Abstract
Rationale
Drug addiction represents a pathological usurpation of neural processes involved in learning and memory. Retrieval of drug-related memories can result in drug craving and relapse. Recently, the insula was identified as part of the neuronal circuit responsible for the processing of drug memory; however, its precise role remains unclear.
Objective
To investigate the involvement of insular muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) in the processing of drug memory.
Method
The morphine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) was used to assess drug memory. All rats were first trained with morphine to establish the CPP. Sub-groups of these rats were used for contextual cue-induced CPP reinstatement. Other sub-groups of rats underwent extinction of the CPP, and 5 m/kg morphine was used for priming-induced CPP reinstatement. Microinjection of mAChR antagonists or agonists into the insula was performed prior to the CPP tests in order to evaluate their effect on CPP expression.
Results
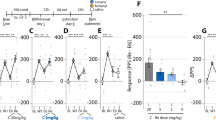
Insular microinjections of the nonselective mAChR antagonist, scopolamine, and the M1 antagonist, pirenzepine, significantly inhibited CPP expression in both contextual cue- and priming-induced CPP reinstatement; the M1 agonist, MCN-A-343, and the M4 antagonist, tropicamide, enhanced CPP expression. The M4 agonist, LY2033298, inhibited CPP expression. The M2 antagonist, methoctramine, and M3 antagonist, 4-DAMP, had no effect on CPP expression.
Conclusion
Our results demonstrate that insular mAChRs play a role in the processing of drug memory. M1 and M4 mAChRs work paradoxically; M1 activation and M4 inhibition attenuate the expression of drug memory, while M1 inhibition and M4 activation augment the expression of drug memory.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman DE, Dudai Y (2001) Memory extinction, learning anew, and learning the new: dissociations in the molecular machinery of learning in cortex. Science (NY) 291:2417–2419
Bosch D, Schmid S (2006) Activation of muscarinic cholinergic receptors inhibits giant neurones in the caudal pontine reticular nucleus. Eur J Neurosci 24:1967–1975
Brady AE, Jones CK, Bridges TM, Kennedy JP, Thompson AD, Heiman JU, Breininger ML, Gentry PR, Yin H, Jadhav SB, Shirey JK, Conn PJ, Lindsley CW (2008) Centrally active allosteric potentiators of the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor reverse amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotor activity in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 327:941–953
Chan WY, McKinzie DL, Bose S, Mitchell SN, Witkin JM, Thompson RC, Christopoulos A, Lazareno S, Birdsall NJ, Bymaster FP, Felder CC (2008) Allosteric modulation of the muscarinic M4 receptor as an approach to treating schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:10978–10983
Coleman CG, Lydic R, Baghdoyan HA (2004) M2 muscarinic receptors in pontine reticular formation of C57BL/6J mouse contribute to rapid eye movement sleep generation. Neuroscience 126:821–830
Conn PJ, Jones CK, Lindsley CW (2009) Subtype-selective allosteric modulators of muscarinic receptors for the treatment of CNS disorders. Trends Pharmacol Sci 30:148–155
Contreras M, Billeke P, Vicencio S, Madrid C, Perdomo G, Gonzalez M, Torrealba F (2012) A role for the insular cortex in long-term memory for context-evoked drug craving in rats. Neuropsychopharmacol Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 37:2101–2108
Contreras M, Ceric F, Torrealba F (2007) Inactivation of the interoceptive insula disrupts drug craving and malaise induced by lithium. Science (NY) 318:655–658
Daglish MR, Weinstein A, Malizia AL, Wilson S, Melichar JK, Lingford-Hughes A, Myles JS, Grasby P, Nutt DJ (2003) Functional connectivity analysis of the neural circuits of opiate craving: “more” rather than “different”? NeuroImage 20:1964–1970
Dencker D, Weikop P, Sorensen G, Woldbye DP, Wortwein G, Wess J, Fink-Jensen A (2012) An allosteric enhancer of M(4) muscarinic acetylcholine receptor function inhibits behavioral and neurochemical effects of cocaine. Psychopharmacology 224:277–287
Esmaeili B, Basseda Z, Dehpour AR (2008) Antagonism of muscarinic M1 receptors by dicyclomine inhibits the consolidation of morphine-associated contextual memory. Brain Res Bull 76:380–387
Fink-Jensen A, Fedorova I, Wortwein G, Woldbye DP, Rasmussen T, Thomsen M, Bolwig TG, Knitowski KM, McKinzie DL, Yamada M, Wess J, Basile A (2003) Role for M5 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in cocaine addiction. J Neurosci Res 74:91–96
Goldstein RZ, Craig AD, Bechara A, Garavan H, Childress AR, Paulus MP, Volkow ND (2009) The neurocircuitry of impaired insight in drug addiction. Trends Cogn Sci 13:372–380
Gutierrez R, Rodriguez-Ortiz CJ, De La Cruz V, Nunez-Jaramillo L, Bermudez-Rattoni F (2003a) Cholinergic dependence of taste memory formation: evidence of two distinct processes. Neurobiol Learn Mem 80:323–331
Gutierrez R, Tellez LA, Bermudez-Rattoni F (2003b) Blockade of cortical muscarinic but not NMDA receptors prevents a novel taste from becoming familiar. Eur J Neurosci 17:1556–1562
Herremans AH, Hijzen TH, Olivier B (1997) Effects of cholinergic drug infusions into the dorsal part of the medial prefrontal cortex on delayed conditional discrimination performance in the rat. Behav Brain Res 84:291–299
Hyman SE (2005) Addiction: a disease of learning and memory. Am J Psychiatry 162:1414–1422
