Abstract
Rationale
We previously reported that systemic administration of a selective delta opioid receptor (DOP) agonist, KNT-127, produced potent anxiolytic-like effects in rats. Interestingly, DOPs are highly distributed in the basolateral region of the amygdala (BLA).
Objectives
In this study, we investigated the effect of intra-BLA administration of KNT-127 on anxiety-like behaviors in rats.
Methods and Results
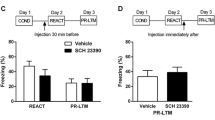
In the elevated plus maze test, bilateral injection of KNT-127 into the BLA significantly and dose-dependently increased time spent in the open arms. The magnitude of KNT-127 (0.08 μg/0.2 μl)-induced anxiolytic-like effects was similar to muscimol (0.1 μg/0.2 μl), which is a selective agonist for the gamma amino butyric acid type A receptors. Further, anxiolytic-like effects of KNT-127 were abolished by pretreatment with naltrindole, a selective DOP antagonist, suggesting that KNT-127-induced anxiolytic-like effects are mediated by DOPs. These anxiolytic-like effects were confirmed using another innate anxiety model, the open field test. Interestingly, intra-BLA administration of KNT-127 also induced anxiolytic-like effects in the contextual fear conditioning test. Moreover, these effects were also abolished by naltrindole pretreatment. Finally, we demonstrated that intra-BLA administration of KNT-127 facilitates extinction learning of contextual fear in conditioned rats.
Conclusions
Altogether, our findings clearly demonstrate that intra-BLA administration of KNT-127 in rats has robust anxiolytic-like effects not only in innate anxiety-like behavioral tests but also in the contextual fear conditioning test.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouton ME, Westbrook RF, Corcoran KA, Maren S (2006) Contextual and temporal modulation of extinction: behavioral and biological mechanisms. Biol Psychiatry 60(4):352–360
Davis M, Rainnie D, Cassell M (1994) Neurotransmission in the rat amygdala related to fear and anxiety. Trends Neurosci 17(5):208–214
Davis M, Ressler K, Rothbaum BO, Richardson R (2006) Effects of D-cycloserine on extinction: translation from preclinical to clinical work. Biol Psychiatry 60(4):369–375
Felix-Ortiz AC, Beyeler A, Seo C, Leppla CA, Wildes CP, Tye KM (2013) BLA to vHPC inputs modulate anxiety-related behaviors. Neuron 79(4):658–664
Grillon C (2002) Associative learning deficits increase symptoms of anxiety in humans. Biol Psychiatry 51(11):851–858
LeDoux J (2003) The emotional brain, fear, and the amygdala. Cell Mol Neurobiol 23(4–5):727–738
Lutz PE, Kieffer BL (2013) Opioid receptors: distinct roles in mood disorders. Trends Neurosci 36(3):195–206
Manko M, Geracitano R, Capogna M (2011) Functional connectivity of the main intercalated nucleus of the mouse amygdala. J Physiol 589(Pt 8):1911–1925
Menard J, Treit D (1999) Effects of centrally administered anxiolytic compounds in animal models of anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23(4):591–613
Moreira CM, Masson S, Carvalho MC, Brandão ML (2007) Exploratory behaviour of rats in the elevated plus-maze is differentially sensitive to inactivation of the basolateral and central amygdaloid nuclei. Brain Res Bull 71(5):466–474
Myers KM, Davis M (2007) Mechanisms of fear extinction. Mol Psychiatry 12(2):120–150
Nagase H, Nemoto T, Matsubara A, Saito M, Yamamoto N, Osa Y, Hirayama S, Nakajima M, Nakao K, Mochizuki H, Fujii H (2010) Design and synthesis of KNT-127, a δ-opioid receptor agonist effective by systemic administration. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20(21):6302–6305
Pare D, Smith Y (1993) The intercalated cell masses project to the central and medial nuclei of the amygdala in cats. Neuroscience 57(4):1077–1090
Paxinos G, Watson C (2013) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 7th edn. Academic Press
Randall-Thompson JF, Pescatore KA, Unterwald EM (2010) A role for delta opioid receptors in the central nucleus of the amygdala in anxiety-like behaviors. Psychopharmacol 212(4):585–595
Saitoh A, Sugiyama A, Nemoto T, Fujii H, Wada K, Oka J, Nagase H, Yamada M (2011) The novel δ opioid receptor agonist KNT-127 produces antidepressant-like and antinociceptive effects in mice without producing convulsions. Behav Brain Res 223(2):271–279
Saitoh A, Sugiyama A, Yamada M, Inagaki M, Oka J, Nagase H, Yamada M (2013) The novel δ opioid receptor agonist KNT-127 produces distinct anxiolytic-like effects in rats without producing the adverse effects associated with benzodiazepines. Neuropharmacology 67:485–493
Sugiyama A, Saitoh A, Iwai T, Takahashi K, Yamada M, Sasaki-Hamada S, Oka J, Inagaki M, Yamada M (2012) Riluzole produces distinct anxiolytic-like effects in rats without the adverse effects associated with benzodiazepines. Neuropharmacol 62(8):2489–2498
Sugiyama A, Saitoh A, Inagaki M, Oka J, Yamada M (2015) Systemic administration of riluzole enhances recognition memory and facilitates extinction of fear memory in rats. Neuropharmacology 97:322–328
Sugiyama A, Saitoh A, Yamada M, Oka JI, Yamada M (2017) Administration of riluzole into the basolateral amygdala has an anxiolytic-like effect and enhances recognition memory in the rat. Behav Brain Res 327:98–102
Sugiyama A, Yamada M, Saitoh A, Oka JI, Yamada M (2018) Administration of riluzole to the basolateral amygdala facilitates fear extinction in rats. Behav Brain Res 336:8–14
Walker DL, Ressler KJ, Lu KT, Davis M (2002) Facilitation of conditioned fear extinction by systemic administration or intra-amygdala infusions of D-cycloserine as assessed with fear-potentiated startle in rats. J Neurosci 22(6):2343–2351
Winters BL, Gregoriou GC, Kissiwaa SA, Wells OA, Medagoda DI, Hermes SM, Burford NT, Alt A, Aicher SA, Bagley EE (2017) Endogenous opioids regulate moment-to-moment neuronal communication and excitability. Nat Commun 8:14611
Acknowledgments
We thank Rachel James, Ph.D., from Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by an Intramural Research Grant (24-2, 27-1, 30-1) for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders provided by the National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry, Japan (NCNP). The funders had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The studies were conducted in accordance with protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Japanese National Center of Neurology and Psychiatry (Approval No. 2010001).
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugiyama, A., Yamada, M., Saitoh, A. et al. Administration of a delta opioid receptor agonist KNT-127 to the basolateral amygdala has robust anxiolytic-like effects in rats. Psychopharmacology 235, 2947–2955 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4984-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4984-7