Abstract
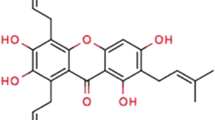
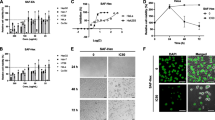
Cervical cancer is among the most frequently observed cancer types in females. New therapeutic targets are needed because of the side impacts of existing cancer drugs and the inadequacy of treatment methods. Thioredoxin reductase 1 (TrxR1) is often overexpressed in many cancer cells, and targeting TrxR1 has become an attractive target for cancer therapy. This study investigated the anticancer impacts of diffractaic and vulpinic acids, lichen secondary metabolites, on the cervical cancer HeLa cell line. XTT findings demonstrated showed that diffractaic and vulpinic acids suppressed the proliferation of HeLa cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner and IC50 values were 22.52 μg/ml and 66.53 μg/ml at 48 h, respectively. Each of these lichen metabolites significantly suppressed migration. Diffractaic acid showed an increase in both the BAX/BCL2 ratio by qPCR analysis and the apoptotic cell population via flow cytometry analysis on HeLa cells. Concerning vulpinic acid, although it decreased the BAX/BCL2 ratio in this cells, it increased apoptotic cells according to the flow cytometry analysis results. Diffractaic and vulpinic acids significantly suppressed TrxR1 enzyme activity rather than the gene and protein expression levels in HeLa cells. This research demonstrated for the first time, that targeting TrxR1 with diffractaic and vulpinic acids was an effective therapeutic strategy for treating cervical cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of the present research are available on request from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Altay A, Caglar S, Caglar B (2022) Silver(I) complexes containing diclofenac and niflumic acid induce apoptosis in human-derived cancer cell lines. Arch Physiol Biochem 128:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1080/13813455.2019.1662454
Baltacı NG, Toraman E, Akyüz M et al (2022) Tip60/Kat5 may be a novel candidate histone acetyltransferase for the regulation of liver iron localization via acetylation. Biometals 35:1187–1197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-022-00435-z
Banerjee R (2012) Redox outside the Box: Linking Extracellular Redox Remodeling with Intracellular Redox Metabolism. J Biol Chem 287:4397–4402. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R111.287995
Barlak N, Capik O, Sanli F et al (2020) ING5 inhibits cancer aggressiveness by inhibiting Akt and activating p53 in prostate cancer. Cell Biol Int 44:242–252. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11227
Bhatia M, McGrath KL, Di Trapani G et al (2016) The thioredoxin system in breast cancer cell invasion and migration. Redox Biol 8:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2015.12.004
Biaglow JE, Miller RA (2005) The thioredoxin reductase/thioredoxin system: Novel redox targets for cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther 4:13–20. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.4.1.1434
Bjørklund G, Zou L, Peana M et al (2022) The Role of the Thioredoxin System in Brain Diseases. Antioxidants 11:2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11112161
Branco V, Godinho-Santos A, Gonçalves J et al (2014) Mitochondrial thioredoxin reductase inhibition, selenium status, and Nrf-2 activation are determinant factors modulating the toxicity of mercury compounds. Free Radic Biol Med 73:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.04.030
Brisdelli F, Perilli M, Sellitri D et al (2013) Cytotoxic Activity and Antioxidant Capacity of Purified Lichen Metabolites: An In Vitro Study. Phyther Res 27:431–437. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.4739
Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW (2011) Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 11:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2981
Dar TUH, Dar SA, Islam SU et al (2022) Lichens as a repository of bioactive compounds: an open window for green therapy against diverse cancers. Semin Cancer Biol 86:1120–1137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.05.028
de la Torre BG, Albericio F (2019) The Pharmaceutical Industry in 2018. An Analysis of FDA Drug Approvals from the Perspective of Molecules. Molecules 24:809. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24040809
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Aaronson SA et al (2018) Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ 25:486–541. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4
Geho DH, Bandle RW, Clair T, Liotta LA (2005) Physiological Mechanisms of Tumor-Cell Invasion and Migration. Physiology 20:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00009.2005
Ghavami S, Hashemi M, Ande SR et al (2009) Apoptosis and cancer: mutations within caspase genes. J Med Genet 46:497–510. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.2009.066944
