Abstract
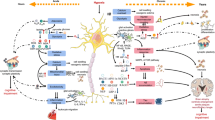
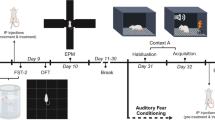
Neurological evidence for the neuroprotective function of α2-adrenoceptors in the cerebral ischemia is inconsistent. It is not examined how pretreatment with a single dose of α2-adrenoceptor agents can affect motor function and anxiety- and memory-related responses in the cerebral ischemic animals. The transient forebrain ischemia model was provided, using a bilateral common carotid arterial occlusion (two-vessel occlusion, 2VO) in male Wistar rats. The 2VO rats impaired motor functions in the Rota-rod and wire grip tests and also decreased the step-through latency and the percentage of time spent on the open arms (%OAT), the percentage of entries into the open arms (%OAE) as well as locomotion in the elevated plus maze (EPM), indicating a memory deficit and anxiety-like behavior. Intraperitoneal single administration of yohimbine (0, 0.001, 0.01, and 0.1 mg/kg) before the 2VO did not alter these parameters while the higher and middle doses of clonidine (0.01 and 0.1 mg/kg) prevented the memory deficit and hypo-locomotion and its middle dose abrogated Rota-rod dysfunction and anxiety-like response. Meanwhile, both drugs did not influence on the measured behaviors in the sham groups by themselves. Moreover, yohimbine (0.001 mg/kg) abolished the beneficial effects of clonidine (0.01 and 0.1 mg/kg) on motor function in the Rota-rod and memory retention and also at its middle dose on the %OAT and locomotion in the 2VO rats. Our findings show a neuroprotective role for clonidine in motor function and memory- and anxiety-related behaviors of 2VO rats and the importance of α2-adrenoceptors in these processes.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander MP, Lafleche G, Schnyer D, Lim C, Verfaellie M (2011) Cognitive and functional outcome after out of hospital cardiac arrest. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 17:364–368. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1355617710001633
Aston-Jones G, Chiang C, Alexinsky T (1991) Discharge of noradrenergic locus coeruleus neurons in behaving rats and monkeys suggests a role in vigilance. Prog Brain Res 88:501–520
Bashiri H, Rezayof A, Sahebgharani M, Tavangar SM, Zarrindast MR (2016) Modulatory effects of the basolateral amygdala alpha2-adrenoceptors on nicotine-induced anxiogenic-like behaviours of rats in the elevated plus maze. Neuropharmacology 105:478–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.02.010
Berridge CW, Page ME, Valentino RJ, Foote SL (1993) Effects of locus coeruleus inactivation on electroencephalographic activity in neocortex and hippocampus. Neuroscience 55:381–393
Brede M, Braeuninger S, Langhauser F, Hein L, Roewer N, Stoll G, Kleinschnitz C (2011) α2-Adrenoceptors do not mediate neuroprotection in acute ischemic stroke in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2011.110
Cole BJ, Robbins TW (1992) Forebrain norepinephrine: role in controlled information processing in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 7:129–142
Devauges V, Sara SJ (1990) Activation of the noradrenergic system facilitates an attentional shift in the rat. Behav Brain Res 39:19–28
Dhooper A, Young C, Reid KH (1997) Ischemia-induced anxiety following cardiac arrest in the rat. Behav Brain Res 84:57–62
Ebrahimi-Ghiri M, Rostampour M, Jamshidi-Mehr M, Nasehi M, Zarrindast MR (2018) Role of CA1 GABAA and GABAB receptors on learning deficit induced by D-AP5 in passive avoidance step-through task. Brain Res 1678:164–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2017.10.004
Globus MY, Busto R, Dietrich WD et al (1989) Direct evidence for acute and massive norepinephrine release in the hippocampus during transient ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 9:892–896. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.1989.123
Gulinello M, Lebesgue D, Jover-Mengual T, Zukin RS, Etgen AM (2006) Acute and chronic estradiol treatments reduce memory deficits induced by transient global ischemia in female rats. Horm Behav 49:246–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2005.07.010
Gupta S, Sharma B (2014) Pharmacological modulation of I(1)-imidazoline and alpha2-adrenoceptors in sub acute brain ischemia induced vascular dementia. Eur J Pharmacol 723:80–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.12.003
Haghani M, Shabani M, Moazzami K (2013) Maternal mobile phone exposure adversely affects the electrophysiological properties of Purkinje neurons in rat offspring. Neuroscience 250:588–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.07.049
Harley CW (1987) A role for norepinephrine in arousal, emotion and learning?: limbic modulation by norepinephrine and the Kety hypothesis. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 11:419–458
Harsing LGJ, Gigler G, Albert M et al (2004) Neurotransmitter release in experimental stroke models: the role of glutamate-GABA interaction. Adv Exp Med Biol 541:21–37
Horstmann A, Frisch S, Jentzsch RT, Muller K, Villringer A, Schroeter ML (2010) Resuscitating the heart but losing the brain: brain atrophy in the aftermath of cardiac arrest. Neurology 74:306–312. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181cbcd6f
Jakala P, Sirvio J, Riekkinen M et al (1999) Guanfacine and clonidine, alpha 2-agonists, improve paired associates learning, but not delayed matching to sample, in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:119–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00055-4
