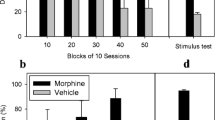
Abstract
Rationale
Opioid addiction is a chronic, recurrent brain disease that is characterised by compulsive drug seeking and a high rate of relapse even after long periods of abstinence. Prevention of relapse is the primary goal of addiction treatment and is still the major limitation in drug therapy.
Objectives
The present study investigated the effects of a Rhodiola rosea L. hydroalcoholic extract (RHO), a well-known traditional oriental medicine, on establishment and reinstatement of morphine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) in mice.
Methods
CPP was induced by intraperitoneal injection of morphine (10 mg/kg) as an 8-day conditioning schedule. The effects of RHO on the rewarding properties of morphine were tested in mice receiving oral administration of RHO (10, 15, and 20 mg/kg) 60 min prior to each morphine injection (acquisition) or prior to the CPP test on day 9 (expression). Once established, CPP was extinguished by repeated testing, during which conditioned mice were injected daily with different doses of RHO. Finally, the efficacy of RHO in blocking reinstatement of CPP provoked by priming injections and physical stress was also evaluated.
Results
RHO administration showed dose dependency for prevention of establishment of CPP and was effective in facilitating extinction of morphine-induced CPP. RHO suppressed both priming- and stress-induced reinstatement of CPP in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusions
In conclusion, as RHO was effective for reducing craving and vulnerability to relapse, it might be a very effective natural remedy for the treatment of opioid addiction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar MA, Manzanedo C, Do Couto BR, Rodríguez-Arias M, Miñarro J (2009a) Memantine blocks sensitization to the rewarding effects of morphine. Brain Res 1288:95–104
Aguilar MA, Rodríguez-Arias M, Miñarro J (2009b) Neurobiological mechanisms of the reinstatement of drug-conditioned place preference. Brain Res Rev 59:253–277
Bardo MT, Rowlett JK, Harris MJ (1995) Conditioned place preference using opiate and stimulant drugs: a meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 19:39–51
Blum K, Chen TJ, Meshkin B, Waite RL, Downs BW, Blum SH et al (2007) Manipulation of catechol-O-methyl-transferase (COMT) activity to influence the attenuation of substance seeking behavior, a subtype of Reward Deficiency Syndrome (RDS), is dependent upon gene polymorphisms: a hypothesis. Med Hypotheses 69:1054–1060
Brådvik L, Berglund M, Frank A, Lindgren A, Löwenhielm P (2009) Number of addictive substances used related to increased risk of unnatural death: a combined medico-legal and case-record study. BMC Psychiatr 9:48
Camí J, Farré M (2003) Drug addiction. N Engl J Med 349:975–986
Chen QG, Zeng YS, Qu ZQ, Tang JY, Qin YJ, Chung P et al (2009) The effects of Rhodiola rosea extract on 5-HT levels, cell proliferation and quantity of neurons at cerebral hippocampus of depressive rats. Phytomedicine 16:830–838
Cifani C, Micioni Db MV, Vitale G, Ruggieri V, Ciccocioppo R, Massi M (2010) Effect of salidroside, the active principle of Rhodiola rosea extract, on binge eating. Physiol Behav 101(5):555–562
Darbinyan V, Kteyan A, Panossian A, Gabrielian E, Wikman G, Wagner H (2000) Rhodiola rosea in stress induced fatigue—a double blind cross-over study of a standardized extract SHR-5 with a repeated low-dose regimen on the mental performance of healthy physicians during night duty. Phytomedicine 7:365–371
Davis M, Myers KM (2002) The role of glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid in fear extinction: clinical implications for exposure therapy. Biol Psychiatry 52:998–1007
Dhawan K (2003) Drug/substance reversal effects of a novel tri-substituted benzoflavone moiety (BZF) isolated from Passiflora incarnata Linn.-- a brief perspective. Addict Biol 8:379–386
Di Chiara G (1995) The role of dopamine in drug abuse viewed from the perspective of its role in motivation. Drug Alcohol Depend 38:95–137
Feily A, Abbasi N (2009) The inhibitory effect of Hypericum perforatum extract on morphine withdrawal syndrome in rat and comparison with clonidine. Phytother Res 23:1549–1552
