Abstract
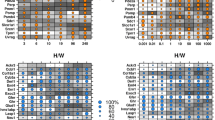
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) mediates many toxic effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). However, the AHR alone does not explain the widely different outcomes among organisms. To identify the other factors involved, we evaluated three transgenic mouse lines, each expressing a different rat AHR isoform (rWT, DEL, and INS) providing widely different resistance to TCDD toxicity, as well as C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice which exhibit a ~ tenfold divergence in TCDD sensitivity (exposures of 5-1000 μg/kg TCDD). We supplement these with whole-genome sequencing, together with transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of the corresponding rat models, Long–Evans (L–E) and Han/Wistar (H/W) rats (having a ~ 1000-fold difference in their TCDD sensitivities; 100 μg/kg TCDD), to identify genes associated with TCDD-response phenotypes. Overall, we identified up to 50% of genes with altered mRNA abundance following TCDD exposure are associated with a single AHR isoform (33.8%, 11.7%, 5.2% and 0.3% of 3076 genes altered unique to rWT, DEL, C57BL/6 and INS respectively following 1000 μg/kg TCDD). Hepatic Pxdc1 was significantly repressed in all three TCDD-sensitive animal models (C57BL/6 and rWT mice, and L–E rat) after TCDD exposure. Three genes, including Cxxc5, Sugp1 and Hgfac, demonstrated different AHRE-1 (full) motif occurrences within their promoter regions between rat strains, as well as different patterns of mRNA abundance. Several hepatic proteins showed parallel up- or downward alterations with their RNAs, with three genes (SNRK, IGTP and IMPA2) showing consistent, strain-dependent changes. These data show the value of integrating genomic, transcriptomic and proteomic evidence across multi-species models in toxicologic studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets supporting the results of this article are publicly available. All transcriptomic datasets are available from NCBI’s Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO; http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/): C57BL/6 mouse data are available at accession GSE61038 (Lee et al. 2015); other mouse data are available from GSE127217 (EXP1) and GSE72270 (EXP2); rat transcriptomic data are available from accessions GSE31411 (Yao et al. 2012) and GSE13513 (Boutros et al. 2011). Combined transcriptomic data are additionally available from the TCDD. Transcriptomics (v2.2.5) package for the R statistical environment (Prokopec et al. 2017). The sequence data generated in this study have been submitted to the NCBI BioProject database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/) under accession number PRJNA480994. Raw and processed LC–MS data are available from MassIVE under accession MSV000083870.
References
Aras S, Pak O, Sommer N, Finley R Jr, Huttemann M, Weissmann N, Grossman LI (2013) Oxygen-dependent expression of cytochrome c oxidase subunit 4-2 gene expression is mediated by transcription factors RBPJ, CXXC5 and CHCHD2. Nucleic Acids Res 41:2255–2266
Assie G, Libe R, Espiard S, Rizk-Rabin M, Guimier A, Luscap W, Barreau O, Lefevre L, Sibony M, Guignat L et al (2013) ARMC5 mutations in macronodular adrenal hyperplasia with Cushing’s syndrome. N Engl J Med 369:2105–2114
Atanur SS, Diaz AG, Maratou K, Sarkis A, Rotival M, Game L, Tschannen MR, Kaisaki PJ, Otto GW, Ma MC et al (2013) Genome sequencing reveals loci under artificial selection that underlie disease phenotypes in the laboratory rat. Cell 154:691–703
Boutros PC, Yan R, Moffat ID, Pohjanvirta R, Okey AB (2008) Transcriptomic responses to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in liver: comparison of rat and mouse. BMC Genom 9:419
Boutros PC, Bielefeld KA, Pohjanvirta R, Harper PA (2009) Dioxin-dependent and dioxin-independent gene batteries: comparison of liver and kidney in AHR-null mice. Toxicol Sci 112:245–256
