Abstract
Rationale
Nicotine improves sensory processing in schizophrenic individuals, as measured by changes in auditory event-related potentials (ERPs). Nicotine administration also alters ERPs in mice by increasing the amplitude and gating of the P20 ERP component while decreasing the amplitude of the N40 ERP component. Less is known about the role of specific nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) subtypes.
Objectives
In this study, we examined whether nAChRs containing the β2 subunit contribute to nicotine’s effects on auditory ERPs.
Materials and methods
We tested the effect of nicotine in wild-type mice and mice lacking the β2 nAChR subunit. Mice underwent stereotaxic implantation of stainless steel electrodes located in the CA3 region of the hippocampus, and 50 paired click stimuli were delivered during each drug condition.
Results
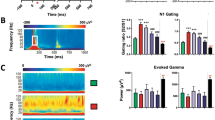
There was no significant difference in P20 or N40 amplitude or gating between genotypes during the control condition, suggesting that β2-containing receptors are not essential for the baseline auditory ERP response. Nicotine increased P20 amplitude and enhanced gating in wild-type and β2 knockout mice, but only decreased N40 amplitude in wild-type mice. There was no effect of nicotine on N40 gating in either genotype.
Conclusions
β2-containing receptors are necessary for nicotine’s effects on the N40 component of the mouse auditory ERP. These results suggest that β2-containing nAChRs modulate sensory processing and may serve as a therapeutic target in schizophrenic individuals.



Similar content being viewed by others

References
Adler LE, Hoffer LJ, Griffith J, Waldo MC, Freedman R (1992) Normalization by nicotine of deficient auditory sensory gating in the relatives of schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 32:607–616
Adler LE, Hoffer LD, Wiser A, Freedman R (1993) Normalization of auditory physiology by cigarette smoking in schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 150:1856–1861
Adler LE, Olincy A, Waldo M, Harris JG, Griffith J, Stevens K, Flach K, Nagamoto H, Bickford P, Leonard S, Freedman R (1998) Schizophrenia, sensory gating, and nicotinic receptors. Schizophr Bull 24:189–202
Bickford-Wimer PC, Nagamoto H, Johnson R, Adler LE, Egan M, Rose GM, Freedman R (1990) Auditory sensory gating in hippocampal neurons: a model system in the rat. Biol Psychiatry 27:183–192
Blumenfeld LD, Clementz BA (2001) Response to the first stimulus determines reduced auditory evoked response suppression in schizophrenia: single trials analysis using MEG. Clin Neurophysiol 112:1650–1649
Brockhaus-Dumke A, Schultze-Lutter F, Mueller R, Tendolkar I, Bechdolf A, Pukrop R, Klosterkoetter J, Ruhrmann S (2008) Sensory gating in schizophrenia: P50 and N100 gating in antipsychotic-free subjects at risk, first-episode, and chronic patients. Biol Psychiatry 64:376–384
Cao YJ, Surowy CS, Puttfarcken PS (2005) Different nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes mediating striatal and prefrontal cortical [3H]dopamine release. Neuropharmacology 48:72–79
Conti DV, Lee W, Li D, Liu J, Van Den Berg D, Thomas PD, Bergen AW, Swan GE, Tyndale RF, Benowitz NL, Lerman C (2008) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor {beta}2 subunit gene implicated in a systems-based candidate gene study of smoking cessation. Hum Mol Genet 17:2834–2848
Crawford HJ, McClain-Furmanski D, Castagnoli N Jr, Castagnoli K (2002) Enhancement of auditory sensory gating and stimulus-bound gamma band (40 Hz) oscillations in heavy tobacco smokers. Neurosci Lett 317:151–155
Davis JA, Gould TJ (2007) beta2 subunit-containing nicotinic receptors mediate the enhancing effect of nicotine on trace cued fear conditioning in C57BL/6 mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 190:343–352
Drago J, McColl CD, Horne MK, Finkelstein DI, Ross SA (2003) Neuronal nicotinic receptors: insights gained from gene knockout and knocking mutant mice. Cell Mol Life Sci 60:1267–1280
Durany N, Zochling R, Boissl KW, Paulus W, Ransmayr G, Tatschner T, Danielczyk W, Jellinger K, Deckert J, Riederer P (2000) Human post-mortem striatal alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor density in schizophrenia and Parkinson’s syndrome. Neurosci Lett 287:109–112