German C, Ramazanov Z, Bernard Suarez M (1999) Artic root (Rodiola rosea): the powerful ginseng alternative. Kensington Publishing Corp, New York
Gupta GL, Rana AC (2008) Effect of Withania somnifera Dunal in ethanol-induced anxiolysis and withdrawal anxiety in rats. Indian J Exp Biol 46:470–475
Hao Y, Yang J, Sun J, Qi J, Dong Y, Wu CF (2008) Lesions of the medial prefrontal cortex prevent the acquisition but not reinstatement of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Neurosci Lett 433:48–53
Kasture S, Vinci S, Ibba F, Puddu A, Marongiu M, Murali B, Pisanu A, Lecca D, Zernig G, Acquas E (2009) Withania somnifera prevents morphine withdrawal-induced decrease in spine density in nucleus accumbens shell of rats: a confocal laser-scanning microscopy study. Neurotox Res 16:343–355
Kauhanen J, Hallikainen T, Tuomainen TP, Koulu M, Karvonen MK, Salonen JT et al (2000) Association between the functional polymorphism of catechol-o-methyltransferase gene and alcohol consumption among social drinkers. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:135–139
Kelly GS (2001) Rhodiola rosea: a possible plant adaptogen. Altern Med Rev 6:293–302
Kim HS, Jang CG, Park WK (1996) Inhibition by MK-801 of morphine-induced conditioned place preference and postsynaptic dopamine receptor supersensitivity in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 55:11–17
Koob GF (1992) Drugs of abuse: anatomy, pharmacology and function of reward pathways. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:177–184
Koob GF, Bloom FE (1985) Corticotropin-releasing factor and behavior. Fed Proc 44:259–263
Lee SY, Song DK, Jang CG (2003) Effects of Coptis japonica on morphine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Arch Pharm Res 26:540–544
Lishmanov YuB, Krylatov AV, Maslov LN, Nariznaya NV, Zamotinkii (1996) Effect of Rhodiola rosea on the level of inducible Hsp-70 in miocardial stress. Bull Exp Biol Med 121:256–258
Lu L, Ceng X, Huang M (2000) Corticotropin-releasing factor receptor type I mediates stress-induced relapse to opiate dependence in rats. Neuroreport 11:2373–2378
Lu L, Shepard JD, Scott Hall F, Shaham Y (2003) Effect of environmental stressors on opiate and psychostimulant reinforcement, reinstatement and discrimination in rats: a review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:457–491
Lu L, Chen H, Su W, Ge X, Yue W, Su F et al (2005) Role of withdrawal in reinstatement of morphine-conditioned place preference. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 181:90–100
Lu L, Liu Y, Zhu W, Shi J, Liu Y, Ling W, Kosten TR (2009) Traditional medicine in the treatment of drug addiction. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 35:1–11
Maldonado R (2003) The neurobiology of addiction. J Neural Transm Suppl 66:1–14
Mattioli L, Perfumi M (2007) Rhodiola rosea L. extract reduces stress- and CRF-induced anorexia in rats. J Psychopharmacol 21:742–750
Mattioli L, Perfumi M (2011a) Effects of a Rhodiola rosea L. extract on acquisition and expression of morphine tolerance and dependence in mice. J Psychopharmacol 25(3):411–420
Mattioli L, Perfumi M (2011b) Evaluation of Rhodiola rosea L. extract on affective and physical signs of nicotine withdrawal in mice. J Psychopharmacol 25(3):402–410
Mattioli L, Funari C, Perfumi M (2009) Effects of Rhodiola rosea L. extract on behavioural and physiological alterations induced by chronic mild stress in female rats. J Psychopharmacol 23:130–142
Nestler EJ (2004) Molecular mechanisms of drug addiction. Neuropharmacology 47(Suppl 1):24–32
O'Brien CP (1997) A range of research-based pharmacotherapies for addiction. Science 278:66–70
Panossian A, Wikman G (2009) Evidence-based efficacy of adaptogens in fatigue, and molecular mechanisms related to their stress-protective activity. Curr Clin Pharmacol 4:198–219
Panossian A, Hambartsumyan M, Hovanissian A, Gabrielyan E, Wikman G (2007) The adaptogens Rhodiola and Schizandra modify the response to immobilization stress in rabbits by suppressing the increase of phosphorylated stress-activated protein kinase, nitric oxide and cortisol. Drug Targets Insights 1:39–54
Panossian A, Nikoyan N, Ohanyan N, Hovhannisyan A, Abrahamyan H, Gabrielyan E et al (2008) Comparative study of Rhodiola preparations on behavioural despair of rats. Phytomedicine 15:84–91
