le KX, Hong S, Caldarone BJ, Stevens B, Lemere CA (2017) Complement C3 deficiency protects against neurodegeneration in aged plaque-rich APP_PS1 mice. Sci Transl Med 9:392
Shin SJ, Jeong Y, Jeon SG, Kim S, Lee S-k, Choi HS, Im CS, Kim SH, Kim SH, Park JH, J-i K, Kim J-J, Moon M (2018) Uncaria rhynchophylla ameliorates amyloid beta deposition and amyloid beta-mediated pathology in 5XFAD mice. Neurochem Int 121:114–124
Shoaib RM, Zhang JY, Mao XF, Wang YX (2019) Gelsemine and koumine, principal active ingredients of Gelsemium, exhibit mechanical antiallodynia via spinal glycine receptor activation-induced allopregnanolone biosynthesis. Biochem Pharmacol 161:136–148
Sultana R, Banks WA, Butterfield DA (2010) Decreased levels of PSD95 and two associated proteins and increased levels of BCl2 and caspase 3 in hippocampus from subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment: insights into their potential roles for loss of synapses and memory, accumulation of Abeta, and neurodegeneration in a prodromal stage of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Res 88: 469–477
Wang WY, Tan MS, Yu JT, Tan L (2015) Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Transl Med 3: 136
Wang Y, Wang Q, Bao X, Ding Y, Shentu J, Cui W, Chen X, Wei X, Xu S (2018) Taxifolin prevents β-amyloid-induced impairments of synaptic formation and deficits of memory via the inhibition of cytosolic phospholipase A2/prostaglandin E2 content. Metab Brain Dis 33:1069–1079
Wen Y, Planel E, Herman M, Figueroa HY, Wang L, Liu L, Lau LF, Yu WH, Duff KE (2008) Interplay between cyclin-dependent kinase 5 and glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta mediated by neuregulin signaling leads to differential effects on tau phosphorylation and amyloid precursor protein processing. J Neurosci 28:2624–2632
Wu YE, Li YD, Luo YJ, Wang TX, Wang HJ, Chen SN, Qu WM, Huang ZL (2015) Gelsemine alleviates both neuropathic pain and sleep disturbance in partial sciatic nerve ligation mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36:1308–1317
Xian YF, Mao QQ, Wu JC, Su ZR, Chen JN, Lai XP, Ip SP, Lin ZX (2014) Isorhynchophylline treatment improves the amyloid-beta-induced cognitive impairment in rats via inhibition of neuronal apoptosis and tau protein hyperphosphorylation. J Alzheimers Dis 39:331–346
Xu Y, Qiu H-Q, Liu H, Liu M, Huang Z-Y, Yang J, Su Y-P, Yu C-X (2012) Effects of koumine, an alkaloid of Gelsemium elegans Benth., on inflammatory and neuropathic pain models and possible mechanism with allopregnanolone. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 101:504–514
Zhang Y, Pi Z, Song F, Liu Z (2016) Ginsenosides attenuate d-galactose- and AlCl3-inducedspatial memory impairment by restoring the dysfunction of the neurotransmitter systems in the rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Ethnopharmacol 194:188–195
Zhao QC, Hua W, Zhang L, Guo T, Zhao MH, Yan M, Shi GB, Wu LJ (2010) Antitumor activity of two gelsemine metabolites in rat liver microsomes. J Asian Nat Prod Res 12:731–739
Zhong L, Liu H, Zhang W, Liu X, Jiang B, Fei H, Sun Z (2018) Ellagic acid ameliorates learning and memory impairment in APP/PS1 transgenic mice via inhibition of beta-amyloid production and tau hyperphosphorylation. Exp Ther Med 16:4951–4958
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81870853), Ningbo Sci & Tech Project for Common Wealth (2017C50042), Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Pathophysiology (201804), Open Project Program of State Key Laboratory of Food Nutrition and Safety, Tianjin University of Science & Technology (SKLFNS-KF-201806), Ningbo municipal innovation team of life science and health (2015C110026), LiDakSum Marine Biopharmaceutical Development Fund, and the K. C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare there thay have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Pan, H., Bai, Y. et al. Gelsemine, a natural alkaloid extracted from Gelsemium elegans Benth. alleviates neuroinflammation and cognitive impairments in Aβ oligomer-treated mice. Psychopharmacology 237, 2111–2124 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05522-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05522-y