Abstract
Rationale and objective
Opiate abuse in adolescent girls has increased in the past decade; however, few animal studies have examined the potential consequences of opiate use occurring at this time. The purpose of the present study was to determine whether exposing female rats to morphine during the peripubertal period can alter the adult behavior of their offspring.
Methods
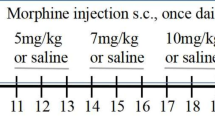
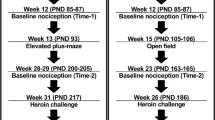
Beginning at 30 days of age, female rats were injected subcutaneously (s.c.) twice daily with either morphine sulfate or saline. The initial morphine dose of 2.5 mg/kg was increased by 2.5 mg/kg daily for a total of 20 days. Ten days after the final drug treatment, all subjects were mated. Their subsequent offspring were then tested as adults on the elevated plus maze, in a novel environment or were examined in a morphine locomotor sensitization paradigm.
Results
Adult female offspring of dams exposed to morphine during puberty spent less time in the open arms of the elevated plus maze and displayed decreased exploration in a novel environment. Female offspring also demonstrated a more rapid induction of morphine sensitization. Finally, male offspring demonstrated a significant enhancement in the expression of morphine sensitization.
Conclusions
Chronic morphine exposure during adolescence can have significant transgenerational effects on adult offspring. Future studies will be needed to determine how these changes are transferred to the offspring and whether these effects are specific to drug exposure that occurs during the peripubertal period.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byrnes EM (2005) Chronic morphine exposure during puberty decreases postpartum prolactin secretion in adult female rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 80:445–451
Byrnes EM, Rigero BA, Bridges RS (2000) Opioid receptor antagonism during early lactation results in the increased duration of nursing bouts. Physiol Behav 70:211–216
Caldji C, Tannenbaum B, Sharma S, Francis D, Plotsky PM, Meaney MJ (1998) Maternal care during infancy regulates the development of neural systems mediating the expression of behavioral fearfulness in adulthood in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:5335–5340
Francis DD, Champagne FA, Liu D, Meaney MJ (1999) Maternal care, gene expression, and the development of individual differences in stress reactivity. Ann NY Acad Sci 896:66–84
Frye CA, Walf AA (2004) Estrogen and/or progesterone administered systemically or to the amygdala can have anxiety-, fear-, and pain-reducing effects in ovariectomized rats. Behav Neurosci 118:306–313
Greenfield SF, O'Leary G (1999) Sex differences in marijuana use in the United States. Harv Rev Psychiatry 6:297–303
Greenfield SF, Manwani SG, Nargiso JE (2003) Epidemiology of substance use disorders in women. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am 30:413–446
Huot RL, Gonzalez ME, Ladd CO, Thrivikraman KV, Plotsky PM (2004) Foster litters prevent hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis sensitization mediated by neonatal maternal separation. Psychoneuroendocrinology 29:279–289
Johnson RA, Gerstein DR (1998) Initiation of use of alcohol, cigarettes, marijuana, cocaine, and other substances in US birth cohorts since 1919. Am J Public Health 88:27–33
Johnston LD, O'Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE (2004a) Monitoring the future national survey results on drug use, 1975–2003. Volume I: secondary school students (NIH Publication No. 04-5507). National Institute on Drug Abuse, Bethesda, MD
Johnston LD, O'Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE (2004b) Monitoring the future national results on adolescent drug use: overview of key findings, 2003 (NIH Publication No. 04-5506). National Institute on Drug Abuse, Bethesda, MD
Kalinichev M, Easterling KW, Holtzman SG (2002) Early neonatal experience of Long–Evans rats results in long-lasting changes in reactivity to a novel environment and morphine-induced sensitization and tolerance. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:518–533
Kalinichev M, Easterling KW, Holtzman SG (2003) Long-lasting changes in morphine-induced locomotor sensitization and tolerance in Long–Evans mother rats as a result of periodic postpartum separation from the litter: a novel model of increased vulnerability to drug abuse? Neuropsychopharmacology 28:317–328
Lister RG (1990) Ethologically-based animal models of anxiety disorders. Pharmacol Ther 46:321–340
Lund TD, Rovis T, Chung WC, Handa RJ (2005) Novel actions of estrogen receptor-beta on anxiety-related behaviors. Endocrinology 146:797–807
Mann PE, Kinsley CH, Bridges RS (1991) Opioid receptor subtype involvement in maternal behavior in lactating rats. Neuroendocrinology 53:487–492
Marcondes FK, Miguel KJ, Melo LL, Spadari-Bratfisch RC (2001) Estrous cycle influences the response of female rats in the elevated plus-maze test. Physiol Behav 74:435–440
Mayer AD, Faris PL, Komisaruk BR, Rosenblatt JS (1985) Opiate antagonism reduces placentophagia and pup cleaning by parturient rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:1035–1044
Meaney MJ (2001) Maternal care, gene expression, and the transmission of individual differences in stress reactivity across generations. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1161–1192
Mora S, Dussaubat N, Diaz-Veliz G (1996) Effects of the estrous cycle and ovarian hormones on the behavioral indices of anxiety in female rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 21:609–620
National Center on Addiction and Substance Abuse at Columbia University (2003) The formative years: pathways to substance abuse among girls and young women ages 8–22. Columbia University, New York, NY
National Institute on Drug Abuse (2000) Heroin abuse and addiction. NIDA research report series. National Institute on Drug Abuse, Bethesda, MD
Nelson EE, Panksepp J (1998) Brain substrates of infant–mother attachment: contributions of opioids, oxytocin, and norepinephrine. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 22:437–452
Panksepp J, Nelson E, Siviy S (1994) Brain opioids and mother–infant social motivation. Acta Paediatr Suppl 397:40–46
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M (1985) Validation of open:closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 14:149–167
Phelps CJ, Romero MI, Hurley DL (2003) Prolactin replacement must be continuous and initiated prior to 21 d of age to maintain hypothalamic dopaminergic neurons in hypopituitary mice. Endocrine 20:139–148
Piazza PV, Deminiere JM, Le Moal M, Simon H (1989) Factors that predict individual vulnerability to amphetamine self-administration. Science 245:1511–1513
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (1993) The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 18:247–291
Vezina P, Lorrain DS, Arnold GM, Austin JD, Suto N (2002) Sensitization of midbrain dopamine neuron reactivity promotes the pursuit of amphetamine. J Neurosci 22:4654–4662
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Dr. Robert Bridges for generously allowing the use of his laboratory facilities. I would also like to thank Ms. Beth A. Rigero and Ms. Victoria Scanlan for their expert technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Institute on Health grant DA14613 awarded to E.M. Byrnes
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Byrnes, E.M. Transgenerational consequences of adolescent morphine exposure in female rats: effects on anxiety-like behaviors and morphine sensitization in adult offspring. Psychopharmacology 182, 537–544 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0122-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0122-4