Abstract
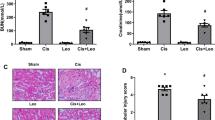
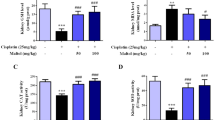
Cisplatin (CP) is an essential chemotherapeutic drug used over the world against many types of cancer. It has several side effects such as ototoxicity, myelosuppression, and nephrotoxicity. Nephrotoxicity is the most dangerous and is considered a dose-limiting one. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis are involved in this toxicity. This study was conducted to focus on the impact of perindopril (PER) against CP-induced nephrotoxicity in rat. Male albino rats were divided to control, rats received a single dose of CP, rats received PER, and rats co-received PER and CP. Nephrotoxicity evoked by CP challenge was characterized histologically and biochemically including significant increase in relative kidney/body weight ratio and serum urea and creatinine. Additionally, CP markedly increased renal tissue content of malondialdehyde (MDA) while decreased reduced glutathione (GSH) and depleted glutathione-S-transferase (GST) activity. CP produced significant increase in the inflammation biomarkers; nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interlukine-6 (IL-6). Administration of CP clearly upregulated caspase-3, while it downregulated B-cell lymphoma-2 (BCL-2) gene expressions. Perindopril treatment showed a significant restoration in the pathological alterations histologically and biochemically, which are provoked by CP administration. Altogether, these results suggested a good therapeutic role of PER against CP-induced nephrotoxicity through its influence on oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banchroft JD, Stevens A, Turner DR (1996) Theory and practice of histological techniques, 4th edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York
Baradaran A, Tavafi M, Ardalan MR et al (2016) Cisplatin; nephrotoxicity and beyond. Ann Res Antioxidants 1:e014
Bartels H, Böhmer M, Heierli C (1972) Serum creatinine determination without protein precipitation. Clin Chim Acta 37:193–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(72)90432-9
Baud V, Karin M (2001) Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor and its relatives. Trends Cell Biol 11:372–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0962-8924(01)02064-5
Benigni A, Cassis P, Remuzzi G (2010) Angiotensin II revisited: new roles in inflammation, immunology and aging. EMBO Mol Med 2:247–257. https://doi.org/10.1002/emmm.201000080
Darwish MA, Abo-Youssef AM, Khalaf MM, Abo-Saif AA, Saleh IG, Abdelghany TM (2017) Vitamin E mitigates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity due to reversal of oxidative/nitrosative stress, suppression of inflammation and reduction of total renal platinum accumulation. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 31:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.21833
De Mello WC (2017) Local renin angiotensin aldosterone systems and cardiovascular diseases. Med Clin 101:117–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2016.08.017
Dehghani A, Saberi S, Nematbakhsh M (2016) Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity alters blood pressure response to angiotensin II administration in rats. Adv Biomed Res 5:53. https://doi.org/10.4103/2277-9175.178797
dos Santos NAG, Rodrigues MAC, Martins NM et al (2012) Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and targets of nephroprotection: an update. Arch Toxicol 86:1233–1250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0821-7
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
Fawcett JK, Scott JE (1960) A rapid and precise method for the determination of urea. J Clin Pathol 13:156–159
Gálvez AS, Fiedler JL, Ocaranza MP et al (2005) Perindopril regulates β-agonist-induced cardiac apoptosis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 46:255–261
Gross JL, De Azevedo MJ, Silveiro SP et al (2005) Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care 28:164–176. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.28.1.164
Guada M, Ganugula R, Vadhanam M, Ravi Kumar MNV (2017) Urolithin A mitigates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibiting renal inflammation and apoptosis in an experimental rat model. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 363:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.117.242420
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hayati F, Hossainzadeh M, Shayanpour S et al (2016) Prevention of cisplatin nephrotoxicity. J Nephropharmacology 5:57
Khan MAH, Sattar MA, Abdullah NA et al (2007) Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity causes altered renal hemodynamics in Wistar Kyoto and spontaneously hypertensive rats: role of augmented renal alpha-adrenergic responsiveness. Exp Toxicol Pathol 59:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2007.05.005
Lee J, Nakagiri T, Oto T, Harada M, Morii E, Shintani Y, Inoue M, Iwakura Y, Miyoshi S, Okumura M, Hirano T, Murakami M (2012) IL-6 amplifier, NF-κB–triggered positive feedback for IL-6 signaling, in grafts is involved in allogeneic rejection responses. J Immunol 189:1928–1936. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1103613
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL et al (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Mazia D, Brewer PA, Alfert M (1953) The cytochemical staining and measurement of protein with mercuric bromphenol blue. BiolBull 104:57–67
Miller RP, Tadagavadi RK, Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2010) Mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins (Basel) 2:2490–2518. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2112490
Ognjanović BI, Djordjević NZ, Matić MM, Obradović JM, Mladenović JM, Štajn AŠ, Saičić ZS (2012) Lipid peroxidative damage on cisplatin exposure and alterations in antioxidant defense system in rat kidneys: a possible protective effect of selenium. Int J Mol Sci 13:1790–1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13021790