Boutros PC, Yao CQ, Watson JD, Wu AH, Moffat ID, Prokopec SD, Smith AB, Okey AB, Pohjanvirta R (2011) Hepatic transcriptomic responses to TCDD in dioxin-sensitive and dioxin-resistant rats during the onset of toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 251:119–129
Boverhof DR, Burgoon LD, Tashiro C, Sharratt B, Chittim B, Harkema JR, Mendrick DL, Zacharewski TR (2006) Comparative toxicogenomic analysis of the hepatotoxic effects of TCDD in Sprague Dawley rats and C57BL/6 mice. Toxicol Sci 94:398–416
Chang C, Smith DR, Prasad VS, Sidman CL, Nebert DW, Puga A (1993) Ten nucleotide differences, five of which cause amino acid changes, are associated with the Ah receptor locus polymorphism of C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice. Pharmacogenetics 3:312–321
Chapman DE, Schiller CM (1985) Dose-related effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in C57BL/6 J and DBA/2 J mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 78:147–157
Chen H, Boutros PC (2011) VennDiagram: a package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinform 12:35
Dai M, Wang P, Boyd AD, Kostov G, Athey B, Jones EG, Bunney WE, Myers RM, Speed TP, Akil H et al (2005) Evolving gene/transcript definitions significantly alter the interpretation of GeneChip data. Nucleic Acids Res 33:e175
Deb S, Bandiera SM (2010) Characterization of a new cytochrome P450 enzyme, CYP2S1, in rats: its regulation by aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonists. Toxicology 267:91–98
Denison MS, Fisher JM, Whitlock JP Jr (1988) The DNA recognition site for the dioxin-Ah receptor complex. Nucleotide sequence and functional analysis. J Biol Chem 263:17221–17224
Dixon WJ (1950) Analysis of extreme values. Ann Math Statist 21:488–506
Dong B, Nishimura N, Vogel CF, Tohyama C, Matsumura F (2010) TCDD-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression is mediated by the nongenomic pathway in mouse MMDD1 macula densa cells and kidneys. Biochem Pharmacol 79:487–497
Fernandez-Salguero PM, Hilbert DM, Rudikoff S, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ (1996) Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice are resistant to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 140:173–179
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA (2004) affy–analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 20:307–315
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Gentry J et al (2004) Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5:R80
Hahn ME, Karchner SI, Shapiro MA, Perera SA (1997) Molecular evolution of two vertebrate aryl hydrocarbon (dioxin) receptors (AHR1 and AHR2) and the PAS family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:13743–13748
Harrill JA, Layko D, Nyska A, Hukkanen RR, Manno RA, Grassetti A, Lawson M, Martin G, Budinsky RA, Rowlands JC et al (2016) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor knockout rats are insensitive to the pathological effects of repeated oral exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Appl Toxicol 36:802–814
Huuskonen H, Unkila M, Pohjanvirta R, Tuomisto J (1994) Developmental toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in the most TCDD-resistant and -susceptible rat strains. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 124:174–180
Irizarry RA, Bolstad BM, Collin F, Cope LM, Hobbs B, Speed TP (2003) Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe level data. Nucleic Acids Res 31:e15
Karolchik D, Baertsch R, Diekhans M, Furey TS, Hinrichs A, Lu YT, Roskin KM, Schwartz M, Sugnet CW, Thomas DJ et al (2003) The UCSC genome browser database. Nucleic Acids Res 31:51–54
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson M, Altman DG (2010) Improving bioscience research reporting: the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol 8:e1000412
Kransler KM, McGarrigle BP, Olson JR (2007) Comparative developmental toxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in the hamster, rat and guinea pig. Toxicology 229:214–225
