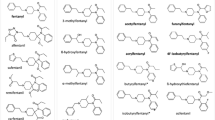
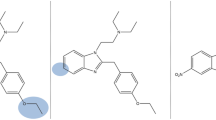
Abstract
N-Piperidinyl etonitazene (‘etonitazepipne’) represents a recent addition to the rapidly expanding class of 2-benzylbenzimidazole ‘nitazene’ opioids. Following its first identification in an online-sourced powder and in biological samples from a patient seeking help for detoxification, this report details its in-depth chemical analysis and pharmacological characterization. Analysis of the powder via different techniques (LC-HRMS, GC–MS, UHPLC-DAD, FT-IR) led to the unequivocal identification of N-piperidinyl etonitazene. Furthermore, we report the first activity-based detection and analytical identification of N-piperidinyl etonitazene in authentic samples. LC-HRMS analysis revealed concentrations of 1.21 ng/mL in serum and 0.51 ng/mL in urine, whereas molecular networking enabled the tentative identification of various (potentially active) urinary metabolites. In addition, we determined that the extent of opioid activity present in the patient’s serum was equivalent to the in vitro opioid activity exerted by 2.5–10 ng/mL fentanyl or 10–25 ng/mL hydromorphone in serum. Radioligand binding assays in rat brain tissue revealed that the drug binds with high affinity (Ki = 14.3 nM) to the µ-opioid receptor (MOR). Using a MOR-β-arrestin2 activation assay, we found that N-piperidinyl etonitazene is highly potent (EC50 = 2.49 nM) and efficacious (Emax = 183% versus hydromorphone) in vitro. Pharmacodynamic evaluation in male Sprague Dawley rats showed that N-piperidinyl etonitazene induces opioid-like antinociceptive, cataleptic, and thermic effects, its potency in the hot plate assay (ED50 = 0.0205 mg/kg) being comparable to that of fentanyl (ED50 = 0.0209 mg/kg), and > 190 times higher than that of morphine (ED50 = 3.940 mg/kg). Taken together, our findings indicate that N-piperidinyl etonitazene is a potent opioid with the potential to cause harm in users.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler MW, Geller EB, Rosow CE, Cochin J (1988) The opioid system and temperature regulation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 28:429–449. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pa.28.040188.002241
Baumann MH, Kopajtic TA, Madras BK (2018) Pharmacological research as a key component in mitigating the opioid overdose crisis. Trends Pharmacol Sci 39:995–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2018.09.006
Bergh MS-S, Bogen IL, Garibay N, Baumann MH (2021) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of cyclopropylfentanyl in male rats. Psychopharmacology 238:3629–3641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05981-x
Brandenberger H (1974) Die Rolle des Massenspektrometers im toxikologisch-chemischen Laboratorium. Dtsch Lebensm Rundsch 70(1):31–39
Bromig G (1958) Über neue starkwirkende Analgetika und ihre klinische Erprobung. Klin Wochenschr 36:960–963. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01486702
Cannaert A, Vasudevan L, Friscia M et al (2018) Activity-based concept to screen biological matrices for opiates and (synthetic) opioids. Clin Chem 64:1221–1229. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2018.289496
Cannaert A, Deventer M, Fogarty M et al (2019) Hide and seek: overcoming the masking effect of opioid antagonists in activity-based screening tests. Clin Chem 65:1604–1605. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2019.309443
Cannaert A, del Ramírez MFM, Theunissen EL et al (2020) Semiquantitative activity-based detection of JWH-018, a synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonist, in oral fluid after vaping. Anal Chem 92:6065–6071. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c00484
Ciccarone D (2019) The triple wave epidemic: Supply and demand drivers of the US opioid overdose crisis. Int J Drug Policy 71:183–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2019.01.010
EMCDDA (2020) Report on the risk assessment of N, N-diethyl-2-[[4-(1-methylethoxy)phenyl]methyl]-5-nitro-1Hbenzimidazole-1-ethanamine (isotonitazene) in accordance with Article 5c of Regulation (EC) No 1920/2006 (as amended). Publications Office, Luxembourg
EMCDDA (2021) European drug report 2021: trends and developments. Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg
Geller EB, Hawk C, Keinath SH et al (1983) Subclasses of opioids based on body temperature change in rats: acute subcutaneous administration. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 225:391–398
