Abstract
Rationale
During the last few decades, alcohol use disorders (AUD) have reached an epidemic prevalence, yet social influences on alcoholism have not been fully addressed. Several factors can modulate alcohol intake. On one hand, stress can reinforce ethanol-induced behaviors and be an important component in AUD and alcoholism. On the other hand, environmental enrichment (EE) has a neuroprotective role and prevents the development of excessive ethanol intake in rodents. However, studies showing the role of EE in chronic psychosocial stress-impaired ethanol-conditioned rewards are nonexistent.
Aim
The purpose of the current study is to explore the potential protective role of EE on extinction and reinstatement of ethanol-conditioned place preference (EtOH-CPP) following chronic psychosocial stress.
Methods
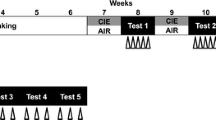
In the first experiment and after the EtOH-CPP test, the mice were subjected to 15 days of chronic stress, then housed in a standard (SE) or enriched environment (EE) while EtOH-CPP extinction was achieved by repeated exposure to the CPP chambers without ethanol injection. In the second experiment and after the EtOH-CPP test, extinction was achieved as described above. Mice were then exposed to chronic stress for 2 weeks before being housed in a SE or EE. EtOH-CPP reinstatement was induced by a single exposure to the conditioning chambers.
Results
As expected, stress exposure increased anxiety-like behavior and reduced weight gain. More importantly, we found that EE significantly shortened chronic stress-delayed extinction and decreased the reinstatement of EtOH-CPP.
Conclusion
These results support the hypothesis that EE reduces the impact of alcohol-associated environmental stimuli, and hence it may be a general intervention for reducing cue-elicited craving and relapse in humans.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPP:
-
Conditioned place preference
- CSC:
-
Chronic subordinate colony
- EE:
-
Enriched environment
- EPM:
-
Elevated plus maze
- EtOH:
-
Ethanol
- OF:
-
Open field
- SE:
-
Standard environment
- SHC:
-
Single housed colony
References
Al Ameri M, Al Mansouri S, Al Maamari A, Bahi A (2014) The histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor valproic acid reduces ethanol consumption and ethanol-conditioned place preference in rats. Brain Res 1583:122–131
Al Maamari E, Al Ameri M, Al Mansouri S, Bahi A (2014) Inhibition of urokinase plasminogen activator “uPA” activity alters ethanol consumption and conditioned place preference in mice. Drug Des Devel Ther 8:1391–1403
Al Mansouri S, Ojha S, Al Maamari E, Al Ameri M, Nurulain SM, Bahi A (2014) The cannabinoid receptor 2 agonist, beta-caryophyllene, reduced voluntary alcohol intake and attenuated ethanol-induced place preference and sensitivity in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 124:260–268
Albrechet-Souza L, Viola TW, Grassi-Oliveira R, Miczek KA, de Almeida RMM (2017) Corticotropin releasing factor in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in socially defeated and non-stressed mice with a history of chronic alcohol intake. Front Pharmacol 8:762
Arai JA, Feig LA (2011) Long-lasting and transgenerational effects of an environmental enrichment on memory formation. Brain Res Bull 85:30–35
Bahi A (2012) The selective metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 allosteric agonist AMN082 prevents reinstatement of extinguished ethanol-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 101:193–200
Bahi A (2013) Increased anxiety, voluntary alcohol consumption and ethanol-induced place preference in mice following chronic psychosocial stress. Stress 16:441–451
Bahi A (2015) The oxytocin receptor impairs ethanol reward in mice. Physiol Behav 139:321–327
Bahi A (2017a) Decreased anxiety, voluntary ethanol intake and ethanol-induced CPP acquisition following activation of the metabotropic glutamate receptor 8 “mGluR8”. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 155:32–42
Bahi A (2017b) Environmental enrichment reduces chronic psychosocial stress-induced anxiety and ethanol-related behaviors in mice. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 77:65–74
Bahi A, Dreyer JL (2012a) Hippocampus-specific deletion of tissue plasminogen activator “tPA” in adult mice impairs depression- and anxiety-like behaviors. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 22:672–682
