Abstract
Rationale
Modafinil is a wake-promoting drug with FDA approval for the treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness that has been prescribed for ADHD and recently assessed as a potential treatment for psychostimulant dependence. Previous research indicates that modafinil modestly increases locomotor activity and produces similar discriminative stimulus effects to psychostimulants in rodents, although the subjective effects of modafinil are reportedly distinct from those of cocaine or amphetamine in humans with a history of psychostimulant abuse.
Objectives
The current study employed drug discrimination procedures in rats to examine the pharmacological actions contributing to modafinil’s discriminative stimulus functions.
Methods
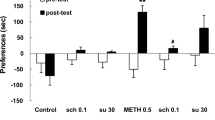
Eight male Sprague–Dawley rats were trained to discriminate intragastric administration of 256 mg/kg modafinil from vehicle (5 % arabic gum) under a FR 20 schedule of food reinforcement. Substitution tests were conducted with various dopaminergic agents (d-amphetamine, cocaine, PNU-91356A, GBR 12909, methylphenidate) and nondopaminergic agents (nicotine, ethanol). Antagonist tests were conducted with the selective D1 antagonist, SCH 39166, and the nonselective D2 antagonist, haloperidol.
Results
Rats trained to discriminate modafinil displayed complete stimulus generalization to cocaine, methylphenidate, and GBR 12909 and the discrimination was completely blocked by both SCH 39166 and haloperidol. Evidence for significant partial substitution was obtained with d-amphetamine, PNU-91356A, and nicotine.
Conclusions
Results strongly support the role of dopaminergic mechanisms in the discriminative stimulus functions of modafinil, although further evaluation regarding the contribution of other neurotransmitter systems to these effects should be continued. The findings are discussed in light of clinical research efforts with modafinil as a treatment for psychostimulant dependence.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen ML, Kessler E, Murnane KS, McClung JC, Tufik S, Howell LL (2010) Dopamine transporter-related effects of modafinil in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 210:439--448
Anderson AL, Reid MS, Shou-Hua L, Holmes T, Shemanski L, Slee A, Elkashef AM (2009) Modafinil for the treatment of cocaine dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend 104:133–139. doi:10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2009.04.015
Anderson A, Li S, Biswas K, McSherry F, Holmes T, Iturriaga E, Elkashef AM (2012) Modafinil for the treatment of methamphetamine dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend 120:135–141
Carter GT, Weiss MD, Lou J, Jensen MP, Abresch RT, Martin TK, Hecht TW, Han JJ, Weydt P, Kraft GH (2005) Modafinil to treat fatigue in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an open label pilot study. Am J Hosp Palliat Med 22:55–59
Dackis CA, Kampman KM, Lynch KG, Pettinati HM, O’Brien CP (2005) A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of modafinil for cocaine dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:205–211
Dean AC, Sevak RJ, Monterosso JR, Hellemann G, Sugar CA, London ED (2011) Acute modafinil effects on attention and inhibitory control in methamphetamine-dependent humans. J Stud Alcohol Drugs 72:943–953
Deroche-Gamonet V, Darnaudery M, Bruins-Slot L, Piat F, Moal ML, Piazza PV (2002) Study of the addictive potential of modafinil in naïve and cocaine-experienced rats. Psychopharmacology 161:387–395. doi:10.1007/s00213-002-1080-8
Di Chiara G (2000) Role of dopamine in the behavioural actions of nicotine related to addiction. Eur J Pharmacol 393:295–314
Dopheide MM, Morgan RE, Rodvelt KR, Schachtman TR, Miller DK (2007) Modafinil evokes striatal [3H]dopamine release and alters the subjective properties of stimulants. Eur J Pharmacol 568:112–123. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.03.044
Extance K, Goudie AJ (1981) Inter-animal olfactory cues in operant drug discrimination procedures in rats. Psychopharmacology 73(4):363–371
Federici M, Latagliata EC, Rizzo FR, Ledonne A, Gu HH, Romigi A, Nistico R, Puglisi-Allegra S, Mercuri NB (2013) Electrophysiological and amperometric evidence that modafinil blocks the dopamine uptake transporter to induce behavioral activation. Neuroscience 252:118–124. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.07.071
Ghahremani DG, Tabibnia G, Monterosso J, Hellemann G, Poldrack RA, London ED (2011) Effect of modafinil on learning and task-related brain activity in methamphetamine-dependent and healthy individuals. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:950–959. doi:10.1038/npp.2010.233
Glennon RA, Young R (2011) Drug discrimination: applications to medicinal chemistry and drug studies. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ
Gold LH, Balster RL (1996) Evaluation of the cocaine-like discriminative stimulus effects and reinforcing effects of modafinil. Psychopharmacology 126:286–292