Dwoskin LP, Crooks PA (2001) Competitive neuronal nicotinic receptor antagonists: a new direction for drug discovery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:395–402
Freedman R, Hall M, Adler LE, Leonard S (1995) Evidence in postmortem brain tissue for decreased numbers of hippocampal nicotinic receptors in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 38:22–33
George TP, Verrico CD, Picciotto MR, Roth RH (2000) Nicotinic modulation of mesoprefrontal dopamine neurons: pharmacologic and neuroanatomic characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:58–66
Gonzales D, Rennard SI, Nides M, Oncken C, Azoulay S, Billing CB, Watsky EJ, Gong J, Williams KE, Reeves KR (2006) Varenicline, an alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, vs sustained-release bupropion and placebo for smoking cessation: a randomized controlled trial. Jama 296:47–55
Gotti C, Zoli M, Clementi F (2006) Brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: native subtypes and their relevance. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27:482–491
Grunwald T, Boutros NN, Pezer N, von Oertzen J, Fernandez G, Schaller C, Elger CE (2003) Neuronal substrates of sensory gating within the human brain. Biol Psychiatry 53:511–519
Guan ZZ, Zhang X, Blennow K, Nordberg A (1999) Decreased protein level of nicotinic receptor alpha7 subunit in the frontal cortex from schizophrenic brain. Neuroreport 10:1779–1782
Halene TB, Siegel SJ (2008) Antipsychotic-like properties of phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors: evaluation of 4-(3-butoxy-4-methoxybenzyl)-2-imidazolidinone (RO-20-1724) with auditory event-related potentials and prepulse inhibition of startle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326:230–239
Hinman CL, Buchwald JS (1983) Depth evoked potential and single unit correlates of vertex midlatency auditory evoked responses. Brain Res 264:57–67
Hurst RS, Hajos M, Raggenbass M, Wall TM, Higdon NR, Lawson JA, Rutherford-Root KL, Berkenpas MB, Hoffmann WE, Piotrowski DW, Groppi VE, Allaman G, Ogier R, Bertrand S, Bertrand D, Arneric SP (2005) A novel positive allosteric modulator of the alpha7 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: in vitro and in vivo characterization. J Neurosci 25:4396–4405
Kawai H, Lazar R, Metherate R (2007) Nicotinic control of axon excitability regulates thalamocortical transmission. Nat Neurosci 10:1168–1175
Leonard S, Gault J, Hopkins J, Logel J, Vianzon R, Short M, Drebing C, Berger R, Venn D, Sirota P, Zerbe G, Olincy A, Ross RG, Adler LE, Freedman R (2002) Association of promoter variants in the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit gene with an inhibitory deficit found in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:1085–1096
Light GA, Malaspina D, Geyer MA, Luber BM, Coleman EA, Sackeim HA, Braff DL (1999) Amphetamine disrupts P50 suppression in normal subjects. Biol Psychiatry 46:990–996
Lu BY, Martin KE, Edgar JC, Smith AK, Lewis SF, Escamilla MA, Miller GA, Canive JM (2007) Effect of catechol O-methyltransferase val(158)met polymorphism on the p50 gating endophenotype in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 62:822–825
Mann C, Croft RJ, Scholes KE, Dunne A, O’Neill B V, Leung S, Copolov D, Phan KL, Nathan PJ (2008) Differential effects of acute serotonin and dopamine depletion on prepulse inhibition and P50 suppression measures of sensorimotor and sensory gating in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1653–1666
Maxwell CR, Liang Y, Weightman BD, Kanes SJ, Abel T, Gur RE, Turetsky BI, Bilker WB, Lenox RH, Siegel SJ (2004) Effects of chronic olanzapine and haloperidol differ on the mouse N1 auditory evoked potential. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:739–746
Maxwell CR, Liang Y, Kelly MP, Kanes SJ, Abel T, Siegel SJ (2006) Mice expressing constitutively active Gsalpha exhibit stimulus encoding deficits similar to those observed in schizophrenia patients. Neuroscience 141:1257–1264
Metherate R (2004) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in sensory cortex. Learn Mem 11:50–59
Metzger KL, Maxwell CR, Liang Y, Siegel SJ (2007) Effects of nicotine vary across two auditory evoked potentials in the mouse. Biol Psychiatry 61:23–30
Olincy A, Stevens KE (2007) Treating schizophrenia symptoms with an alpha7 nicotinic agonist, from mice to men. Biochem Pharmacol 74:1192–1201