Bahi A, Dreyer JL (2012b) Involvement of tissue plasminogen activator “tPA” in ethanol-induced locomotor sensitization and conditioned-place preference. Behav Brain Res 226:250–258
Bahi A, Dreyer JL (2014) Chronic psychosocial stress causes delayed extinction and exacerbates reinstatement of ethanol-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Psychopharmacology 231:367–377
Bahi A, Dreyer JL (2018) Lentiviral-mediated let-7d microRNA overexpression induced anxiolytic- and anti-depressant-like behaviors and impaired dopamine D3 receptor expression. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 28:1394–1404
Bahi A, Dreyer JL (2019) Dopamine transporter (DAT) knockdown in the nucleus accumbens improves anxiety- and depression-related behaviors in adult mice. Behav Brain Res 359:104–115
Bahi A, Tolle V, Fehrentz JA, Brunel L, Martinez J, Tomasetto CL, Karam SM (2013) Ghrelin knockout mice show decreased voluntary alcohol consumption and reduced ethanol-induced conditioned place preference. Peptides 43:48–55
Bahi A, Al Mansouri S, Al Memari E, Al Ameri M, Nurulain SM, Ojha S (2014a) Beta-Caryophyllene, a CB2 receptor agonist produces multiple behavioral changes relevant to anxiety and depression in mice. Physiol Behav 135:119–124
Bahi A, Nurulain SM, Ojha S (2014b) Ethanol intake and ethanol-conditioned place preference are reduced in mice treated with the bioflavonoid agent naringin. Alcohol 48:677–685
Bardo MT, Bowling SL, Rowlett JK, Manderscheid P, Buxton ST, Dwoskin LP (1995) Environmental enrichment attenuates locomotor sensitization, but not in vitro dopamine release, induced by amphetamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 51:397–405
Berton O, Aguerre S, Sarrieau A, Mormede P, Chaouloff F (1998) Differential effects of social stress on central serotonergic activity and emotional reactivity in Lewis and spontaneously hypertensive rats. Neuroscience 82:147–159
Blanchard DC, Spencer RL, Weiss SM, Blanchard RJ, McEwen B, Sakai RR (1995) Visible burrow system as a model of chronic social stress: behavioral and neuroendocrine correlates. Psychoneuroendocrinology 20:117–134
Britton DR, Britton KT (1981) A sensitive open field measure of anxiolytic drug activity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:577–582
Calvo-Torrent A, Brain PF, Martinez M (1999) Effect of predatory stress on sucrose intake and behavior on the plus-maze in male mice. Physiol Behav 67:189–196
Caruso MJ, Seemiller LR, Fetherston TB, Miller CN, Reiss DE, Cavigelli SA, Kamens HM (2018) Adolescent social stress increases anxiety-like behavior and ethanol consumption in adult male and female C57BL/6J mice. Sci Rep 8:10040
Cason AM, Aston-Jones G (2014) Role of orexin/hypocretin in conditioned sucrose-seeking in female rats. Neuropharmacology 86:97–102
Chauvet C, Lardeux V, Goldberg SR, Jaber M, Solinas M (2009) Environmental enrichment reduces cocaine seeking and reinstatement induced by cues and stress but not by cocaine. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2767–2778
Cloutier RM, Blumenthal H, Trim RS, Douglas ME, Anderson KG (2019) Real-time social stress response and subsequent alcohol use initiation among female adolescents. Psychol Addict Behav 33:254–265
Conway KP, Compton W, Stinson FS, Grant BF (2006) Lifetime comorbidity of DSM-IV mood and anxiety disorders and specific drug use disorders: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions. J Clin Psychiatry 67:247–257
D’Cunha TM, Sedki F, Macri J, Casola C, Shalev U (2013) The effects of chronic food restriction on cue-induced heroin seeking in abstinent male rats. Psychopharmacology 225:241–250
Di Chiara G (1997) Alcohol and dopamine. Alcohol Health Res World 21:108–114
Eckel RH, Grundy SM, Zimmet PZ (2005) The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 365:1415–1428
El Rawas R, Thiriet N, Lardeux V, Jaber M, Solinas M (2009) Environmental enrichment decreases the rewarding but not the activating effects of heroin. Psychopharmacology 203:561–570
Erhardt A, Muller MB, Rodel A, Welt T, Ohl F, Holsboer F, Keck ME (2009) Consequences of chronic social stress on behaviour and vasopressin gene expression in the PVN of DBA/2OlaHsd mice—influence of treatment with the CRHR1-antagonist R121919/NBI 30775. J Psychopharmacol 23:31–39
Ewin SE, Kangiser MM, Stairs DJ (2015) The effects of environmental enrichment on nicotine condition place preference in male rats. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 23:387–394
