Abstract
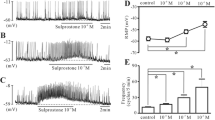
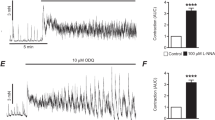
We investigated the role of nitric oxide (NO) in pacemaker activity and signal mechanisms in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) of the mouse small intestine using whole cell patch-clamp techniques at 30°C. ICC generated pacemaker potential in the current clamp mode and pacemaker currents at a holding potential of –70 mV. (±)-S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine (SNAP; a NO donor) produced membrane hyperpolarization and inhibited the amplitude and frequency of the pacemaker currents, and increased resting currents in the outward direction. These effects were blocked by the use of glibenclamide (an ATP-sensitive K+ channel blocker), but not by the use of 5-hydroxydecanoic acid (a mitochondrial ATP-sensitive K+ channel blocker). Pretreatment with ODQ (a guanylate cyclase inhibitor) almost blocked the NO-induced effects. The use of cell-permeable 8-bromo-cyclic GMP also mimicked the action of SNAP. However, the use of KT-5823 (a protein kinase G inhibitor) did not block the NO-induced effects. Spontaneous [Ca2+]i oscillations in ICC were inhibited by the treatment of SNAP, as seen in recordings of intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i). These results suggest that NO inhibits pacemaker activity by the activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels via a cyclic GMP dependent mechanism in ICC, and the activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels mediates the inhibition of spontaneous [Ca2+]i oscillations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolotina VM, Najibi S, Palacino JJ, Pagano PJ, Cohen RA (1994) Nitric oxide directly activates calcium-dependent potassium channels in vascular smooth muscle. Nature 368:850–853
Brayden JE (2002) Clinical roles of KATP channels in vascular smooth muscle. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 29:312–316
Burns AJ, Lomax AE, Torihashi S, Sanders KM, Ward SM (1996) Interstitial cells of Cajal mediate inhibitory neurotransmission in the stomach. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:12008–12013
Burnstock G, Lavin S (2002) Interstitial cells of Cajal and purinergic signaling. Autonomic Neuroscience 97:68–72
Choi S, Park DY, Yeum CH, Chang Iym, You HJ, Park CK, Kim MY, Kong ID, So I, Kim KW, Jun JY (2006) Activating of ATP-dependent K+ channels comprised of Kir6.2 and SUR 2B by PGE2 through EP2 receptor in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestine. Cell Physil Biochem 18:187–198
Deka DK, Brading AF (2004) Nitric oxide activates glibenclamide-sensitive K+ channels in urinary bladder myocytes through a c-GMP-dependent mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol 492:13–19
Epperson A, Hatton WJ, Callaghan B, Doherty P, Walker RL, Sanders KM, Ward SM, Horowitz B (2000) Molecular components expressed in cultured and freshly isolated interstitial cells of Cajal. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279:C529–C539
Franck H, Sweeney KM, Sanders KM, Shuttleworth CWR (1997) Effects of a novel guanylate cyclase inhibitor on nitric oxide-dependent inhibitory neurotransmission in canine proximal colon. Br J Pharmacol 122:1223–1229
Han J, Kim N, Joo H, Kim E, Earm YE (2002) ATP-sensitive K+ channel activation by nitric oxide and protein kinase G in rabbit ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol 283:H1545–H1554
Huizinga JD, Thuneberg L, Kluppel M, Malysz J, Mikkelsen HB, Bernstein A (1995) W/kit gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature 373:347–349
Jain D, Khalid M, Manishi T, Joan CM, Deborah DP (2003) Role of Interstitial cells of Cajal in motility disorders of the bowel. Am J Gastroenterol 98:618–624
Jun JY, Choi S, Yeum CH, Chang IY, Park CK, Kim MY, Kong ID, So I, Kim KW, You HJ (2004a) Noradrenaline inhibits pacemaker currents through stimulation of beta 1-drenoceptors in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestine. Br J Pharmacol 141:670–677
Jun JY, Choi S, Yeum CH, Chang IY, You HJ, Park CK, Kim MY, Kong ID, Kim MJ, Lee KP, So I, Kim KW (2004b) Substance P induces inward current and regulates pacemaker currents through tachykinin NK1 receptor in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal of murine small intestine. Eur J Pharmacol 495:35–42
