Abstract
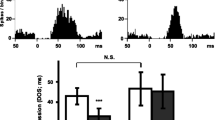
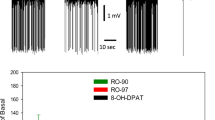
Using extracellular ex vivo recording we studied changes in the reactivity of rat frontal cortical neurons to the 5-HT1A, 5-HT2 and 5-HT4 receptor agonists (±)-2-dipropyloamino-8-hydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphtalene hydrobromide (8-OH-DPAT), (±)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine hydrochloride (DOI) and zacopride, respectively, induced by a repeated treatment with imipramine or citalopram. Rats were treated with imipramine or citalopram for 14 days (10 mg/kg p.o.) twice daily. Frontal cortical slices were prepared 2 days after the last drug administration. Spontaneous epileptiform discharges were induced in slices by perfusion with a medium devoid of Mg2+ ions and with added picrotoxin (30 μM). While the application of 2 μM 8-OH-DPAT resulted in a reversible decrease of the discharge frequency, in the presence of DOI (1 μM) or zacopride (5 μM), the discharge frequency was increased. Both repeated imipramine and citalopram enhanced the effect of the activation of 5-HT1A receptor and attenuated the effect related to 5-HT2 receptor activation, while the effect of the activation of 5-HT4 receptor remained unchanged. Moreover, imipramine, but not citalopram, induced a reduction of epileptiform discharge frequency and an increase of the time of occurrence of epileptiform activity. These data indicate that antidepressants enhance the 5-HT-mediated inhibition in neuronal circuitry of the frontal cortex.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK, Marek GJ (1997) Serotonin induces excitatory postsynaptic potentials in apical dendrites of neocortical pyramidal cells. Neuropharmacology 36:589–599
Akiyoshi J, Tsuchiyama K, Yamada K, Mizobe Y, Nakamura M, Nagayama H (1992) Effect of IAP and chronic antidepressant administration on the 5-HT1A receptor in rat cortical membranes. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 16:339–349
Albowitz B, Kuhnt U (1995) Epileptiform activity in the guinea-pig neocortical slice spreads preferentially along supragranular layers—recordings with voltage-sensitive dyes. Eur J Neurosci 7:1273–1284
Andrade R, Chaput Y (1991) 5-Hydroxytryptamine4-like receptors mediate the slow excitatory response to serotonin in the rat hippocampus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257:930–937
Andrade R, Malenka RC, Nicoll RA (1986) A G protein couples serotonin and GABAB receptors to the same channels in hippocampus. Science 234:1261–1265
Ansanay H, Dumuis A, Sebben M, Bockaert J, Fagni L (1995) cAMP-dependent, long-lasting inhibition of a K+ current in mammalian neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6635–6639
Araneda R, Andrade R (1991) 5-hydroxytryptamine2 and 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptors mediate opposing responses on membrane excitability in rat association cortex. Neuroscience 40:399–412
Aram JA, Lodge D (1988) Validation of a neocortical slice preparation for the study of epileptiform activity. J Neurosci Methods 23:211–224
Attar-Levy D, Martinot JL, Blin J, Dao-Castellana MH, Crouzel C, Mazoyer B, Poirier MF, Bourdel MC, Aymard N, Syrota A, Feline A (1999) The cortical serotonin2 receptors studied with positron-emission tomography and [18F]-setoperone during depressive illness and antidepressant treatment with clomipramine. Biol Psychiatry 45:180–186
Barnes NM, Sharp T (1999) A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 38:1083–1152
Beck SG, Birnstiel S, Choi CK, Pouliot WA (1997) Fluoxetine selectively alters 5-hydroxytryptamine1A and gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptor-mediated hyperpolarization in area CA1, but not area CA3, hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 281:115–122
Bijak M, Tokarski K (1994) Prolonged administration of imipramine and (+)-oxaprotiline, but not citalopram, results in sensitizaton of the rat hippocampal CA1 neurons to serotonin ex vivo. Pol J Pharmacol 46:163–167
Bijak M, Tokarski K, Czyrak A, Mackowiak M, Wedzony K (1996) Imipramine increases the 5-HT1A receptor-mediated inhibition of hippocampal neurons without changing the 5-HT1A receptor binding. Eur J Pharmacol 305:79–85
Bijak M, Tokarski K, Maj J (1997) Repeated treatment with antidepressant drugs induces subsensitivity to the excitatory effect of 5-HT4 receptor activation in the rat hippocampus. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 355:14–19
Bobula B, Tokarski K, Hess G (2001a) Repeated imipramine administration enhances the effects of NMDA receptor ligands on synchronous acticity in rat frontal cortex. Pol J Pharmacol 53:635–639