Owens JC, Balogh SA, McClure-Begley TD, Butt CM, Labarca C, Lester HA, Picciotto MR, Wehner JM, Collins AC (2003) Alpha 4 beta 2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors modulate the effects of ethanol and nicotine on the acoustic startle response. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:1867–1875
Phillips JM, Ehrlichman RS, Siegel SJ (2007) Mecamylamine blocks nicotine-induced enhancement of the P20 auditory event-related potential and evoked gamma. Neuroscience 144:1314–1323
Picciotto MR, Zoli M, Lena C, Bessis A, Lallemand Y, Le Novere N, Vincent P, Pich EM, Brulet P, Changeux JP (1995) Abnormal avoidance learning in mice lacking functional high-affinity nicotine receptor in the brain. Nature 374:65–67
Radek RJ, Miner HM, Bratcher NA, Decker MW, Gopalakrishnan M, Bitner RS (2006) Alpha4beta2 nicotinic receptor stimulation contributes to the effects of nicotine in the DBA/2 mouse model of sensory gating. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 187:47–55
Rao TS, Correa LD, Adams P, Santori EM, Sacaan AI (2003) Pharmacological characterization of dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin release in the rat prefrontal cortex by neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists. Brain Res 990:203–208
Rentzsch J, Jockers-Scherubl MC, Boutros NN, Gallinat J (2008) Test–retest reliability of P50, N100 and P200 auditory sensory gating in healthy subjects. Int J Psychophysiol 67:81–90
Sanchez-Morla EM, Garcia-Jimenez MA, Barabash A, Martinez-Vizcaino V, Mena J, Cabranes-Diaz JA, Baca-Baldomero E, Santos JL (2008) P50 sensory gating deficit is a common marker of vulnerability to bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 117:313–318
Siegel SJ, Connolly P, Liang Y, Lenox RH, Gur RE, Bilker WB, Kanes SJ, Turetsky BI (2003) Effects of strain, novelty, and NMDA blockade on auditory-evoked potentials in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:675–682
Siegel SJ, Maxwell CR, Majumdar S, Trief DF, Lerman C, Gur RE, Kanes SJ, Liang Y (2005) Monoamine reuptake inhibition and nicotine receptor antagonism reduce amplitude and gating of auditory evoked potentials. Neuroscience 133:729–738
Stevens KE, Freedman R, Collins AC, Hall M, Leonard S, Marks MJ, Rose GM (1996a) Genetic correlation of inhibitory gating of hippocampal auditory evoked response and alpha-bungarotoxin-binding nicotinic cholinergic receptors in inbred mouse strains. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:152–162
Stevens KE, Luthman J, Lindqvist E, Johnson RG, Rose GM (1996b) Effects of neonatal dopamine depletion on sensory inhibition in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53:817–823
Sumich A, Kumari V, Gordon E, Tunstall N, Brammer M (2008) Event-related potential correlates of paranormal ideation and unusual experiences. Cortex (in press)
Tregellas JR, Davalos DB, Rojas DC, Waldo MC, Gibson L, Wylie K, Du YP, Freedman R (2007) Increased hemodynamic response in the hippocampus, thalamus and prefrontal cortex during abnormal sensory gating in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 92:262–272
Umbricht D, Vyssotky D, Latanov A, Nitsch R, Brambilla R, D’Adamo P, Lipp HP (2004) Midlatency auditory event-related potentials in mice: comparison to midlatency auditory ERPs in humans. Brain Res 1019:189–200
Walters CL, Brown S, Changeux JP, Martin B, Damaj MI (2006) The beta2 but not alpha7 subunit of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is required for nicotine-conditioned place preference in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 184:339–344
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Caryn Lerman and Dr. Tobias Halene for critical readings of the manuscript. This work was supported by P50-CA-084718 (Caryn Lerman, PI) and P50 MH-064045 (Raquel E. Gur, PI) and AA15632, DA00436 (Marina R. Picciotto, PI).
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report and agree to share data with the journal if requested. All experiments comply with the laws of the United States of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rudnick, N.D., Koehler, C., Picciotto, M.R. et al. Role of β2-containing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in auditory event-related potentials. Psychopharmacology 202, 745–751 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1358-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1358-6