Lee JM, Grabb MC, Zipfel GJ, Choi DW (2000) Brain tissue responses to ischemia. J Clin Invest 106:723–731. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI11003
Li Y, Yu M, Zhao B, Wang Y, Zha Y, Li Z, Yu L, Yan, Chen Z, Zhang W, Zeng X, He Z (2018) Clonidine preconditioning improved cerebral ischemia-induced learning and memory deficits in rats via ERK1/2-CREB/ NF-κB-NR2B pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 818:167–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.10.041
Lu Y, Li C, Zhou M, Luo P, Huang P, Tan J, Lu Q, Xu X, He Z, Guo L (2015) Clonidine ameliorates cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion via up-regulation of the GABABR1 and GAD67 in hippocampal CA1 in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 132:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2015.01.018
Martin JA, Smith BL, Mathews TJ, Ventura SJ (1999) Births and deaths: preliminary data for 1998. Natl Vital Stat Rep 47:1–45
Milot M, Plamondon H (2008) Ischemia-induced hyperactivity: effects of dim versus bright illumination on open-field exploration and habituation following global ischemia in rats. Behav Brain Res 192:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2008.03.044
Milot MR, Plamondon H (2009) Time-dependent effects of global cerebral ischemia on anxiety, locomotion, and habituation in rats. Behav Brain Res 200:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2009.01.009
Nakashima MN, Ajiki K, Nakashima K, Takahashi M (2003) Possible role of nitric oxide in anxiety following transient cerebral ischemia in mice. J Pharmacol Sci 91:47–52
Nasehi M, Hajikhani M, Ebrahimi-Ghiri M, Zarrindast M-R (2017) Interaction between NMDA and CB2 function in the dorsal hippocampus on memory consolidation impairment: an isobologram analysis. Psychopharmacology 234:507–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4481-9
Nishigaya K, Yoshida Y, Sasuga M, Nukui H, Ooneda G (1991) Effect of recirculation on exacerbation of ischemic vascular lesions in rat brain. Stroke 22:635–642
Norozpour Y, Nasehi M, Sabouri-Khanghah V, Torabi-Nami M, Zarrindast MR (2016) The effect of CA1 α2 adrenergic receptors on memory retention deficit induced by total sleep deprivation and the reversal of circadian rhythm in a rat model. Neurobiol Learn Mem 133:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2016.06.004
Park SI, Jang D-K, Han Y-M, Sunwoo YY, Park MS, Chung YA, Maeng LS, Im R, Kim MW, Jeun SS, Jang KS (2010) Effect of combination therapy with sodium ozagrel and panax ginseng on transient cerebral ischemia model in rats. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:893401–893408. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/893401
Shang JL, Cheng Q, Duan SJ et al (2018) Cognitive improvement following ischemia/reperfusion injury induced by voluntary running-wheel exercise is associated with LncMALAT1-mediated apoptosis inhibition. Int J Mol Med 41:2715–2723. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3484
Siesjo BK (1988) Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage. Crit Care Med 16:954–963
Torgersen J, Strand K, Bjelland TW et al (2010) Cognitive dysfunction and health-related quality of life after a cardiac arrest and therapeutic hypothermia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 54:721–728. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2010.02219.x
Wachelder EM, Moulaert VRMP, van Heugten C, Verbunt JA, Bekkers SCAM, Wade DT (2009) Life after survival: long-term daily functioning and quality of life after an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 80:517–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2009.01.020
Yan B, He J, Xu H et al (2007) Quetiapine attenuates the depressive and anxiolytic-like behavioural changes induced by global cerebral ischemia in mice. Behav Brain Res 182:36–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2007.05.002
Yanli L, Xizhou Z, Yan W, Bo Z, Yunhong Z, Zicheng L, Lingling Y, lingling Y, Zhangao C, Min Z, Zhi H (2016) Clonidine preconditioning alleviated focal cerebral ischemic insult in rats via up-regulating p-NMDAR1 and down-regulating NMDAR2A / p-NMDAR2B. Eur J Pharmacol 793:89–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.10.036
Zhang Y (2004) Clonidine preconditioning decreases infarct size and improves neurological outcome from transient forebrain ischemia in the rat. Neuroscience 125:625–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.02.011
Zhang Y, Kimelberg HK (2005) Neuroprotection by alpha 2-adrenergic agonists in cerebral ischemia. Curr Neuropharmacol 3:317–323. https://doi.org/10.2174/157015905774322534
Contributors
EI and VS acquired the animal data. ME wrote the manuscript. MN, ME, and MZ were responsible for the study concept, design, and proteomics analysis as well as assisted with the data analysis and interpretation of findings. All authors critically reviewed the content and approved the final version for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was carried out in accordance with ethical standards in all aspects.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nasehi, M., Imani, E., Ebrahimi-Ghiri, M. et al. Effects of precondition α2-adrenoceptor agents on memory- and anxiety-related processes in the transient cerebral ischemic rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 393, 315–324 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01723-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-019-01723-1