Bobula B, Zahorodna A, Bijak M (2001b) Different receptor subtypes are involved in the serotonin-induced modulation of epileptiform activity in rat frontal cortex in vitro. J Physiol Pharmacol 52:265–274
Burnet PW, Michelson D, Smith MA, Gold PW, Sternberg EM (1994) The effect of chronic imipramine administration on the densities of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors and the abundances of 5-HT receptor and transporter mRNA in the cortex, hippocampus and dorsal raphe of three strains of rat. Brain Res 638:311–324
Butler MO, Morinobu S, Duman RS (1993) Chronic electroconvulsive seizures increase the expression of serotonin2 receptor mRNA in rat frontal cortex. J Neurochem 61:1270–1276
Chaput Y, de Montigny C, Blier P (1986) Effects of a selective 5-HT reuptake blocker, citalopram, on the sensitivity of 5-HT autoreceptors: electrophysiological studies in the rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 333:342–348
Chaput Y, de Montigny C, Blier P (1991) Presynaptic and postsynaptic modifications of the serotonin system by long-term administration of antidepressant treatments. An in vivo electrophysiologic study in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 5:219–229
Connors BW (1984) Initiation of synchronized neuronal bursting in neocortex. Nature 310:685–687
De Montigny C, Aghajanian GK (1978) Tricyclic antidepressants: long-term treatment increases responsivity of rat forebrain neurons to serotonin. Science 202:1303–1306
De Vry J (1995) 5-HT1A receptor agonists: recent developments and controversial issues. Psychopharmacology 121:1–26
Drevets WC (2001) Neuroimaging and neuropathological studies of depression: implications for the cognitive-emotional features of mood disorders. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:240–249
Eglen RM, Wong EHF, Dumuis A, Bockaert J (1995) Central 5-HT4 receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 16:391–398
Feng J, Cai X, Zhao J, Yan Z (2001) Serotonin receptors modulate GABAA receptor channels through activation of anchored protein kinase C in prefrontal cortical neurons. J Neurosci 21:6502–6511
Flint AC, Connors BW (1996) Two types of network oscillations in neocortex mediated by distinct glutamate receptor subtypes and neuronal populations. J Neurophysiol 75:951–957
Fulton B, Brogden RN (1997) Buspirone: an updated review of its clinical pharmacology and therapeutic applications. CNS Drugs 7:68–88
Gill CH, Soffin EM, Hagan JJ, Davies CH (2002) 5-HT7 receptors modulate synchronized network activity in rat hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 42:82–92
Haddjeri N, Blier P, de Montigny C (1998) Long-term antidepressant treatments result in a tonic activation of forebrain 5-HT1A receptors. J Neurosci 18:10150–10156
Jakab RL, Goldman-Rakic PS (1998) 5-Hydroxytryptamine2A serotonin receptors in the primate cerebral cortex: possible site of action of hallucinogenic and antipsychotic drugs in pyramidal cell apical dendrites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:735–740
Kia HK, Miquel MC, Brisorgueil MJ, Daval G, Riad M, El Mestikawy S, Hamon M, Verge D (1996) Immunocytochemical localization of serotonin1A receptors in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 365:289–305
Klimek V, Zak-Knapik J, Mackowiak M (1994) Effects of repeated treatment with fluoxetine and citalopram, 5-HT uptake inhibitors, on 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors in the rat brain. J Psychiatry Neurosci 19:63–67
Lopez JF, Chalmers DT, Little KY, Watson SJ (1998) Regulation of serotonin1A, glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptor in rat and human hippocampus: implications for neurobiology and depression. Biol Psychiatry 43:547–573
Maes M, Meltzer HY (1995) The serotonin hypothesis of major depression. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ (eds) Psychopharmacology: the fourth generation in progress. Raven, New York, pp 933–944
Maj J, Bijak M, Dziedzicka-Wasylewska M, Rogoz R, Rogoz Z, Skuza G, Tokarski K (1996) The effects of paroxetine given repeatedly on the 5-HT receptor subpopulations in the rat brain. Psychopharmacology 127:73–82
Manji HK, Drevets WC, Charney DS (2001) The cellular neurobiology of depression. Nat Med 7:541–547
McCormick DA, Wang Z, Huguenard J (1993) Neurotransmitter control of neocortical activity and excitability. Cereb Cortex 3:387–398
Meltzer HY (1999) The role of serotonin in antipsychotic drug action. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:S106–S115
Mizuta T, Segawa T (1989) Chronic effects of imipramine and lithium on 5-HT receptor subtypes in rat frontal cortex, hippocampus and choroid plexus: quantitative receptor autoradiographic studies. Jpn J Pharmacol 50:315–326