Fu R, Chen X, Zuo W, Li J, Kang S, Zhou LH, Siegel A, Bekker A, Ye JH (2016) Ablation of mu opioid receptor-expressing GABA neurons in rostromedial tegmental nucleus increases ethanol consumption and regulates ethanol-related behaviors. Neuropharmacology 107:58–67
Fuchsl AM, Neumann ID, Reber SO (2014) Stress resilience: a low-anxiety genotype protects male mice from the consequences of chronic psychosocial stress. Endocrinology 155:117–126
Gauthier JM, Lin A, Nic Dhonnchadha BA, Spealman RD, Man HY, Kantak KM (2017) Environmental enrichment facilitates cocaine-cue extinction, deters reacquisition of cocaine self-administration and alters AMPAR GluA1 expression and phosphorylation. Addict Biol 22:152–162
Grant BF, Stinson FS, Dawson DA, Chou SP, Dufour MC, Compton W, Pickering RP, Kaplan K (2004) Prevalence and co-occurrence of substance use disorders and independent mood and anxiety disorders: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry 61:807–816
Grimm JW, Osincup D, Wells B, Manaois M, Fyall A, Buse C, Harkness JH (2008) Environmental enrichment attenuates cue-induced reinstatement of sucrose seeking in rats. Behav Pharmacol 19:777–785
Grinan-Ferre C, Izquierdo V, Otero E, Puigoriol-Illamola D, Corpas R, Sanfeliu C, Ortuno-Sahagun D, Pallas M (2018) Environmental enrichment improves cognitive deficits, AD hallmarks and epigenetic alterations presented in 5xFAD mouse model. Front Cell Neurosci 12:224
Hasin DS, Stinson FS, Ogburn E, Grant BF (2007) Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence in the United States: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:830–842
Heilig M, Goldman D, Berrettini W, O’Brien CP (2011) Pharmacogenetic approaches to the treatment of alcohol addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:670–684
Heinrichs SC, Pich EM, Miczek KA, Britton KT, Koob GF (1992) Corticotropin-releasing factor antagonist reduces emotionality in socially defeated rats via direct neurotropic action. Brain Res 581:190–197
Hess SE, Rohr S, Dufour BD, Gaskill BN, Pajor EA, Garner JP (2008) Home improvement: C57BL/6J mice given more naturalistic nesting materials build better nests. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci 47:25–31
Huang H, Zhang X, Fu X, Zhang X, Lang B, Xiang X, Hao W (2018) Alcohol-induced conditioned place preference negatively correlates with anxiety-like behavior in adolescent mice: inhibition by a neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist. Psychopharmacology 235:2847–2857
Hwa LS, Holly EN, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2016) Social stress-escalated intermittent alcohol drinking: modulation by CRF-R1 in the ventral tegmental area and accumbal dopamine in mice. Psychopharmacology 233:681–690
Imperio CG, McFalls AJ, Hadad N, Blanco-Berdugo L, Masser DR, Colechio EM, Coffey AA, Bixler GV, Stanford DR, Vrana KE, Grigson PS, Freeman WM (2018) Exposure to environmental enrichment attenuates addiction-like behavior and alters molecular effects of heroin self-administration in rats. Neuropharmacology 139:26–40
Li X, Meng L, Huang K, Wang H, Li D (2015) Environmental enrichment blocks reinstatement of ethanol-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Neurosci Lett 599:92–96
Lima FB, Spinelli de Oliveira E (2014) What is the impact of low testosterone levels on the anatomical and behavioral repertoire of long-term enriched housing of male mice? Behav Process 108:57–64
Lopatina O, Yoshihara T, Nishimura T, Zhong J, Akther S, Fakhrul AA, Liang M, Higashida C, Sumi K, Furuhara K, Inahata Y, Huang JJ, Koizumi K, Yokoyama S, Tsuji T, Petugina Y, Sumarokov A, Salmina AB, Hashida K, Kitao Y, Hori O, Asano M, Kitamura Y, Kozaka T, Shiba K, Zhong F, Xie MJ, Sato M, Ishihara K, Higashida H (2014) Anxiety- and depression-like behavior in mice lacking the CD157/BST1 gene, a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease. Front Behav Neurosci 8:133
Lopez MF, Laber K (2015) Impact of social isolation and enriched environment during adolescence on voluntary ethanol intake and anxiety in C57BL/6J mice. Physiol Behav 148:151–156
Marcus DJ, Henderson-Redmond AN, Gonek M, Zee ML, Farnsworth JC, Amin RA, Andrews MJ, Davis BJ, Mackie K, Morgan DJ (2017) Mice expressing a “hyper-sensitive” form of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1) show modestly enhanced alcohol preference and consumption. PLoS One 12:e0174826