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(79)90738-3
Olafiranye O, Zizi F, Brimah P, Jean-louis G, Makaryus AN, McFarlane S, Ogedegbe G (2011) Management of hypertension among patients with coronary heart disease. Int J Hypertens 2011:1–6. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/653903
Peres LAB, Cunha Júnior AD (2013) Acute nephrotoxicity of cisplatin: molecular mechanisms. JBras Nefrol 35:332–340. https://doi.org/10.5935/0101-2800.20130052
Portt L, Norman G, Clapp C, Greenwood M, Greenwood MT (2011) Anti-apoptosis and cell survival: a review. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Res 1813:238–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.10.010
Ruiz-Ortega M, Rupérez M, Esteban V, Rodríguez-Vita J, Sánchez-López E, Carvajal G, Egido J (2005) Angiotensin II: a key factor in the inflammatory and fibrotic response in kidney diseases. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21:16–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfi265
Rüster C, Wolf G (2006) Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and progression of renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2985–2991. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2006040356
Sachse A, Wolf G (2007) Angiotensin II–induced reactive oxygen species and the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2439–2446. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2007020149
Sánchez-González PD, López-Hernández FJ, López-Novoa JM, Morales AI (2011) An integrative view of the pathophysiological events leading to cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Crit Rev Toxicol 41:803–821. https://doi.org/10.3109/10408444.2011.602662
Silici S, Ekmekcioglu O, Kanbur M, Deniz K (2011) The protective effect of royal jelly against cisplatin-induced renal oxidative stress in rats. World J Urol 29:127–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-010-0543-5
Slomka T, Lennon ES, Akbar H, Gosmanova EO, Bhattacharya SK, Oliphant CS, Khouzam RN (2016) Effects of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with end-stage renal disease. Am J Med Sci 351:309–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjms.2015.12.021
Strange RC, Jones PW, Fryer AA (2000) Glutathione S-transferase: genetics and role in toxicology. Toxicol Lett 112:357–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4274(99)00230-1
Sun HL, Sun L, Li YY, Shao M, Cheng X, Ge N, Lu J, Li S (2009) ACE-inhibitor suppresses the apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress in renal tubular in experimental diabetic rats. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 117:336–344. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0028-1112148
Tak PP, Firestein GS (2001) NF-κB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest 107:7–11. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI11830
Tang SCW, Leung JCK, Chan LYY, Eddy AA, Lai KN (2008) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor but not angiotensin receptor blockade or statin ameliorates murine adriamycin nephropathy. Kidney Int 73:288–299. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ki.5002674
Topcu-Tarladacalisir Y, Sapmaz-Metin M, Karaca T (2016) Curcumin counteracts cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by preventing renal tubular cell apoptosis. Ren Fail 38:1741–1748. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886022X.2016.1229996
Yang Y, Liu H, Liu F (2014) Mitochondrial dysregulation and protection in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 88:1249–1256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1239-1
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N, Nugent K (2007) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Am J Med Sci 334:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31812dfe1e
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Kawata M et al (2001) The angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitor perindopril suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis: possible role of the vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 7:1073–1078
Zhang H, Sun SC (2015) NF-κB in inflammation and renal diseases. Cell Biosci 5:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-015-0056-4
Zhu S, Pabla N, Tang C, He L, Dong Z (2015) DNA damage response in cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Arch Toxicol 89:2197–2205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-015-1633-3
Zhu X, Jiang X, Li A, Zhao Z, Li S (2017) S-Allylmercaptocysteine attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity through suppression of apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Nutrients 9:166. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9020166
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Prof. Dr. Dr. Kawkab A. Ahmed, Professor of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University, Egypt, for her kind help in performing the histopathological examination.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS Shalkami and MIA Hassan conceived and designed this research. All the authors conducted experiments. AS Shalkami and AA Abd El-Ghany analyzed data. AS Shalkami and MIA Hassan wrote the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animals’ procedures in this work were conducted according to the Animal Ethics Committee, Faculty of Medicine, Assiut University, Egypt.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shalkami, AG.S., Hassan, M.I.A. & Abd El-Ghany, A.A. Perindopril regulates the inflammatory mediators, NF-κB/TNF-α/IL-6, and apoptosis in cisplatin-induced renal dysfunction. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 391, 1247–1255 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1550-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-018-1550-0