Newman ME, Shapira B, Lerer B (1992) Regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor function in rat hippocampus by short and long-term administration of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A agonist and antidepressants. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 260:16–20
Newman-Tancredi A, Chaput C, Verriele L, Millan MJ (1996) S 15535 and WAY 100,635 antagonise 5-HT-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS binding at cloned human 5-HT1A receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 307:107–111
Sanders-Bush E, Conn PJ (1986) Effector systems coupled to serotonin receptors in brain: serotonin stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis. Psychopharmacol Bull 22:829–836
Sargent PA, Kjaer KH, Bench CJ, Rabiner EA, Messa C, Meyer J, Gunn RN, Grasby PM, Cowen PJ (2000) Brain serotonin1A receptor binding measured by positron emission tomography with [11C]WAY-100635: effects of depression and antidepressant treatment. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:174–180
Schreiber R, De Vry J (1993) 5-HT1A receptor ligands in animal models of anxiety, impulsivity and depression: multiple mechanism of action? Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 17:87–107
Shen C, Li H, Meller E (2002) Repeated treatment with antidepressants differentially alters 5-HT1A agonist-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding in rat brain neurons. Neuropharmacology 42:1031–1038
Silva LR, Amitai Y, Connors BW (1991) Intrinsic oscillations of neocortex generated by layer 5 pyramidal neurons. Science 252:432–435
Skolnick P (1999) Antidepressants for the new millennium. Eur J Pharmacol 375:31–40
Spurlock G, Buckland P, O'Donovan M, McGuffin P (1994) Lack of the effect of antidepressant drugs on the levels of mRNAs encoding serotonergic receptors, synthetic enzymes and 5-HT transporter. Neuropharmacology 33:433–440
Srinivas BN, Subhash MN, Vinod KY (2001) Cortical 5-HT(1A) receptor downregulation by antidepressants in rat brain. Neurochem Int 38:573–579
Subhash MN, Jagadeesh S (1997) Imipramine-induced changes in 5-HT2 receptor sites and inositoltrisphosphate levels in rat brain. Neurochem Res 22:1095–1099
Tsau Y, Guan L, Wu J-Y (1998) Initiation of spontaneous epileptiform activity in the neocortical slice. J Neurophysiol 80:978–982
Tsau Y, Guan L, Wu J-Y (1999) Epileptiform activity can be initiated in various neocortical layers: an optical imaging study. J Neurophysiol 82:1965–1973
Vetulani J, Nalepa I (2000) Antidepressants: past, present and future. Eur J Pharmacol 405:351–363
Wadman WJ, Gutnick MJ (1993) Non-uniform propagation of epileptiform discharge in brain slices of rat neocortex. Neuroscience 52:255–262
Walther H, Lambert JD, Jones RS, Heinemann U, Hamon B (1986) Epileptiform activity in combined slices of the hippocampus, subiculum and entorhinal cortex during perfusion with low magnesium medium. Neurosci Lett 69:156–161
Watanabe Y, Saito H, Abe K (1993a) Tricyclic antidepressants block NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic responses and induction of long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal slices. Neuropharmacology 32:479–486
Watanabe Y, Sakai RR, McEwen BS, Mendelson S (1993b) Stress and antidepressant effects on hippocampal and cortical 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors and transport sites for serotonin. Brain Res 625:87–94
Waterhouse BD, Mouradian R, Sessler FM, Lin RC (2000) Differential modulatory effects of norepinephrine on synaptically driven responses of layer V barrel field cortical neurons. Brain Res 868:39–47
Willins DL, Deutch AY, Roth BL (1997) Serotonin 5-HT2A receptors are expressed on pyramidal cells and interneurons in the rat cortex. Synapse 27:79–82
Yatham LN, Liddle PF, Shiah IS, Scarrow G, Lam RW, Adam MJ, Zis AP, Ruth TJ (2000) Brain serotonin2 receptors in major depression: a positron emission tomography study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:850–858
Zahorodna A, Tokarski K, Bijak M (2002) Imipramine but not 5-HT1A receptor agonists or neuroleptics induces adaptive changes in hippocampal 5-HT1A and 5-HT4 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 443:51–57
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the State Committee for Scientific Research (Warsaw) grant 6 P05A 074 20. The experiments were carried out in accordance with the Polish Animal Protection Law (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bobula, B., Tokarski, K., Zahorodna, A. et al. Adaptive changes in the reactivity of 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 receptors induced in rat frontal cortex by repeated imipramine and citalopram. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 367, 444–450 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-003-0744-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-003-0744-1