Günaydın Ş, Sulukoğlu EK, Kalın ŞN et al (2023) Diffractaic acid exhibits thioredoxin reductase 1 inhibition in lung cancer A549 cells. J Appl Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.4505
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 100:57–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81683-9
Hukkamlı B, Dağdelen B, Sönmez Aydın F, Budak H (2023) Comparison of the efficacy of the mouse hepatic and renal antioxidant systems against inflammation-induced oxidative stress. Cell Biochem Biophys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-023-01126-3
Kalın ŞN, Altay A, Budak H (2022) Diffractaic acid, a novel TrxR1 inhibitor, induces cytotoxicity, apoptosis, and antimigration in human breast cancer cells. Chem Biol Interact 361:109984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2022.109984
Kalın ŞN, Altay A, Budak H (2022) Inhibition of thioredoxin reductase 1 by vulpinic acid suppresses the proliferation and migration of human breast carcinoma. Life Sci 310:121093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121093
Kalın ŞN, Altay A, Budak H (2023) Effect of Evernic Acid on Human Breast Cancer MCF-7 and MDA-MB-453 Cell Lines via Thioredoxin Reductase 1: a Molecular Approach. J Appl Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.4451
Kılıc N, Derici MK, Buyuk I et al (2018) Evaluation of in vitro Anticancer Activity of Vulpinic Acid and its Apoptotic Potential Using Gene Expression and Protein Analysis. Indian J Pharm Educ Res 52:626–634. https://doi.org/10.5530/ijper.52.4.73
Kim S, So HM, Roh H-S et al (2017) Vulpinic acid contributes to the cytotoxicity of Pulveroboletus ravenelii to human cancer cells by inducing apoptosis. RSC Adv 7:35297–35304. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA05059C
Kondo N, Nakamura H, Masutani H, Yodoi J (2006) Redox Regulation of Human Thioredoxin Network. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1881–1890. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2006.8.1881
Koparal AT (2015) Anti-angiogenic and antiproliferative properties of the lichen substances (-)-usnic acid and vulpinic acid. Zeitschrift Für Naturforsch C 70:159–164. https://doi.org/10.1515/znc-2014-4178
Lincoln DT, Ali Emadi EM, Tonissen KF, Clarke FM (2003) The thioredoxin-thioredoxin reductase system: over-expression in human cancer. Anticancer Res 23:2425–2433
Lincoln DT, Al-Yatama F, Mohammed FMA et al (2010) Thioredoxin and thioredoxin reductase expression in thyroid cancer depends on tumour aggressiveness. Anticancer Res 30:767–775
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Marzano C, Gandin V, Folda A et al (2007) Inhibition of thioredoxin reductase by auranofin induces apoptosis in cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med 42:872–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.12.021
Mattiuzzi C, Lippi G (2019) Current Cancer Epidemiology. J Epidemiol Glob Health 9:217. https://doi.org/10.2991/jegh.k.191008.001
Mohammadi F, Soltani A, Ghahremanloo A et al (2019) The thioredoxin system and cancer therapy: a review. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 84:925–935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-019-03912-4
Moloney JN, Cotter TG (2018) ROS signalling in the biology of cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol 80:50–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2017.05.023
Nakamura H, Masutani H, Yodoi J (2006) Extracellular thioredoxin and thioredoxin-binding protein 2 in control of cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 16:444–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2006.09.001
Narayan K, Lin MY (2015) Staging for cervix cancer: Role of radiology, surgery and clinical assessment. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 29:833–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2015.01.005
Nguyen P, Awwad RT, Smart DDK et al (2006) Thioredoxin reductase as a novel molecular target for cancer therapy. Cancer Lett 236:164–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2005.04.028
Nogueira V, Hay N (2013) Molecular Pathways: Reactive Oxygen Species Homeostasis in Cancer Cells and Implications for Cancer Therapy. Clin Cancer Res 19:4309–4314. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1424
Oettl SK, Gerstmeier J, Khan SY et al (2013) Imbricaric Acid and Perlatolic Acid: Multi-Targeting Anti-Inflammatory Depsides from Cetrelia monachorum. PLoS One 8:e76929. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076929
Ouyang Y, Peng Y, Li J et al (2018) Modulation of thiol-dependent redox system by metal ions via thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems. Metallomics 10:218–228. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7MT00327G
Ozgencli I, Budak H, Ciftci M, Anar M (2019) Lichen Acids May Be Used as A Potential Drug For Cancer Therapy; by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Thioredoxin Reductase Purified From Rat Lung. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 18:1599–1605. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520618666180525095520
