Abstract
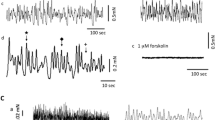
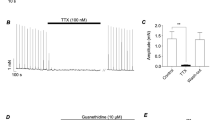
Recently, a cholinergic neurogenic component of contraction has been characterised in the aganglionic mouse vas deferens. In this paper, a cholinergic component of contraction in the guinea-pig vas deferens is characterised pharmacologically. A residual, tetrodotoxin-sensitive (TTX, 0.3 μM), neurogenic contraction was revealed after prolonged exposure (5 h) to the adrenergic neurone blocker bretylium (20 μM) or in the presence of prazosin (100 nM) and α,β-methylene ATP (1 μM), a purinergic agonist which desensitizes P2X receptors. The bretylium-resistant component was potentiated by the acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor neostigmine (10 μM) and inhibited by the muscarinic-receptor (mAChR) antagonist cyclopentolate (1 μM). Nicotine (30 μM) enhanced the bretylium-resistant component. Neostigmine increased the second component of contraction in the presence of prazosin and α,β-methylene ATP, whilst yohimbine (1 μM), an α2 adrenergic receptor antagonist, enhanced both the first and second components of the electrically evoked contraction. These enhanced contractions were blocked by cyclopentolate in both cases. Nicotine enhanced the cholinergic component of contraction revealed by neostigmine but failed to have any detectable effects in the presence of cyclopentolate. Neostigmine alone increased the slow component of contraction which was reversed by cyclopentolate to control levels. The M3 receptor-antagonist 4-DAMP (10 nM) markedly inhibited the cholinergic component of contraction to a level comparable with cyclopentolate. Laser microscopy has shown that neostigmine also increased the frequency of spontaneous Ca2+ transients remaining in smooth muscle cells after perfusion with prazosin and α,β-methylene ATP, an effect blocked by 4-DAMP. These experimental data show that there is a functional cholinergic innervation in the guinea-pig vas deferens whose action is limited by acetylcholinesterase, blocked by cyclopentolate and mediated through M3 receptors. Moreover, by blocking the cholinesterase, the increased amount of ACh generates spontaneous Ca2+ transients in smooth muscle cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- α,β-MeATP:
-
α,β-Methylene ATP
- mAchR:
-
Muscarinic receptor
- nAchR:
-
Nicotinic receptor
- TTX:
-
Tetrodotoxin
References
Aberdeen J, Corr L, Milner P, Lincoln J, Burnstock G (1990) Marked increases in calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing nerves in the developing rat following long-term sympathectomy with guanethidine. Neuroscience 35:175–184
Bell C (1967) An electrophysiological study of the effects of atropine and physostigmine on transmission to the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol 189:31–42
Bell C, McLean JR (1967) Localization of norepinephrine and acetylcholinesterase in separate neurons supplying the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 157(1):69–73
Bentley GA (1966) The effect of local anaesthetic and anti-adrenaline drugs on the response of sympathetically innervated smooth muscle preparations to electrical stimulation at different frequencies. Br J Pharmac Chemother 27:64–80
Bhargava KP, Kar K, Parmar SS (1965) Independent cholinergic and adrenergic mechanisms in the guinea-pig isolated nerve vas deferens preparation. B J Pharmcol 24:641–650
Bolton TB (2006) Calcium events in smooth muscles and their interstitial cells; physiological roles of sparks. J Physiol 570(1):5–11
Brain KL, Trout SJ, Jackson VM, Dass N, Cunnane TC (2001) Nicotine induces calcium spikes in single nerve terminal varicosities: a role for intracellular calcium stores. Neuroscience 106(2):395–403
Brain KL, Jackson VM, Trout SJ, Cunnane TC (2002) Intermittent ATP release from nerve terminals elicits focal smooth muscle Ca2+ transients in mouse vas deferens. J Physiol 541(3):849–862
Carneiro RC, Markus RP, Dubocovich ML (1993) Presynaptic modulation by melatonin of the nicotinic-induced calcium-dependent release of norepinephrine from the rat vas deferens. Biol Signals 2(4):199–206
Clementi F, Naimzada KM, Montegazza P (1969) Study of the nerve endings in the vas deferens and seminal vesicles of the guinea-pig. Int J Neuropharmacol 8:399–403
Cuprian AM, Solanki P, Jackson MV, Cunnane TC (2005) Cholinergic innervation of the mouse isolated vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 146:927–934
Ferry CB (1967) The innervation of the vas deferens of the guinea-pig. J Physiol Lond 192:463–478
Fukushi Y, Wakui M (1986a) Possible interactions of cholinergic nerves with two different (pre and post) sites of the neuromuscular junction in guinea-pig vas deferens. J Auton Pharmac 5:291–297
Fukushi Y, Wakui M (1986b) Pharmacological studies on the role of cholinergic nerves in the neuromuscular transmission in the circular smooth muscle of the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Auton Pharmac 5:299–304
Furness JB, Iwayama T (1972) The arrangement and identification of axons innervating the vas deferens of the guinea-pig. J Anat 113(2):179–196
Geppetti P, Frilli S, Renzi D, Santicioli P, Maggi CA, Theodorsson E, Franciullacci M (1988) Distribution of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity in various rat tissues: correlation with substance P and other tachykinins and sensitivity to capsaicin. Regul Pept 23:289–298
