Abstract
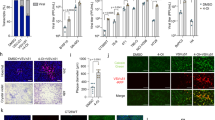
Econazole, miconazole, and sertaconazole, the structurally related azoles with imidazole moiety, were evaluated for their cytotoxicity and their ability to bind to mammalian tubulin. Our results indicated that sertaconazole and econazole bound to goat brain tubulin with a dissociation constant of 9 and 19 μM respectively, while miconazole did not bind to goat brain tubulin. Econazole, miconazole, and sertaconazole inhibited the proliferation of HeLa cells with an IC50 of 28, 98, and 38 μM respectively with sertaconazole alone inducing a mitotic block in the treated cells. Since sertaconazole bound to goat brain tubulin with higher affinity and blocked the cells at mitosis, we hypothesized that its cytotoxic mechanism might involve inhibition of tubulin and econazole which did not block the cells at mitosis may have additional targets than tubulin. Sertaconazole inhibited the polymerization of tubulin in HeLa cells and the in vitro assembled goat brain tubulin. Competitive tubulin-binding assay using colchicine and computational simulation studies showed that sertaconazole bound closer to the colchicine site and induced the tubulin dimer to adopt a “bent” conformation which is incompetent for the polymerization. Results from RT-PCR analysis of the A549 cells treated with sertaconazole indicated activation of apoptosis. Sertaconazole significantly inhibited the migration of HeLa cells and showed synergistic antiproliferative potential with vinblastine. Collectively, the results suggest that sertaconazole which is already in clinical practice could be useful as a topical chemotherapy agent for the treatment of skin cancers in combination with other systemic anticancer agents.
Graphical abstract














Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data analyzed during this study are included as Electronic supplementary material (ESM).
References
Aneja R, Ghaleb AM, Zhou J, Yang VW, Joshi HC (2007) p53 and p21 determine the sensitivity of noscapine-induced apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 67:3862–3870
Ashraf SM, Sebastian J, Rathinasamy K (2018) Zerumbone, a cyclic sesquiterpene, exerts antimitotic activity in HeLa cells through tubulin binding and exhibits synergistic activity with vinblastine and paclitaxel. Cell Prolif 52:e12558
Bae SH, Park JH, Choi HG, Kim H, Kim SH (2018) Imidazole antifungal drugs inhibit the cell proliferation and invasion of human breast cancer cells. Biomol Ther 26:494–502
Beale JM, Block JH (2011) Wilson and Gisvold’s Textbook of Organic Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry, twelfth edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, New York
Best RB, Zhu X, Shim J, Lopes PE, Mittal J, Feig M, MacKerell AD Jr (2012) Optimization of the additive CHARMM all-atom protein force field targeting improved sampling of the backbone ϕ, ψ and side-chain χ1 and χ2 dihedral angles. J Chem Theory Comput 8:3257–3273
Bhalla KN (2003) Microtubule-targeted anticancer agents and apoptosis. Oncogene 22:9075–9086
Bhattacharyya B, Wolff J (1974) Promotion of fluorescence upon binding of colchicine to tubulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 71:2627–2631
Brugmans J, Van Cutsem J, Heykants J, Schuermans V, Thienpont D (1972) Systemic antifungal potential, safety, biotransport and transformation of miconazole nitrate. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 5:93–99
Brunton LL, Lazo JS, Parker KL (2006) Goodman and Gilman’s the Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, eleventh edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Cao R, Liu M, Yin M, Liu Q, Wang Y, Huang N (2012) Discovery of novel tubulin inhibitors via structure-based hierarchical virtual screening. J Chem Inf Model 52:2730–2740
Carrillo-Muñoz AJ, Giusiano G, Ezkurra PA, Quindós G (2005) Sertaconazole: updated review of a topical antifungal agent. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 3:333–342
Carrillo-Muñoz AJ, Tur-Tur C, Giusiano G, Marcos-Arias C, Eraso E, Jauregizar N, Quindós G (2013) Sertaconazole: an antifungal agent for the topical treatment of superficial candidiasis. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 11:347–358