Lee J, Prokopec SD, Watson JD, Sun RX, Pohjanvirta R, Boutros PC (2015) Male and female mice show significant differences in hepatic transcriptomic response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. BMC Genom 16:625
Linden J, Lensu S, Pohjanvirta R (2014) Effect of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) on hormones of energy balance in a TCDD-sensitive and a TCDD-resistant rat strain. Int J Mol Sci 15:13938–13966
Lusska A, Shen E, Whitlock JP Jr (1993) Protein-DNA interactions at a dioxin-responsive enhancer. Analysis of six bona fide DNA-binding sites for the liganded Ah receptor. J Biol Chem 268:6575–6580
Matsumura F (2009) The significance of the nongenomic pathway in mediating inflammatory signaling of the dioxin-activated Ah receptor to cause toxic effects. Biochem Pharmacol 77:608–626
Mimura J, Yamashita K, Nakamura K, Morita M, Takagi TN, Nakao K, Ema M, Sogawa K, Yasuda M, Katsuki M et al (1997) Loss of teratogenic response to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) in mice lacking the Ah (dioxin) receptor. Genes Cells 2:645–654
Moffat ID, Roblin S, Harper PA, Okey AB, Pohjanvirta R (2007) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor splice variants in the dioxin-resistant rat: tissue expression and transactivational activity. Mol Pharmacol 72:956–966
Moffat ID, Boutros PC, Chen H, Okey AB, Pohjanvirta R (2010) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR)-regulated transcriptomic changes in rats sensitive or resistant to major dioxin toxicities. BMC Genom 11:263
Morgan MA, Morgan JI (2012) Pcp4l1 contains an auto-inhibitory element that prevents its IQ motif from binding to calmodulin. J Neurochem 121:843–851
Nebert DW, Puga A, Vasiliou V (1993) Role of the Ah receptor and the dioxin-inducible [Ah] gene battery in toxicity, cancer, and signal transduction. Ann NY Acad Sci 685:624–640
Okey AB, Vella LM, Harper PA (1989) Detection and characterization of a low affinity form of cytosolic Ah receptor in livers of mice nonresponsive to induction of cytochrome P1-450 by 3-methylcholanthrene. Mol Pharmacol 35:823–830
P’ng C, Green J, Chong LC, Waggott D, Prokopec SD, Shamsi M, Nguyen F, Mak DYF, Lam F, Albuquerque MA et al (2017) BPG: seamless, automated and interactive visualization of scientific data. bioRxiv
Pohjanvirta R (1990) TCDD resistance is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait in the rat. Toxicol Lett 50:49–56
Pohjanvirta R (2009) Transgenic mouse lines expressing rat AH receptor variants–a new animal model for research on AH receptor function and dioxin toxicity mechanisms. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 236:166–182
Pohjanvirta R (ed) (2011) The AH receptor in biology and toxicology. Wiley, Hoboken
Pohjanvirta R, Tuomisto J (1990) Mechanism of action of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 105:508–509
Pohjanvirta R, Kulju T, Morselt AF, Tuominen R, Juvonen R, Rozman K, Mannisto P, Collan Y, Sainio EL, Tuomisto J (1989) Target tissue morphology and serum biochemistry following 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) exposure in a TCDD-susceptible and a TCDD-resistant rat strain. Fundam Appl Toxicol 12:698–712
Pohjanvirta R, Unkila M, Tuomisto J (1993) Comparative acute lethality of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), 1,2,3,7,8-pentachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and 1,2,3,4,7,8-hexachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in the most TCDD-susceptible and the most TCDD-resistant rat strain. Pharmacol Toxicol 73:52–56
Pohjanvirta R, Wong JM, Li W, Harper PA, Tuomisto J, Okey AB (1998) Point mutation in intron sequence causes altered carboxyl-terminal structure in the aryl hydrocarbon receptor of the most 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-resistant rat strain. Mol Pharmacol 54:86–93
Pohjanvirta R, Viluksela M, Tuomisto JT, Unkila M, Karasinska J, Franc MA, Holowenko M, Giannone JV, Harper PA, Tuomisto J et al (1999) Physicochemical differences in the AH receptors of the most TCDD-susceptible and the most TCDD-resistant rat strains. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 155:82–95