Grigoryev A, Kavanagh P, Dowling G, Rodin I (2022) Tentative identification of Etazene (etodesnitazene) metabolites in rat serum and urine by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and accurate mass liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkac001
Gross F, Turrian H (1957) Über Benzimidazolderivate mit starker analgetischer Wirkung. Experientia 13:401–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02161117
Hunger A, Kebrle J, Rossi A, Hoffmann K (1957) Synthese basisch substituierter, analgetisch wirksamer Benzimidazol-Derivate. Experientia 13:400–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02161116
Hunger A, Kebrle J, Rossi A, Hoffmann K (1960a) Benzimidazol-derivate und verwandte heterocyclen II. Synthese von 1-aminoalkyl-2-benzyl-benzimidazolen. Helv Chim Acta 43:800–809. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.19600430323
Hunger A, Kebrle J, Rossi A, Hoffmann K (1960b) Benzimidazol-derivate und verwandte Heterocyclen III. Synthese von 1-aminoalkyl-2-benzyl-nitro-benzimidazolen. Helv Chim Acta 43:1032–1046. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.19600430412
Hunger A, Kebrle J, Rossi A, Hoffmann K (1960c) Benzimidazol-derivate und verwandte heterocyclen VI. Synthese von Phenyl-[1-aminoalkyl-benzimidazolyl-(2)]-essigsäure-estern und -amiden. Helv Chim Acta 43:1727–1733. https://doi.org/10.1002/hlca.19600430634
Krotulski AJ, Papsun DM, Kacinko SL, Logan BK (2020) Isotonitazene quantitation and metabolite discovery in authentic forensic casework. J Anal Toxicol 44:521–530. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkaa016
Krotulski AJ, Manini A, Calello D et al (2021a) N-piperidinyl etonitazene. https://www.npsdiscovery.org/wp-content/uploads/2021a/11/N-Piperidinyl-Etonitazene_112221_ToxicologyAnalyticalReport.pdf?mc_cid=09d08f4c2f&mc_eid=UNIQID. Accessed 22 Nov 2021
Krotulski AJ, Papsun DM, Walton SE, Logan BK (2021b) Metonitazene in the United States—forensic toxicology assessment of a potent new synthetic opioid using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. Drug Test Anal. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.3115
Mardal M, Andreasen MF, Mollerup CB et al (2019) HighResNPS.com: an online crowd-sourced HR-MS database for suspect and non-targeted screening of new psychoactive substances. J Anal Toxicol 43:520–527. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkz030
Morris H (2009) Synthetic opioids: the most addictive drugs in the world. In: Vice. https://www.vice.com/en/article/9bdymy/hamiltons-pharmacopeia-804-v16n4. Accessed 26 Oct 2020
Nothias L-F, Petras D, Schmid R et al (2020) Feature-based molecular networking in the GNPS analysis environment. Nat Methods 17:905–908. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-020-0933-6
Ortiz de Montellano PR, Nelson SD (2011) Rearrangement reactions catalyzed by cytochrome P450s. Arch Biochem Biophys 507:95–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2010.10.016
Pluskal T, Castillo S, Villar-Briones A, Orešič M (2010) MZmine 2: modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform 11:395. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-395
Pottie E, Tosh DK, Gao Z-G et al (2020) Assessment of biased agonism at the A3 adenosine receptor using β-arrestin and miniGαi recruitment assays. Biochem Pharmacol 177:113934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113934
Pöyhiä R, Kalso EA (1992) Antinociceptive effects and central nervous system depression caused by oxycodone and morphine in rats. Pharmacol Toxicol 70:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0773.1992.tb00441.x
Rawls SM, Benamar K (2011) Effects of opioids cannabinoids and vanilloids on body temperature. Front Biosci S3:822–845. https://doi.org/10.2741/s190
Reavy P (2003) Utah case of potent drug is US first. In: Deseret News. https://www.deseret.com/2003/6/3/19726293/utah-case-of-potent-drug-is-u-s-first. Accessed 26 Oct 2020
Sharma KK, Hales TG, Rao VJ et al (2019) The search for the “next” euphoric non-fentanil novel synthetic opioids on the illicit drugs market: current status and horizon scanning. Forensic Toxicol 37:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-018-0454-5
Sorokin VI (1999) Illegal synthesis of etonitazene. J Clandest Lab Investig Chem Assoc 9:20
Sorokin VI, Ponkratov KV, Drozdov MA (1999) Etonitazene encountered in Moscow. Microgram 32:239–244
Taracha E, Mierzejewski P, Lehner M et al (2009) Stress-opioid interactions: a comparison of morphine and methadone. Pharmacol Rep 61:424–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1734-1140(09)70083-0