Chen J, Wang Z, Li CM, Lu Y, Vaddady PK, Meibohm B, Dalton JT, Miller DD, Li W (2010) Discovery of novel 2-aryl-4-benzoyl-imidazoles targeting the colchicines binding site in tubulin as potential anticancer agents. J Med Chem 53:7414–7427
Choi EK, Park EJ, Phan TT, Kim HD, Hoe KL, Kim DU (2020) Econazole induces p53-dependent apoptosis and decreases metastasis ability in gastric cancer cells. Biomol Ther 28:370–379
Chou TC, Talalay P (1983) Analysis of combined drug effects: a new look at a very old problem. Trends Pharmacol Sci 4:450–454
Chou TC, Talalay P (1984) Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzym Regul 22:27–55
Clément MJ, Rathinasamy K, Adjadj E, Toma F, Curmi PA, Panda D (2008) Benomyl and colchicine synergistically inhibit cell proliferation and mitosis: evidence of distinct binding sites for these agents in tubulin. Biochemistry 47:13016–13025
Coker PS, Radecke J, Guy C, Camper ND (2003) Potato disc tumor induction assay: a multiple mode of drug action assay. Phytomedicine 10:133–138
Croxtall JD, Plosker GL (2009) Sertaconazole: a review of its use in the management of superficial mycoses in dermatology and gynaecology. Drugs 69:339–359
de Forges H, Bouissou A, Perez F (2012) Interplay between microtubule dynamics and intracellular organization. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 44:266–274
Desai A, Mitchison TJ (1997) Microtubule polymerization dynamics. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 13:83–117
Green RA, Kaplan KB (2003) Chromosome instability in colorectal tumor cells is associated with defects in microtubule plus-end attachments caused by a dominant mutation in APC. J Cell Biol 163:949–961
Gupta K, Panda D (2002) Perturbation of microtubule polymerization by quercetin through tubulin binding: a novel mechanism of its antiproliferative activity. Biochemistry 41:13029–13038
Gupta K, Bishop J, Peck A, Brown J, Wilson L, Panda D (2004) Antimitotic antifungal compound benomyl inhibits brain microtubule polymerization and dynamics and cancer cell proliferation at mitosis, by binding to a novel site in tubulin. Biochemistry 43:6645–6655
Gupta KK, Bharne SS, Rathinasamy K, Naik NR, Panda D (2006) Dietary antioxidant curcumin inhibits microtubule assembly through tubulin binding. FEBS J 273:5320–5332
Hamel E, Lin CM (1981) Glutamate-induced polymerization of tubulin: characteristics of the reaction and application to the large-scale purification of tubulin. Arch Biochem Biophys 209:29–40
Heel RC, Brogden RN, Speight TM, Avery GS (1978) Econazole: a review of its antifungal activity and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs 16:177–201
Ho YS, Wu CH, Chou HM, Wang YJ, Tseng H, Chen CH, Chen LC, Lee CH, Lin SY (2005) Molecular mechanisms of econazole-induced toxicity on human colon cancer cells: G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and caspase 8-independent apoptotic signaling pathways. Food Chem Toxicol 43:1483–1495
Jordan MA, Wilson L (2004) Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 4:253–265
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79:926–935
Kaur IP, Kakkar S (2010) Topical delivery of antifungal agents. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 7:1303–1327
Kumari R, Kumar R, Open source drug discovery consortium, Lynn A (2014) g_mmpbsa: a GROMACS tool for high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations. J Chem Inf Model 54:1951–1962
Li W, Sun H, Xu S, Zhu Z, Xu J (2017) Tubulin inhibitors targeting the colchicine binding site: a perspective of privileged structures. Future Med Chem 9:1765–1794
Lu Y, Chen J, Xiao M, Li W, Miller DD (2012) An overview of tubulin inhibitors that interact with the colchicine binding site. Pharm Res 29:2943–2971
Luduena RF, Roach MC (1991) Tubulin sulfhydryl groups as probes and targets for antimitotic and antimicrotubule agents. Pharmacol Therapeut 49:133–152
McLoughlin EC, O’Boyle NM (2020) Colchicine-binding site inhibitors from chemistry to clinic: a review. Pharmaceuticals 13:1–43
Mini SS, Raudaskoski M (1993) Response of ectomycorrhizal fungi to benomyl and nocodazole: growth inhibition and microtubule depolymerization. Mycorrhiza 3:83–91
Mokhtari RB, Homayouni TS, Baluch N, Morgatskaya E, Kumar S, Das B, Yeger H (2017) Combination therapy in combating cancer. Oncotarget 8:38022–38043
Najid A, Ratinaud MH (1991) Comparative studies of steroidogenesis inhibitors (econazole, ketoconazole) on human breast cancer MCF-7 cell proliferation by growth experiments, thymidine incorporation and flow cytometric DNA analysis. Tumori J 77:385–390