Powis G, Gasdaska JR, Gasdaska PY et al (1997) Selenium and the thioredoxin redox system: effects on cell growth and death. Oncol Res 9:303–312
Ray PD, Huang B-W, Tsuji Y (2012) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell Signal 24:981–990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.01.008
Roser LA, Erkoc P, Ingelfinger R et al (2022) Lecanoric acid mediates anti-proliferative effects by an M phase arrest in colon cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother 148:112734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112734
Rubartelli A, Bajetto A, Allavena G et al (1992) Secretion of thioredoxin by normal and neoplastic cells through a leaderless secretory pathway. J Biol Chem 267:24161–24164. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(18)35742-9
Schenk H, Vogt M, Dröge W, Schulze-Osthoff K (1996) Thioredoxin as a potent costimulus of cytokine expression. J Immunol 156:765–771
Shang W, Xie Z, Lu F et al (2019) Increased Thioredoxin-1 Expression Promotes Cancer Progression and Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Gastric Cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9291683
Solárová Z, Liskova A, Samec M et al (2020) Anticancer Potential of Lichens’ Secondary Metabolites. Biomolecules 10:87. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010087
Sönmez Aydın F, Hukkamlı B, Budak H (2021) Coaction of hepatic thioredoxin and glutathione systems in iron overload‐induced oxidative stress. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 35. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22704
Stocker-Wörgötter E (2008) Metabolic diversity of lichen-forming ascomycetous fungi: culturing, polyketide and shikimatemetabolite production, and PKS genes. Nat Prod Rep 25:188–200. https://doi.org/10.1039/B606983P
Sun Y, Rigas B (2008) The Thioredoxin System Mediates Redox-Induced Cell Death in Human Colon Cancer Cells: Implications for the Mechanism of Action of Anticancer Agents. Cancer Res 68:8269–8277. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2010
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Trachootham D, Alexandre J, Huang P (2009) Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:579–591. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2803
Truong TL, Nga VT, Huy DT et al (2014) A New Depside from Usnea aciculifera Growing in Vietnam. Nat Prod Commun 9:1934578X1400900. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X1400900831
Ulus G (2021) Antiangiogenic properties of lichen secondary metabolites. Phyther Res 35:3046–3058. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7023
Witte A-B, Anestål K, Jerremalm E et al (2005) Inhibition of thioredoxin reductase but not of glutathione reductase by the major classes of alkylating and platinum-containing anticancer compounds. Free Radic Biol Med 39:696–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.04.025
Yan C, Siegel D, Newsome J et al (2012) Antitumor Indolequinones Induced Apoptosis in Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells via Inhibition of Thioredoxin Reductase and Activation of Redox Signaling. Mol Pharmacol 81:401–410. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.111.076091
Yin F, Sancheti H, Cadenas E (2012) Mitochondrial Thiols in the Regulation of Cell Death Pathways. Antioxid Redox Signal 17:1714–1727. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4639
Zhang J, Li X, Han X et al (2017) Targeting the Thioredoxin System for Cancer Therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 38:794–808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2017.06.001
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Harun Budak at Atatürk University and Dr. Ahmet Altay at Erzincan Binali Yıldırım University for their technical support.
Funding
The Coordination Unit of Scientific Research Project of Atatürk University (ATAUNI-BAP) provided financial support for the present work (Project number: TTU-2021–9285).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: Dr. Büşra Budak (BB), Dr. Şeyda Nur Kalın (ŞNK), and Dr. Ömer Erkan Yapça (ÖEY). Performed the experiments: ŞNK and BB. Analyzed the data: ŞNK and BB. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: ÖEY, ŞNK, and BB. Wrote the paper: ŞNK. All authors read and approved the manuscript’s final version. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing ınterests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Budak, B., Kalın, Ş.N. & Yapça, Ö.E. Antiproliferative, antimigratory, and apoptotic effects of diffractaic and vulpinic acids as thioredoxin reductase 1 inhibitors on cervical cancer. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 397, 1525–1535 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02698-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02698-w