Abstract
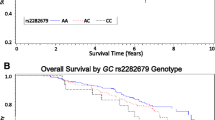
Vitamin E is effective for preventing the risk of cancer. However, few studies have elucidated the mechanism of vitamin E in cancer occurrence. Herein, we aimed to identify the genetic variants in vitamin E-related pathway genes associated with colorectal cancer risk. We applied logistic regression models to assess the association between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in vitamin E-related pathway genes and colorectal cancer risk in the Chinese and European population. The false discovery rate (FDR) method was used to correct multiple comparisons. The mRNA and protein expression analysis were evaluated in public database and in-house RNA-Seq data. SCARB1 rs73227586 was identified significantly increased risk of colorectal cancer in the Chinese population (odd ratio (OR) = 1.46, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.22–1.75, P = 2.99 × 10–5). This finding was further validated in the European population (OR = 1.11, 95% CI = 1.02–1.20, P = 1.44 × 10–2). Additionally, the mRNA and protein expression of SCARB1 were markedly up-regulated in colorectal tumor tissues. Moreover, rs73227586 T allele could increase the minimum free energy (MFE) and weaken binding ability to transcription factor ELL2. Our findings indicated that SCARB1 may play a carcinogenic role in colorectal cancer. Genetic variants in vitamin E-related pathway genes may concern to be predictors of colorectal cancer risk.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- MAF:
-
Minor allele frequency
- HWE:
-
Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium
- LD:
-
Linkage disequilibrium
- FDR:
-
False discovery rate
- eQTL:
-
Expression quantitative trait loci
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association study
References
Abraham A, Kattoor A, Saldeen T et al (2019) Vitamin E and its anticancer effects. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59:2831–2838. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1474169
Celhay O, Bousset L, Guy L et al (2019) Individual comparison of cholesterol metabolism in normal and tumour areas in radical prostatectomy specimens from patients with prostate cancer: results of the CHOMECAP Study. Eur Urol Oncol 2:198–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euo.2018.08.001
Chan J, Darke A, Penney K et al (2016) Selenium- or vitamin E-related gene variants, interaction with supplementation, and risk of high-grade prostate cancer in SELECT cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention : a publication of the American Association for Cancer Research, cosponsored by the American Society of Preventive. Oncology 25:1050–1058. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.Epi-16-0104
Chen X, Mangala LS, Mooberry L et al (2019) Identifying and targeting angiogenesis-related microRNAs in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 38:6095–6108. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0862-y
Cui L, Li L, Tian Y et al (2018) Association between dietary vitamin E intake and esophageal cancer risk: an updated meta-analysis. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10070801
Danilo C, Gutierrez-Pajares JL, Mainieri MA et al (2013) Scavenger receptor class B type I regulates cellular cholesterol metabolism and cell signaling associated with breast cancer development. Breast Cancer Res 15:R87. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3483
Deng N, Zhou H, Fan H et al (2017) Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Cancer Susceptibility. Oncotarget 8:110635–110649. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.22372
Galmés S, Serra F, Palou A (2018) Vitamin E metabolic effects and genetic variants: a challenge for precision nutrition in obesity and associated disturbances. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121919
Gordon JA, Noble JW, Midha A et al (2019) Upregulation of scavenger receptor B1 is required for steroidogenic and nonsteroidogenic cholesterol metabolism in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 79:3320–3331. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-2529
Gu D, Li S, Ben S et al (2018) Circadian clock pathway genes associated with colorectal cancer risk and prognosis. Arch Toxicol 92:2681–2689. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-018-2251-7
Hamada T, Nowak J, Masugi Y et al (2019) Smoking and risk of colorectal cancer sub-classified by tumor-infiltrating T cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 111:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djy137
He F, Wei R, Zhou Z et al (2019) Integrative analysis of somatic mutations in non-coding regions altering RNA secondary structures in cancer genomes. Sci Rep 9:8205. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44489-5
Hong Y, Rao Y (2019) Current status of nanoscale drug delivery systems for colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Biomed Pharma 114:108764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108764
Jiang Q (2019) Natural forms of vitamin E and metabolites-regulation of cancer cell death and underlying mechanisms. IUBMB Life 71:495–506. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1978
Jun SY, Brown AJ, Chua NK et al (2020) Reduction of squalene epoxidase by cholesterol accumulation accelerates colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2020.09.009
Kato T, Lee D, Huang H et al (2018) Personalized siRNA-nanoparticle systemic therapy using metastatic lymph node specimens obtained with EBUS-TBNA in lung cancer. Mol Cancer Res 16:47–57. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.Mcr-16-0341
Li J, Yuan Y, Yang F et al (2019) Expert consensus on multidisciplinary therapy of colorectal cancer with lung metastases. J Hematol Oncol 12:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0702-0 (2019 edition)
Major J, Yu K, Wheeler W et al (2011) Genome-wide association study identifies common variants associated with circulating vitamin E levels. Hum Mol Genet 20:3876–3883. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddr296