McBlane JW, Handley SL (1994) Effects of two stressors on behaviour in the elevated X-maze: preliminary investigation of their interaction with 8-OH-DPAT. Psychopharmacology 116:173–182
McCormick CM, Smith C, Mathews IZ (2008) Effects of chronic social stress in adolescence on anxiety and neuroendocrine response to mild stress in male and female rats. Behav Brain Res 187:228–238
Nephew BC, Bridges RS (2011) Effects of chronic social stress during lactation on maternal behavior and growth in rats. Stress 14:677–684
Newman EL, Albrechet-Souza L, Andrew PM, Auld JG, Burk KC, Hwa LS, Zhang EY, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2018) Persistent escalation of alcohol consumption by mice exposed to brief episodes of social defeat stress: suppression by CRF-R1 antagonism. Psychopharmacology 235:1807–1820
Nithianantharajah J, Hannan AJ (2006) Enriched environments, experience-dependent plasticity and disorders of the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:697–709
Norman KJ, Seiden JA, Klickstein JA, Han X, Hwa LS, DeBold JF, Miczek KA (2015) Social stress and escalated drug self-administration in mice I. Alcohol and corticosterone Psychopharmacology (Berl) 232:991–1001
Nyuyki KD, Beiderbeck DI, Lukas M, Neumann ID, Reber SO (2012) Chronic subordinate colony housing (CSC) as a model of chronic psychosocial stress in male rats. PLoS One 7:e52371
Okhuarobo A, Igbe I, Yahaya A, Sule Z (2018) Effect of caffeine on alcohol consumption and alcohol-induced conditioned place preference in rodents. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 30:19–28
Pang TY, Hannan AJ, Lawrence AJ (2019) Novel approaches to alcohol rehabilitation: modification of stress-responsive brain regions through environmental enrichment. Neuropharmacology 145:25–36
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M (1985) Validation of open:closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 14:149–167
Pham TM, Ickes B, Albeck D, Soderstrom S, Granholm AC, Mohammed AH (1999) Changes in brain nerve growth factor levels and nerve growth factor receptors in rats exposed to environmental enrichment for one year. Neuroscience 94:279–286
Reber SO, Birkeneder L, Veenema AH, Obermeier F, Falk W, Straub RH, Neumann ID (2007) Adrenal insufficiency and colonic inflammation after a novel chronic psycho-social stress paradigm in mice: implications and mechanisms. Endocrinology 148:670–682
Reber SO, Obermeier F, Straub RH, Veenema AH, Neumann ID (2008) Aggravation of DSS-induced colitis after chronic subordinate colony (CSC) housing is partially mediated by adrenal mechanisms. Stress 11:225–234
Rodgers RJ, Cole JC (1993) Anxiety enhancement in the murine elevated plus maze by immediate prior exposure to social stressors. Physiol Behav 53:383–388
Rodriguez-Arias M, Navarrete F, Blanco-Gandia MC, Arenas MC, Bartoll-Andres A, Aguilar MA, Rubio G, Minarro J, Manzanares J (2016) Social defeat in adolescent mice increases vulnerability to alcohol consumption. Addict Biol 21:87–97
Rosenzweig MR, Bennett EL (1996) Psychobiology of plasticity: effects of training and experience on brain and behavior. Behav Brain Res 78:57–65
Rygula R, Abumaria N, Havemann-Reinecke U, Ruther E, Hiemke C, Zernig G, Fuchs E, Flugge G (2008) Pharmacological validation of a chronic social stress model of depression in rats: effects of reboxetine, haloperidol and diazepam. Behav Pharmacol 19:183–196
Sale A (2018) A systematic look at environmental modulation and its impact in Brain development. Trends Neurosci 41:4–17
Sanberg PR (1989) Neuroleptic-induced emotional defecation: effects of pimozide and apomorphine. Physiol Behav 46:199–202
Schnabel J (2009) Neuroscience: rethinking rehab. Nature 458:25–27
Sedki F, Abbas Z, Angelis S, Martin J, D’Cunha T, Shalev U (2013a) Is it stress? The role of stress related systems in chronic food restriction-induced augmentation of heroin seeking in the rat. Front Neurosci 7:98
Sedki F, D’Cunha T, Shalev U (2013b) A procedure to study the effect of prolonged food restriction on heroin seeking in abstinent rats. J Vis Exp:e50751
Segovia G, Del Arco A, de Blas M, Garrido P, Mora F (2008) Effects of an enriched environment on the release of dopamine in the prefrontal cortex produced by stress and on working memory during aging in the awake rat. Behav Brain Res 187:304–311