Hata F, Kunio T, Yoshio M, Ron-Tsan L, Hajime I, Hiroshi Y (1980) Specific changes in the cholinergic system in guinea-pig vas deferens after denervation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 215(3):716–722
Hökfelt TG, Ljungdahl AS (1972) Histochemical determination of neurotransmitter distribution. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis 50:1–24
Iram S, Hoyle C (2005) Potentiation of sympathetic neuromuscular transmission mediated by muscarinic receptors in guinea-pig isolated vas deferens. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 371:212–220
Jackson VM, Cunnane TC (2002) Bretylium or 6-OHDA-resistant, action potential-evoked Ca2+ transients in varicosities of the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 135:1845–1850
Jackson VM, Trout SJ, Brain KL, Cunnane TC (2001) Characterisation of action potential-evoked calcium transients in postganglionic sympathetic axon bundles. J Physiol 537:3–16
Majcen Z (1984) Cholinesterases and choline acetyltransferase in the ductus deferens of the guinea-pig. Histochemistry 81(2):195–199
Markus RP, Zago WM, Carneiro RC (1996) Melatonin modulation of presynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the rat vas deferens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 279(1):18–22
Matsuno K, Mita S (1992) Involvement of the muscarinic receptors in the postsynaptic potentiation of neurogenic twitch contraction in the mouse vas deferens. Lif Sci 50(11):799–806
Miranda HF, Wolstenholme WW (1985) Presynaptic regulation of Ach of the NE mediated responses in the rat vas deferens. J Recept Res 5(4):231–243
Miranda HF, Wolstenholme WW, Moreu GM, Santiago PA (1987) Ontogenesis of autonomic receptors and AchE activity in the rat vas deferens. Gen Pharmacol 18(4):425–429
Miranda HF, Wolstenholme WW, Moreu GM, Santiago PA (1988) Effects of haloperidol on neurotransmitter activity in the rat vas deferens. Gen Pharmacol 19(1):123–127
Miranda HF, Duran E, Bustamante D, Paeile C, Pinardi G (1994) Pre- and postjunctional muscarinic receptors subtyes in the vas deferens of rat. Gen Pharmacol 25(8):1643–1647
Miranda HF, Duran E, Fernandez E, Pinardi G (1995) Muscarinic receptors subtypes in the bisected vas deferens of the rat. Gen Pharmacol 26(2):387–391
Morris JL, Gibbins IL (1992) Co-transmission and neuromodulation, in autonomic neuroeffector mechanisms. Harwood Academic, Philadelphia, pp 33–121
Robinson PM (1969) A cholinergic component in the innervation of the longitudinal smooth muscle of the guinea-pig vas deferens - the fine structural localization of acetylcholinesterase. J Cell Biol 41:462–476
Saito A, Tomobe Y, Goto K (1987) Effect of capsaicin on smooth muscles of rat vas deferens: involvement of calcitonin gene-related peptide? J Pharmacol Exp Ther 242:665–672
Silva WI, Wolstenholme WW, Miranda HI (1988) Pre- and postsynaptic muscarinic receptors of the rat vas deferens: an update. P R Health Sci J 7(2):105–110
Sjöstrand NO (1965) The adrenergic innervation of the vas deferens and the accessory male genital organs. Acta Physiol Scand, Suppl 257:1–82
Sjöstrand NO (1973) Effects of acetylcholine and some other smooth stimulants on the electrical and mechanical responses of the guinea-pig vas deferens to nerve stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand 89:1–9
Sneddon P, McLaren GJ, Kennedy C (1996) Purinergic co-transmission: sympathetic nerves. Sem Neurosci 8:201–205
Starke K, Bultmann R, Bulloch JM, Von Kulgelgen I (1991) Noradrenaline-ATP corelease and cotransmission following activation of nicotine receptors at postganglionic sympathetic axons. J Neural Transm Suppl 34:93–98
Todorov L, Windisch K, Shersen H, Lajitha A, Papasova M, Vizi ES (1991) Prejunctional nicotinic receptors involved in facilitation of stimulation-evoked noradrenaline release from the vas deferens of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol 102(1):186–190
Trendelenburg AU, Gomeza J, Klebroff W, Zhou H, Wess J (2003) Heterogeneity of presynaptic muscarinic receptors mediating inhibition of sympathetic transmitter release: a study with M2- and M4-receptor-deficient mice. Br J Pharmacol 138:469–480
Ventura S, Bavetta S, Milner P, Ralevic V, Burnstock G (1998) Nitric oxide synthase is co-localized with vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in postganglionic parasympathetic nerves innervating the rat vas deferens. Neuroscience 83:607–616
Von Kugelgen I, Starke K (1991) Release of noradrenaline and ATP by electrical stimulation and nicotine in guinea-pig vas deferens. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 344(4):419–429
Wanigasekara Y, Kepper ME, Keast JR (2003) Immunohistochemical characterisation of pelvic autonomic ganglia in male mice. Cell Tiss Res 311(2):175–185
Zago WM, Markus RP (1999) Melatonin modulation of presynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors located on short noradrenergic neurons of the rat vas deferens: a pharmacological characterization. Braz J Med Biol Res 32(8):999–1006
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank The Wellcome Trust for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0256-5.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solanki, P., Cuprian-Beltechi, A.M. & Cunnane, T.C. Cholinergic innervation of the guinea-pig isolated vas deferens. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 376, 265–274 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0198-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0198-y