MontagnaniMarelli M, Marzagalli M, Fontana F et al (2019) Anticancer properties of tocotrienols: a review of cellular mechanisms and molecular targets. J Cell Physiol 234:1147–1164. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27075
Murphy A, Woollard K, Hoang A et al (2008) High-density lipoprotein reduces the human monocyte inflammatory response. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biol 28:2071–2077. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.108.168690
Nacev BA, Jones KB, Intlekofer AM et al (2020) The epigenomics of sarcoma. Nat Rev Cancer 20:608–623. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-020-0288-4
Njoroge R, Unno K, Zhao J et al (2017) Organoids model distinct vitamin E effects at different stages of prostate cancer evolution. Sci Rep 7:16285. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16459-2
Peh H, Tan W, Liao W et al (2016) Vitamin E therapy beyond cancer: tocopherol versus tocotrienol. Pharmacol Ther 162:152–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.12.003
Pośpiech E, Ligęza J, Wilk W et al (2015) Variants of SCARB1 and VDR involved in complex genetic interactions may be implicated in the genetic susceptibility to clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BioMed Res Int 2015:860405. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/860405
Qi S, Li Z, Schulze-Gahmen U et al (2017) Structural basis for ELL2 and AFF4 activation of HIV-1 proviral transcription. Nat Commun 8:14076. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14076
Rimbach G, Minihane A, Majewicz J et al (2002) Regulation of cell signalling by vitamin E. Proc Nutr Soc 61:415–425. https://doi.org/10.1079/pns2002183
Sharma B, Gupta V, Dahiya D et al (2019) Clinical Relevance of Cholesterol Homeostasis Genes in Colorectal Cancer. BBA Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1864:1314–1327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2019.06.008
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE et al (2021) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 71:7–33. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21654
Sigurdson AJ, Brenner AV, Roach JA et al (2016) Selected single-nucleotide polymorphisms in FOXE1, SERPINA5, FTO, EVPL, TICAM1 and SCARB1 are associated with papillary and follicular thyroid cancer risk: replication study in a German population. Carcinogenesis 37:677–684. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgw047
Spielmann M, Lupiáñez DG, Mundlos S (2018) Structural variation in the 3D genome. Nat Rev Genet 19:453–467. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-018-0007-0
Takahashi Y, Sugimachi K, Yamamoto K et al (2017) Japanese genome-wide association study identifies a significant colorectal cancer susceptibility locus at chromosome 10p14. Cancer Sci 108:2239–2247. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13391
Tanskanen T, van den Berg L, Välimäki N et al (2018) Genome-wide association study and meta-analysis in Northern European populations replicate multiple colorectal cancer risk loci. Int J Cancer 142:540–546. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31076
Tian J, Chang J, Gong J et al (2019) Systematic functional interrogation of genes in GWAS loci identified ATF1 as a key driver in colorectal cancer modulated by a promoter-enhancer interaction. Am J Hum Genet 105:29–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.05.004
Torre L, Bray F, Siegel R et al (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA: Cancer J Clin 65:87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262
Umemoto T, Han C, Mitra P et al (2013) Apolipoprotein AI and high-density lipoprotein have anti-inflammatory effects on adipocytes via cholesterol transporters: ATP-binding cassette A-1, ATP-binding cassette G-1, and scavenger receptor B-1. Circ Res 112:1345–1354. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.111.300581
Wang M, Gu D, Du M et al (2016) Common genetic variation in ETV6 is associated with colorectal cancer susceptibility. Nat Communi 7:11478. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11478
Wu J, Xue Y, Gao X et al (2020) Host cell factors stimulate HIV-1 transcription by antagonizing substrate-binding function of Siah1 ubiquitin ligase to stabilize transcription elongation factor ELL2. Nucleic Acid Res 48:7321–7332. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa461
Xin J, Du M, Gu D et al (2019) Combinations of single nucleotide polymorphisms identified in genome-wide association studies determine risk for colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 145:2661–2669. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.32267
Yang C, Luo P, Zeng Z et al (2020) Vitamin E and cancer prevention: Studies with different forms of tocopherols and tocotrienols. Mol Carcinog 59:365–389. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.23160
Zhu Y, Bo Y, Liu X et al (2017) Association of dietary vitamin E intake with risk of lung cancer: a dose-response meta-analysis. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 26:271–277. https://doi.org/10.6133/apjcn.032016.04
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81822039 and 81872697), the Qinlan Project of Jiangsu (M.W.), Six Talent Peaks Project of Jiangsu Province (YY‐020) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (Public Health and Preventive Medicine).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Meilin Wang conceived and designed the experiments. Mulong Du, Shuwei Li and Junyi Xin contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. Qiuyi Zhang and Yixuan Meng wrote the paper. Zhengdong Zhang, Dongying Gu and Shuai Ben revised the paper. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors indicate no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Meng, Y., Du, M. et al. Evaluation of common genetic variants in vitamin E-related pathway genes and colorectal cancer susceptibility. Arch Toxicol 95, 2523–2532 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-03078-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-021-03078-0