Truver MT, Smith CR, Garibay N et al (2020) Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the novel synthetic opioid, U-47700, in male rats. Neuropharmacology 177:108195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108195
Ujváry I, Christie R, Evans-Brown M et al (2021) DARK classics in chemical neuroscience: etonitazene and related benzimidazoles. ACS Chem Neurosci 12:1072–1092. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00037
UNODC (2020) The growing complexity of the opioid crisis. Global SMART Update, Volume 24. Vienna
UNODC (2021) CND Decision on international control of isotonitazene enters into force. In: https://www.unodc.org/LSS/announcement/Details/65247392-26c7-4446-a2b6-270226103036. Accessed 10 Jun 2021
Vandeputte MM, Krotulski AJ, Papsun DM et al (2021a) The rise and fall of isotonitazene and brorphine: two recent stars in the synthetic opioid firmament. J Anal Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkab082
Vandeputte MM, Krotulski AJ, Walther D et al (2022) Pharmacological evaluation and forensic case series of N-pyrrolidino etonitazene (etonitazepyne), a newly emerging 2-benzylbenzimidazole ‘nitazene’ synthetic opioid. Arch Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03276-4(in press)
Vandeputte MM, Van Uytfanghe K, Layle NK et al (2021b) Synthesis, chemical characterization, and μ-opioid receptor activity assessment of the emerging group of “nitazene” 2-benzylbenzimidazole synthetic opioids. ACS Chem Neurosci 12:1241–1251. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00064
Vasudevan L, Vandeputte MM, Deventer M et al (2020) Assessment of structure–activity relationships and biased agonism at the Mu opioid receptor of novel synthetic opioids using a novel, stable bio-assay platform. Biochem Pharmacol 177:113910. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113910
Verougstraete N, Vandeputte MM, Lyphout C et al (2020) First report on brorphine: the next opioid on the deadly new psychoactive substances’ horizon? J Anal Toxicol 44:937–946. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkaa094
Volpe DA, McMahon Tobin GA, Mellon RD et al (2011) Uniform assessment and ranking of opioid μ receptor binding constants for selected opioid drugs. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 59:385–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2010.12.007
Walton SE, Krotulski AJ, Logan BK (2021) A forward-thinking approach to addressing the new synthetic opioid 2-benzylbenzimidazole nitazene analogs by liquid chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry (LC–QQQ-MS). J Anal Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkab117
Wang M, Carver JJ, Phelan VV et al (2016) Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with global natural products social molecular networking. Nat Biotechnol 34:828–837. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3597
Williams JT, Ingram SL, Henderson G et al (2013) Regulation of µ-opioid receptors: desensitization, phosphorylation, internalization, and tolerance. Pharmacol Rev 65:223–254. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.112.005942
Wong B, Perkins MW, Tressler J et al (2017) Effects of inhaled aerosolized carfentanil on real-time physiological responses in mice: a preliminary evaluation of naloxone. Inhal Toxicol 29:65–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/08958378.2017.1282065
Acknowledgements
The patient is gratefully acknowledged for the cooperation. We kindly thank Dr. Donna Iula (Cayman Chemical) for gifting of the N-piperidinyl etonitazene reference standard.
Funding
This work was supported by the Research Foundation-Flanders (FWO) [1S81522N to M.V., 1703320 N to N.V, and G069419N to C.S.] and the Ghent University Special Research Fund (BOF) [01J15517 to C.S.]. Dr. Baumann’s research is generously supported by the Intramural Research Program (IRP) of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), National Institutes of Health, US.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vandeputte, M.M., Verougstraete, N., Walther, D. et al. First identification, chemical analysis and pharmacological characterization of N-piperidinyl etonitazene (etonitazepipne), a recent addition to the 2-benzylbenzimidazole opioid subclass. Arch Toxicol 96, 1865–1880 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03294-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03294-2