Herin DV, Rush CR, Grabowski J (2010) Agonist-like pharmacotherapy for stimulant dependence: preclinical, human laboratory, and clinical studies. Ann NY Acad Science 1187:76–100
Hermant J, Rambert FA, Duteil J (1991) Awakening properties of modafinil: effect on nocturnal activity in monkeys (Macaca mulatta) after acute and repeated administration. Psychopharmacology 103:28–32
Hogl B, Saletu M, Brandauer E, Glatzi S, Frauscher B, Seppi K, Ulmer H, Wenning G, Poewe W (2002) Modafinil for the treatment of daytime sleepiness in Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind, randomized, crossover, placebo-controlled polygraphic trial. Sleep 25:62–66
Howcroft DJ, Jones RW (2005) Does modafinil have the potential to improve disrupted sleep pattern in patients with dementia. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 20:492–495. doi:10.1002/gps.1305
Jasinski DR (2000) An evaluation of the abuse potential of modafinil using methylphenidate as a reference. J Psychopharmacol 14:53–60
Kamien JB, Woolverton WL (1989) A pharmacological analysis of the discriminative stimulus properties of d-amphetamine in Rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248:938–946
Keating GM, Raffin MJ (2005) Modafinil: a review of its use in excessive sleepiness associated with obstructive sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome and shift work sleep disorder. CNS Drugs 19:785–803
Kleven MS, Koek W (1998) Discriminative stimulus properties of cocaine: enhancement by monoamine reuptake blockers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284:1015–1025
Korotkova TM, Klyuch BP, Ponomarenko AA, Lin JS, Hass HL, Sergeeva OA (2007) Modafinil inhibits rat midbrain dopaminergic neurons through D2-like receptors. Neuropharmacology 52:626–633. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2006.09.005
Li SM, Campbell BL, Katz JL (2006) Interaction of cocaine with dopamine uptake inhibitors or dopamine releasers in rats discriminating cocaine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:1988–1096
Lin JS, Gervasoni D, Hou Y, Vanni-Mercier G, Ramber F, Frydman A, Jouvet M (2000) Effects of amphetamine and modafinil on the sleep/wake cycle during experimental hypersomnia induced by sleep deprivation in the cat. J Sleep Res 9:89--96. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2869.2000.00181.x
Loland CJ, Mereu M, Okunola OM, Cao J, Prisinzano TE, Mazier S, Kopajtic T, Shi L, Katz JL, Tanda G, Newman AH (2012) R-modafinil (armodafinil): a unique dopamine uptake inhibitor and potential medication for psychostimulant abuse. Biol Psychiatry 72:405–413
Makris AP, Rush CR, Frederich RC, Taylor AC, Kelly TH (2007) Behavioral and subjective effects of d-amphetamine and modafinil in healthy adults. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 15:123–133. doi:10.1037/1064-1297.15.2.123
Malcolm R, Swayngim K, Donovan JL, DeVane CL, Elkashef A, Chiang N, Khan R, Mojsiak J, Myrick DL, Hedden S, Cochran K, Woolson RF (2006) Modafinil and cocaine interactions. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 32:577–587. doi:10.1080/00952990600920425
Mann N, Bitsios P (2008) Modafinil treatment of amphetamine abuse in adult ADHD. J Psychopharmacol 23:468–471. doi:10.1177/0269881108091258
Minzenberg MJ, Carter CS (2008) Modafinil: a review of neurochemical actions and effects on cognition. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1477–1502
Myrick H, Malcolm R, Taylor B, LaRowe S (2004) Modafinil: preclinical, clinical, and post-marketing surveillance—a review of abuse liability issues. Ann Clin Psychiatry 16:101–109
National Research Council of the National Academies Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (2011). Available at https://grants.nih.gov/grants/olaw/Guide-for-the-Care-and-Use-of-Laboratory-Animals.pdf
Newman JL, Negus SS, Lozama A, Prisinzano TE, Mello NK (2010) Behavioral evaluation of modafinil and the abuse-related effects of cocaine in rhesus monkeys. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 18:395–408. doi:10.1037/a0021042
Nguyen T, Tian Y, You I, Lee S, Jang C (2011) Modafinil-induced conditioned place preference via dopaminergic system in mice. Synapse 65:733–741. doi:10.1002/syn.20.892
Paterson NE, Fedolak A, Olivier B, Hanania T, Ghavami A, Caldarone B (2010) Psychostimulant-like discriminative stimulus and locomotor sensitization of the wake-promoting agent modafinil in rodents. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 95:449–456. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2010.03.006
Prisinzano T, Podobinski J, Tidgewell K, Luo M, Swenson D (2004) Synthesis and determination of the absolute configuration of the enantiomers of modafinil. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 15:1053–1058
Quisenberry AJ, Prisinzano TE, Baker LE (2013a) Combined effects of modafinil and d-amphetamine in male Sprague–Dawley rats trained to discriminate d-amphetamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 110:208–215
Quisenberry AJ, Prisinzano TE, Baker LE (2013b) Modafinil alone and in combination with low dose amphetamine does not establish conditioned place preference in male Sprague–Dawley rats. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 21:252–258