Panossian A, Wikman G, Sarris J (2010) Rosenroot (Rhodiola rosea): traditional use, chemical composition, pharmacology and clinical efficacy. Phytomedicine 17:481–493
Pechnick RN (1993) Effects of opioids on the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 33:353–382
Perfumi M, Mattioli L (2007) Adaptogenic and central nervous system effects of single doses of 3 % rosavin and 1 % salidroside Rhodiola rosea L. extract in mice. Phytother Res 21:37–43
Qu ZQ, Zhou Y, Zeng YS, Li Y, Chung P (2009) Pretreatment with Rhodiola rosea extract reduces cognitive impairment induced by intracerebroventricular streptozotocin in rats: implication of anti-oxidative and neuroprotective effects. Biomed Environ Sci 22:318–326
Ribeiro Do Couto B, Aguilar MA, Manzanedo C, Rodríguez-Arias M, Miñarro J (2003) Reinstatement of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in mice by priming injections. Neural Plast 10:279–290
Ribeiro Do Couto B, Aguilar MA, Manzanedo C, Rodríguez-Arias M, Armario A, Miñarro J (2006) Social stress is as effective as physical stress in reinstating morphine-induced place preference in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 185:459–470
Sahraei H, Fatemi SM, Pashaei-Rad S, Faghih-Monzavi Z, Salimi SH, Kamalinegad M (2006) Effects of Papaver rhoeas extract on the acquisition and expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 103:420–424
Sarnyai Z, Shaham Y, Heinrichs SC (2001) The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in drug addiction. Pharmacol Rev 53:209–244
Shalev U, Grimm JW, Shaham Y (2002) Neurobiology of relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking: a review. Pharmacol Rev 54:1–42
Sharifzadeh M, Hadjiakhoondi A, Khanavi M, Susanabadi M (2006) Effects of aqueous, methanolic and chloroform extracts of rhizome and aerial parts of Valeriana officinalis L. on naloxone-induced jumping in morphine-dependent mice. Addict Biol 11:145–151
Shippenberg TS, Bals-Kubik R, Herz A (1993) Examination of the neurochemical substrates mediating the motivational effects of opioids: role of the mesolimbic dopamine system and D-1 vs. D-2 dopamine receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 265(1):53–59
Tzschentke TM (2007) Measuring reward with the conditioned place preference (CPP) paradigm: update of the last decade. Addict Biol 12:227–462
van Diermen D, Marston A, Bravo J, Reist M, Carrupt PA, Hostettmann K (2009) Monoamine oxidase inhibition by Rhodiola rosea L. roots. J Ethnopharmacol 122:397–401
Veilleux JC, Colvin PJ, Anderson J, York C, Heinz AJ (2010) A review of opioid dependence treatment: pharmacological and psychosocial interventions to treat opioid addiction. Clin Psychol Rev 30:155–166
Wang B, Luo F, Zhang WT, Han JS (2000) Stress or drug priming induces reinstatement of extinguished conditioned place preference. Neuroreport 11:2781–2784
Wang J, Fang Q, Liu Z, Lu L (2006) Region-specific effects of brain corticotropin-releasing factor receptor type 1 blockade on footshock-stress- or drug-priming-induced reinstatement of morphine conditioned place preference in rats. Psychopharmacology 185:19–28
Weiss F (2005) Neurobiology of craving, conditioned reward and relapse. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:9–19
Yoshikawa M, Shimada H, Shimoda H, Murakami N, Yamahara J, Matsuda H (1996) Bioactive constituents of Chinese natural medicines. II. Rhodiolae radix. (1). Chemical structures and anti-allergic activity of rhodiocyanosides A and B from the underground part of Rhodiola quadrifida (Pal1.) Fisch. et Mey. (Crassulaceae). Chem Pharm Bull(Tokyo) 44:2086–2091
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Francesco Nicotra and Dr. Raffaella Gatti from EPO S.r.1., Milan, Italy, for the generous gift of R. rosea extract and for the acquisition of HPLC data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mattioli, L., Titomanlio, F. & Perfumi, M. Effects of a Rhodiola rosea L. extract on the acquisition, expression, extinction, and reinstatement of morphine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Psychopharmacology 221, 183–193 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2686-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2686-0