Jeon J, Dencker D, Wortwein G, Woldbye DP, Cui Y, Davis AA, Levey AI, Schutz G, Sager TN, Mork A, Li C, Deng CX, Fink-Jensen A, Wess J (2010) A subpopulation of neuronal M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors plays a critical role in modulating dopamine-dependent behaviors. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 30:2396–2405
Kelley JB, Anderson KL, Itzhak Y (2007) Long-term memory of cocaine-associated context: disruption and reinstatement. Neuroreport 18:777–780
Leach K, Loiacono RE, Felder CC, McKinzie DL, Mogg A, Shaw DB, Sexton PM, Christopoulos A (2010) Molecular mechanisms of action and in vivo validation of an M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor allosteric modulator with potential antipsychotic properties. Neuropsychopharmacol Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 35:855–869
Li Y, Wu X, Zhu J, Yan J, Owyang C (2003) Hypothalamic regulation of pancreatic secretion is mediated by central cholinergic pathways in the rat. J Physiol 552:571–587
Liu Y, Le Foll B, Liu Y, Wang X, Lu L (2008) Conditioned place preference induced by licit drugs: establishment, extinction, and reinstatement. Sci World J 8:1228–1245
Lu L, Xu NJ, Ge X, Yue W, Su WJ, Pei G, Ma L (2002) Reactivation of morphine conditioned place preference by drug priming: role of environmental cues and sensitization. Psychopharmacology 159:125–132
Lynch MR (1991) Scopolamine enhances expression of an amphetamine-conditioned place preference. Neuroreport 2:715–718
Miranda MI, Bermudez-Rattoni F (2007) Cholinergic activity in the insular cortex is necessary for acquisition and consolidation of contextual memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 87:343–351
Miranda MI, Ferreira G, Ramirez-Lugo L, Bermudez-Rattoni F (2003) Role of cholinergic system on the construction of memories: taste memory encoding. Neurobiol Learn Mem 80:211–222
Miranda MI, McGaugh JL (2004) Enhancement of inhibitory avoidance and conditioned taste aversion memory with insular cortex infusions of 8-Br-cAMP: involvement of the basolateral amygdala. Learn Mem (Cold Spring Harb NY) 11:312–317
Naor C, Dudai Y (1996) Transient impairment of cholinergic function in the rat insular cortex disrupts the encoding of taste in conditioned taste aversion. Behav Brain Res 79:61–67
Naqvi NH, Bechara A (2009) The hidden island of addiction: the insula. Trends Neurosci 32:56–67
Naqvi NH, Rudrauf D, Damasio H, Bechara A (2007) Damage to the insula disrupts addiction to cigarette smoking. Science (NY) 315:531–534
Ramirez-Lugo L, Miranda MI, Escobar ML, Espinosa E, Bermudez-Rattoni F (2003) The role of cortical cholinergic pre- and post-synaptic receptors in taste memory formation. Neurobiol Learn Mem 79:184–193
Ramos AC, Andersen ML, Oliveira MG, Soeiro AC, Galduroz JC (2012) Biperiden (M(1) antagonist) impairs the expression of cocaine conditioned place preference but potentiates the expression of cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization. Behav Brain Res 231:213–216
Rezayof A, Nazari-Serenjeh F, Zarrindast MR, Sepehri H, Delphi L (2007) Morphine-induced place preference: involvement of cholinergic receptors of the ventral tegmental area. Eur J Pharmacol 562:92–102
Schmidt LS, Thomsen M, Weikop P, Dencker D, Wess J, Woldbye DP, Wortwein G, Fink-Jensen A (2011) Increased cocaine self-administration in M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor knockout mice. Psychopharmacology 216:367–378
Schroeder JP, Packard MG (2002) Posttraining intra-basolateral amygdala scopolamine impairs food- and amphetamine-induced conditioned place preferences. Behav Neurosci 116:922–927
Scott D, Hiroi N (2011) Deconstructing craving: dissociable cortical control of cue reactivity in nicotine addiction. Biol Psychiatry 69:1052–1059
Tan H, Liu N, Wilson FA, Ma Y (2007) Effects of scopolamine on morphine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Addict Biol 12:463–469
Tayebati SK, Di Tullio MA, Amenta F (2006) Muscarinic cholinergic receptor subtypes in cerebral cortex of Fisher 344 rats: a light microscope autoradiography study of age-related changes. Mech Ageing Dev 127:115–122
Yang G (2002) Muscarinic receptors: a novel therapeutic target for drug addiction. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:551
Zacarias MS, Ramos AC, Alves DR, Galduroz JC (2012) Biperiden (an M1 antagonist) reduces memory consolidation of cocaine-conditioned place preference. Neurosci Lett 513:129–131
Zhai H, Wu P, Chen S, Li F, Liu Y, Lu L (2008) Effects of scopolamine and ketamine on reconsolidation of morphine conditioned place preference in rats. Behav Pharmacol 19:211–216
Zhang L, Chen S, Liu H, Lu L, Zhai H (2010) Synthetic double-stranded RNA polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid augments morphine-induced conditioned place preference in rats. Behav Pharmacol 21:369–373
Acknowledgments
This project was jointly sponsored by the National Science Foundation (no. 30873051, 81271473) and Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (no. 7112087) of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, W., Li, H., Liu, Y. et al. Involvement of insular muscarinic cholinergic receptors in morphine-induced conditioned place preference in rats. Psychopharmacology 231, 4109–4118 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3550-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3550-1