Rowley H L, Kulkarni R S, Gosden J, Brammer R J, Hackett D, Heal D J (2013) Differences in the neurochemical and behavioural profiles of lisdexamfetamine methylphenidate and modafinil revealed by simultaneous dual-probe microdialysis and locomotor activity measurements in freely-moving rats. J Psychopharmacol 0: 1–16. doi: 10.1177/0269881113513850
Rush CR, Kelly TH, Hays LR, Wooten AF (2002a) Discriminative stimulus effects of modafinil in cocaine-trained humans. Drug Alcohol Depend 67:311–322
Rush CR, Kelly TH, Hays LR, Baker RW, Wooten AF (2002b) Acute behavioral and physiological effects of modafinil in drug abusers. Behav Pharmacol 13:105–115
Schmitz JM, Rathnayake N, Green CE, Moeller G, Dougherty AE, Grabowski J (2012) Combination of modafinil and d-amphetamine for the treatment of cocaine dependence: a preliminary investigation. Front Psychol 3:1–6. doi:10.3389/psyt.2012.00077
Shearer J, Darke S, Rodgers C, Slade T, van Beek I, Lewis J, Brady D, McKetin R, Mattick RP, Wodak A (2009) A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of modafinil (200 mg/day) for methamphetamine dependence. Addiction 104:224–233. doi:10.1111/j.1360-0443.2008.02437.x
Sheng P, Hou L, Wang X, Wang X, Huang C, Yu M, Han X, Dong Y (2013) Efficacy of modafinil in fatigue and excessive daytime sleepiness associated with neurological disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 8:1–11
Silvestri AJ, Sanford LD, Ross RJ, Mann GL, Pavlock A, Morrison AR (2002) The central nucleus of the amygdala and the wake-promoting effects of modafinil. Brain Res 941:43–52
Stoops WW, Lile JA, Fillmore MT, Glaser PEA, Rush CR (2005) Reinforcing effects of modafinil: influence of dose and behavioral demands following drug administration. Psychopharmacology 182:186–193
Turkington D, Hedwat D, Rider I, Young AH (2004) Recovery from chronic fatigue syndrome with modafinil. Hum Psychopharmacol 19:63–64
Turner DC, Robbins TW, Clark L, Aron AR, Dowson J, Sahakian BJ (2003) Cognitive enhancing effects of modafinil in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 165:260–269
van Vilet SAM, Jongsma MJ, Vanwersch RAP, Olivier B, Philippens I (2006) Behavioral effects of modafinil in marmoset monkeys. Psychopharmacology 185:433–440. doi:10.1007/s00212-006-0340-4
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Logan J, Alexoff D, Wei Zhu BSE, Telang F et al (2009) Effects of modafinil on dopamine and dopamine transporters in the male human brain: clinical implications. JAMA 301:1148–1154. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.351
Ward CP, Harsh JR, York KM, Stewart KL, McCoy JG (2004) Modafinil facilitates performance on a delayed nonmatching to position swim task in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 78:735–741
Warot D, Corruble E, Payan C, Weil JS, Puech AJ (1993) Subjective effects of modafinil, a new central adrenergic stimulant in healthy volunteers: a comparison with amphetamine, caffeine, and placebo. Eur Psychiatry 8:201–208
Webb IA, Pollock MS, Mistlberger RE (2006) Modafinil [2-[(diphenylmethyl)sulfinyl]acetamide] and circadian rhythms in Syrian hamsters: assessment of the chronobiotic potential of a novel alerting compound. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:882–889. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.099010
Willie JT, Rental W, Chemelli RM, Miller MS, Scammell TE, Yanagisawa M, Sinton CM (2005) Modafinil more effectively induces wakefulness in orexin-null mice than in wild-type littermates. Neuroscience 130:983–995. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.10.005
Wisor JP, Nishino S, Sora I, Uhl GH, Mignot E, Edgar DM (2001) Dopaminergic role in stimulant-induced wakefulness. J Neurosci 21:1787–1794
Young JW, Kooistra K, Geyer MA (2011) Dopamine receptor mediation of the exploratory/hyperactivity effects of modafinil. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:1385–1396
Zolkowska D, Jain R, Rothman RB, Partilla JS, Roth BL, Setola V, Prisinzano TE, Baumann MH (2009) Evidence for the involvement of dopamine transporters in behavioral stimulant effects of modafinil. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 329:738–746. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.146142
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Mike Caspers and Dr. Thomas Prisinzano, Department of Medicinal Chemistry, University of Kansas, for preparation of the modafinil used in this study. Through the generous contribution of GBR 12909, a portion of this work was supported by the intramural research programs of the National Institute on Drug Abuse and the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. All procedures in this experiment complied with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quisenberry, A.J., Baker, L.E. Dopaminergic mediation of the discriminative stimulus functions of modafinil in rats. Psychopharmacology 232, 4411–4419 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-4065-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-4065-0