Singewald GM, Nguyen NK, Neumann ID, Singewald N, Reber SO (2009) Effect of chronic psychosocial stress-induced by subordinate colony (CSC) housing on brain neuronal activity patterns in mice. Stress 12:58–69
Slattery DA, Uschold N, Magoni M, Bar J, Popoli M, Neumann ID, Reber SO (2012) Behavioural consequences of two chronic psychosocial stress paradigms: anxiety without depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 37:702–714
Smith MA, Chisholm KA, Bryant PA, Greene JL, McClean JM, Stoops WW, Yancey DL (2005) Social and environmental influences on opioid sensitivity in rats: importance of an opioid’s relative efficacy at the mu-receptor. Psychopharmacology 181:27–37
Solinas M, Chauvet C, Thiriet N, El Rawas R, Jaber M (2008) Reversal of cocaine addiction by environmental enrichment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:17145–17150
Solinas M, Thiriet N, El Rawas R, Lardeux V, Jaber M (2009) Environmental enrichment during early stages of life reduces the behavioral, neurochemical, and molecular effects of cocaine. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:1102–1111
Stefanski V (2001) Social stress in laboratory rats: behavior, immune function, and tumor metastasis. Physiol Behav 73:385–391
Tamashiro KL, Nguyen MM, Fujikawa T, Xu T, Yun Ma L, Woods SC, Sakai RR (2004) Metabolic and endocrine consequences of social stress in a visible burrow system. Physiol Behav 80:683–693
Tamashiro KL, Hegeman MA, Nguyen MM, Melhorn SJ, Ma LY, Woods SC, Sakai RR (2007) Dynamic body weight and body composition changes in response to subordination stress. Physiol Behav 91:440–448
Thiel KJ, Painter MR, Pentkowski NS, Mitroi D, Crawford CA, Neisewander JL (2012) Environmental enrichment counters cocaine abstinence-induced stress and brain reactivity to cocaine cues but fails to prevent the incubation effect. Addict Biol 17:365–377
Thiriet N, Gennequin B, Lardeux V, Chauvet C, Decressac M, Janet T, Jaber M, Solinas M (2011) Environmental enrichment does not reduce the rewarding and neurotoxic effects of methamphetamine. Neurotox Res 19:172–182
Vahid-Ansari F, Daigle M, Manzini MC, Tanaka KF, Hen R, Geddes SD, Beique JC, James J, Merali Z, Albert PR (2017) Abrogated Freud-1/Cc2d1a repression of 5-HT1A autoreceptors induces fluoxetine-resistant anxiety/depression-like behavior. J Neurosci 37:11967–11978
van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH (2000) Neural consequences of environmental enrichment. Nat Rev Neurosci 1:191–198
Veena J, Srikumar BN, Mahati K, Bhagya V, Raju TR, Shankaranarayana Rao BS (2009) Enriched environment restores hippocampal cell proliferation and ameliorates cognitive deficits in chronically stressed rats. J Neurosci Res 87:831–843
Veenema AH, Reber SO, Selch S, Obermeier F, Neumann ID (2008) Early life stress enhances the vulnerability to chronic psychosocial stress and experimental colitis in adult mice. Endocrinology 149:2727–2736
Xie Q, Buck LA, Bryant KG, Barker JM (2019) Sex differences in ethanol reward seeking under conflict in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 43:1556–1566
Zheng D, Cabeza de Vaca S, Carr KD (2012) Food restriction increases acquisition, persistence and drug prime-induced expression of a cocaine-conditioned place preference in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 100:538–544
Zuo W, Fu R, Hopf FW, Xie G, Krnjevic K, Li J, Ye JH (2017) Ethanol drives aversive conditioning through dopamine 1 receptor and glutamate receptor-mediated activation of lateral habenula neurons. Addict Biol 22:103–116
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Mr. Mohamed Shafiullah for his technical assistance and Dr. Mahmoud Hag Ali from the Central Animal Facility for his advice on animal care and welfare. The authors thank the three anonymous reviewers whose comments and suggestions have greatly improved this manuscript.
Funding
AB was supported by grants from the United Arab Emirates University (No. NP/13/05) and the National Research foundation (No. 31M082). The funders had no further role in study design; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahi, A., Dreyer, JL. Environmental enrichment decreases chronic psychosocial stress-impaired extinction and reinstatement of ethanol conditioned place preference in C57BL/6 male mice. Psychopharmacology 237, 707–721 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05408-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05408-8