Jun JY, Choi S, Chang IY, Yoon CK, Jeong HG, Kong ID, So I, Kim KW, You HJ (2005) Deoxycholic acid inhibits pacemaker currents by activating ATP-dependent K+ channels through prostaglandin E2 in interstitial cells of Cajal from the murine small intestine. Br J Pharmacol 144:242–251
Keef KD, Murray DC, Sanders KM, Smith TK (1997) Basal release of nitric oxide induces an oscillatory motor pattern in canine colon. J Physiol 499:773–786
Kitamura K, Lian Q, Carl A, Kuriyama H (1993) S-nitrocyctein, but not sodium nitroprusside, produces apamin-sensitive hyperpolarization in rat gastric fundus. Br J Pharmacol 109:415–423
Kito Y, Suzuki H (2003) Properties of pacemaker potentials recorded from myenteric interstitial cells of Cajal distributed in the mouse small intestine. J Physiol 553:803–818
Koh SD, Campbell JD, Carl A, Sanders KM (1995) Nitric oxide activates multiple potassium channels in canine colonic smooth muscle. J Physiol 489:735–747
Koh SD, Bradley KK, Rae MG, Keef KD, Horowitz B, Sanders KM (1998a) Basal activation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels in murine colonic smooth muscle cells. Biophys J 75:1793–1800
Koh SD, Sanders KM, Ward SM (1998b) Spontaneous electrical rhythmicity in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from the murine small intestine. J Physiol 513:203–213
Koh SD, Kim TW, Jun JY, Glasgow NJ, Ward SM, Sanders KM (2000) Regulation of pacemaker currents in interstitial cells of Cajal from murine small intestine by cyclic nucleotides. J Physiol 527:149–162
Kubo M, Nakaya Y, Matsuoka S, Saito K, Kuroda Y (1994) Atrial natriuretic or and isosorbide dinitrate modulate the gating of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Cir Res 74:471–476
Lin YF, Raab-Graham K, Jan YN, Jan LY (2004) NO stimulation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels: Involvement of Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and contribution to neuroprotection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:7799–7804
Lincoln TM, Cornwell TL (1993) Intracellular cyclic GMP receptor proteins. FASEB 7:328–338
Martins SL, De Oliveira RB, Ballejo G (1995) Rat duodenum nitrergic-induced relaxations are cGMP-independent and apamin-sensitive. Eur J Pharmacol 284:265–270
Murphy ME, Brayden JE (1995) Nitric oxide hyperpolarizes rabbit mesenteric arteries via ATP-sensitive potassium channels. J Physiol 486:47–58
Nakamura E, Lee KP, So I, Kim KW, Suzuki H (2004) Effects of endogenous and exogenous nitric oxide on electrical responses of circular smooth muscle isolated from the guinea-pig stomach antrum. J Smooth Muscle Res 40:183–198
Olsson C, Holmgren S (2001) The control of gut motility. Comp Biochem Physiol 128:481–503
Publicova NG, Hammond EM, Sanders KM (1993) Amplification of nitric oxide signaling by interstitial cells isolated from canine colon. Proc Natl Acad Sci 90:2087–2091
Salmhofer H, Neuhuber WL, Ruth P, Huber A, Russwurm M, Allescher HD (2001) Pivotal role of the interstitial cells of Cajal in the nitric oxide signaling pathway of rat small intestine. Morphological evidence. Cell Tissue Res 305:331–340
Sanders KM (1996) A case for interstitial cells of Cajal as pacemakers and mediators of neurotransmission in the gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 111:492–515
Sanders KM, Ward SM (1992) Nitric oxide as a mediator of nonadrenergic noncholinergic neurotransmission. Am J Physiol 262:G379–G392
Seino S, Miki T (2003) Physiological and pathological roles of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Prog Biophy Mol Biol 81:133–176
Sergeant GP, Johnston L, McHale NG, Thornbury KD, Hollywood MA (2006) Activation of the cGMP/PKG pathway inhibits electrical activity in rabbit urethral interstitial cells of Cajal by reducing the spatial spread of Ca2+ waves. J Physiol 574:167–181
Shuttleworth CW, Xue C, Ward SM, de Vent J, Sanders KM (1993) Immunohisochemical localization of 3′,5′-cyclic guanosine monophosphate in the canine proximal colon: response to nitric oxide and electrical stimulation of enteric inhibitory neurons. Neuroscience 56:513–522
Small RC, Berry JL, Foster RW (1992) Potassium channel opening drugs and the airways. Braz J Med Biol Res 25:983–998