Nogales E, Whittaker M, Milligan RA, Downing KH (1999) High-resolution model of the microtubule. Cell 96:79–88
Panda D, Rathinasamy K, Santra MK, Wilson L (2005) Kinetic suppression of microtubule dynamic instability by griseofulvin: implications for its possible use in the treatment of cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:9878–9883
Peng LX, Hsu MT, Bonomi M, Agard DA, Jacobson MP (2014) The free energy profile of tubulin straight-bent conformational changes, with implications for microtubule assembly and drug discovery. PLoS Comput Biol 10:e1003464
Rathinasamy K, Panda D (2006) Suppression of microtubule dynamics by benomyl decreases tension across kinetochore pairs and induces apoptosis in cancer cells. FEBS J 273:4114–4128
Rathinasamy K, Panda D (2008) Kinetic stabilization of microtubule dynamic instability by benomyl increases the nuclear transport of p53. Biochem Pharmacol 76:1669–1680
Reid JL (1995) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic aspects of the choice of components of combination therapy. J Hum Hypertens 9:S19–S23
Sebastian J, Rathinasamy K (2019) Benserazide perturbs Kif15-kinesin binding protein interaction with prolonged metaphase and defects in chromosomal congression: a study based on in silico modeling and cell culture. Mol Inform 39:1900035
Stanton RA, Gernert KM, Nettles JH, Aneja R (2011) Drugs that target dynamic microtubules: a new molecular perspective. Med Res Rev 31:443–481
Sun J, Yu CH, Zhao XL, Wang Y, Jiang SG, Gong XF (2014) Econazole nitrate induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells via mitochondrial and caspase pathways. Iran J Pharm Res 13:1327–1334
Taman A, Azab M (2014) Present-day anthelmintics and perspectives on future new targets. Parasitol Res 113:2425–2433
Van Der Spoel D, Lindahl E, Hess B, Groenhof G, Mark AE, Berendsen HJ (2005) GROMACS: fast, flexible, and free. J Comput Chem 26:1701–1718
Vanommeslaeghe K, MacKerell AD Jr (2012) Automation of the CHARMM general force field (CGenFF) I: bond perception and atom typing. J Chem Inf Model 52:3144–3154
Wang LG, Liu XM, Kreis W, Budman DR (1999) The effect of antimicrotubule agents on signal transduction pathways of apoptosis: a review. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 44:355–361
Wu CH, Jeng JH, Wang YJ, Tseng CJ, Liang YC, Chen CH, Lee HM, Lin JK, Lin CH, Lin SY, Li CP (2002) Antitumor effects of miconazole on human colon carcinoma xenografts in nude mice through induction of apoptosis and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 180:22–35
Xu K, Schwarz PM, Ludueña RF (2002) Interaction of nocodazole with tubulin isotypes. Drug Dev Res 55:91–96
Zhang L, Peng XM, Damu GL, Geng RX, Zhou CH (2014) Comprehensive review in current developments of imidazole-based medicinal chemistry. Med Res Rev 34:340–437
Zhang R, Alushin GM, Brown A, Nogales E (2015) Mechanistic origin of microtubule dynamic instability and its modulation by EB proteins. Cell 162:849–859
Funding
This study is funded by the NITC and MHRD, Government of India in the form of scholarship to Mr. Jomon Sebastian and Infrastructural facilities to Dr. Rathinasamy K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JS performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. KR designed the experiments, provided the resources for the work, critically analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. All the authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PZF 193 kb)
ESM 2
(PZF 192 kb)
ESM 3
(PZF 202 kb)
ESM 4
(PZF 101 kb)
ESM 5
(PZF 97 kb)
ESM 6
(PZF 31 kb)
ESM 7
(PZF 107 kb)
ESM 8
(PZF 120 kb)
ESM 9
(PZF 34 kb)
ESM 10
(PZF 514 kb)
ESM 11
(PZF 545 kb)
ESM 12
(PZF 205 kb)
ESM 13
(PZF 110 kb)
ESM 14
(PZF 110 kb)
ESM 15
(PZF 129 kb)
ESM 16
(PZF 115 kb)
ESM 17
(PZF 99 kb)
ESM 18
(PZF 113 kb)
ESM 19
(PZF 134 kb)
ESM 20
(PZF 1832 kb)
ESM 21
(PDF 723 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sebastian, J., Rathinasamy, K. Sertaconazole induced toxicity in HeLa cells through mitotic arrest and inhibition of microtubule assembly. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 394, 1231–1249 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02059-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-021-02059-5