Sternini C, Wong H, Wu SV, De Giorgio R, Yang M, Reeve J Jr, Brecha NC, Walsh JH (1997) Somatostatin 2A receptor is expressed by enteric neurons, and by interstitial cells of Cajal and enterochromaffin-like cells of the gastrointestinal tract. J Comp Neurol 386:393–408
Suzuki H, Ward SM, Bayguinov YR, Edwards FR, Hirst GDS (2003) Involvement of intramuscular interstitial cells in nitrergic inhibition in the mouse gastric antrum. J Physiol 546:751–763
Szurszewski JH (1987) Electrical basis for gastrointestinal motility. In: Johnson LR (ed) Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York, pp 383–422
Takeuchi T, Fujinami K, Fuzita A, Okishio Y, Takewaki T, Hata F (2004) Essential role of the interstitial cells of Cajal in nitric oxide-mediated relaxation of longitudinal muscle of the mouse ileum. J Pharmacol Sci 95:71–80
Thomsen L, Robinson TL, Lee JC, Farraway LA, Hughes MJ, Andrews DW, Huizinga JD (1998) Interstitial cells of Cajal generate a rhythmic pacemaker current. Nat Med 4:848–851
Thornbury KD, Ward SM, Dalziel HH, Carl A, Westfall DP, Sanders KM (1991) Nitric oxide and nitrosocystein mimic nonadrenergic, noncholinergic hyperpolarization in canine proximal colon. Am J Physiol 261:G553–G557
Ueno T, Duenes JA, Zarroug AE, Sarr MG (2004) Nitrergic mechanisms mediating inhibitory control of longitudinal smooth muscle contraction in mouse small intestine. J Gastrointest Surg 8:831–841
Uenoyama S, Kobayashi T, Takeuchi Y, Yamashita K, Koide Y, Kazui T (2004) Improvement of intestinal motility using S-methylisothiourea in postoperative ileus. Am J Surg 187:93–97
Vanderwinden JM, Rumessen JJ (1999) Interstitial cells of Cajal in human gut and gastrointestinal disease. Micros Res Tech 47:344–360
Vannucchi MG, De Giorgio R, Faussone-Pellegrini MS (1997) NK1 receptor expression in the interstitial cells of Cajal and neurons and tachykinins distribution in rat ileum during development. J Comp Neurol 383:153–162
Vannucchi MG, Corsani L, Bani D, Faussone-Pellegrini MS (2002) Myenteric neurons and interstitial cells of Cajal of mouse colon express several nitric oxide synthase isoforms. Neurosci Lett 326:191–195
Wang XY, Paterson C, Huizinga JD (2003) Cholinergic and nitrergic innervation of ICC-DMP and ICC-IM in the human small intestine. Neurogastroenterol Motil 15:531–543
Ward SM, Sanders KM (2001) Interstitial cells of Cajal: primary Targets of enteric motor innervation. Anat Rec 262:125–135
Ward SM, Dalziel HH, Bradley ME, Buxton, IL, Keef K, Westfall DP, Sanders KM (1992) Involvement of cyclic GMP in non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic inhibitory neurotransmission in dog proximal colon. Br J Pharmacol 107:1075–1082
Ward SM, Burns AJ, Torihashi S, Sanders KM (1994) Mutation of proto-oncogene c-kit blocks development of interstitial cells and electrical rhythmicity in murine intestine. J Physiol 480:91–97
Ward SM, Beckett EA, Wang X, Baker F, Khoyi M, Sanders KM (2000a) Interstitial cells of Cajal mediate cholinergic neurotransmission from enteric motor neurons. J Neurosci 20:1393–1403
Ward SM, Ordog T, Koh SD, Baker A, Jun JY, Amberg G, Monaghan K, Sanders KM (2000b) Pacemaking in interstitial cells of Cajal depends upon calcium handling by endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. J Physiol 525:355–361
Williams BA, Liu C, De Young L, Brock GB, Sims SM (2005) Regulation of intracellular Ca2+ release in corpus cavernosum smooth muscle: synergism between nitric oxide and cGMP. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C650–C658
Xue C, Pollock J, Schmidt HHHW, Ward SM, Sanders KM (1994) Expression of nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity by interstitial cells of the canine proximal colon. J Auton Nerv Syst 49:1–14
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Clinical Research Center of the Chosun University Hospital (2006) and by the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation (KOSEF) funded by the Korea Government (MOST) [M10639010001].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, C.G., Kim, Y.D., Kim, M.Y. et al. Inhibition of pacemaker currents by nitric oxide via activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in cultured interstitial cells of Cajal from the mouse small intestine. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 376, 175–184 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0187-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0187-1