Pohjanvirta R, Korkalainen M, Moffat ID, Boutros PC, Okey AB (2011) Role of the AHR and its structure in TCDD toxicity. In: Pohjanvirta R (ed) The AH receptor in biology and toxicology. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 181–196
Pohjanvirta R, Miettinen H, Sankari S, Hegde N, Linden J (2012) Unexpected gender difference in sensitivity to the acute toxicity of dioxin in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 262:167–176
Prokopec SD, Watson JD, Lee J, Pohjanvirta R, Boutros PC (2015) Sex-related differences in murine hepatic transcriptional and proteomic responses to TCDD. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 284:188–196
Prokopec SD, Houlahan KE, Sun RX, Watson JD, Yao CQ, Lee J, P’ng C, Pang R, Wu AH, Chong LC et al (2017) Compendium of TCDD-mediated transcriptomic response datasets in mammalian model systems. BMC Genom 18:78
Rowlands JC, Gustafsson JA (1997) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated signal transduction. Crit Rev Toxicol 27:109–134
Rushmore TH, Morton MR, Pickett CB (1991) The antioxidant responsive element. Activation by oxidative stress and identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for functional activity. J Biol Chem 266:11632–11639
Schmidt JV, Su GH, Reddy JK, Simon MC, Bradfield CA (1996) Characterization of a murine Ahr null allele: involvement of the Ah receptor in hepatic growth and development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:6731–6736
Scifo E, Szwajda A, Soliymani R, Pezzini F, Bianchi M, Dapkunas A, Debski J, Uusi-Rauva K, Dadlez M, Gingras AC et al (2015) Proteomic analysis of the palmitoyl protein thioesterase 1 interactome in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. J Proteom 123:42–53
Shen ES, Whitlock JP Jr (1992) Protein-DNA interactions at a dioxin-responsive enhancer. Mutational analysis of the DNA-binding site for the liganded Ah receptor. J Biol Chem 267:6815–6819
Smyth GK (2004) Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.2202/1544-6115.1027
Sogawa K, Numayama-Tsuruta K, Takahashi T, Matsushita N, Miura C, Nikawa J, Gotoh O, Kikuchi Y, Fujii-Kuriyama Y (2004) A novel induction mechanism of the rat CYP1A2 gene mediated by Ah receptor-Arnt heterodimer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318:746–755
Storey JD, Tibshirani R (2003) Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9440–9445
Sun RX, Chong LC, Simmons TT, Houlahan KE, Prokopec SD, Watson JD, Moffat ID, Lensu S, Linden J, P’ng C et al (2014) Cross-species transcriptomic analysis elucidates constitutive aryl hydrocarbon receptor activity. BMC Genom 15:1053
Swanson HI, Chan WK, Bradfield CA (1995) DNA binding specificities and pairing rules of the Ah receptor, ARNT, and SIM proteins. J Biol Chem 270:26292–26302
Tijet N, Boutros PC, Moffat ID, Okey AB, Tuomisto J, Pohjanvirta R (2006) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates distinct dioxin-dependent and dioxin-independent gene batteries. Mol Pharmacol 69:140–153
Tuomisto JT, Viluksela M, Pohjanvirta R, Tuomisto J (1999) The AH receptor and a novel gene determine acute toxic responses to TCDD: segregation of the resistant alleles to different rat lines. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 155:71–81
Von Burg R (1988) Tcdd. J Appl Toxicol 8:145–148
Watson JD, Prokopec SD, Smith AB, Okey AB, Pohjanvirta R, Boutros PC (2014) TCDD dysregulation of 13 AHR-target genes in rat liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 274:445–454
Wisniewski JR, Zougman A, Nagaraj N, Mann M (2009) Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat Methods 6:359–362
Yao CQ, Prokopec SD, Watson JD, Pang R, P’ng C, Chong LC, Harding NJ, Pohjanvirta R, Okey AB, Boutros PC (2012) Inter-strain heterogeneity in rat hepatic transcriptomic responses to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 260:135–145
Yeager RL, Reisman SA, Aleksunes LM, Klaassen CD (2009) Introducing the “TCDD-inducible AhR-Nrf2 gene battery”. Toxicol Sci 111:238–246
Zeeberg BR, Qin H, Narasimhan S, Sunshine M, Cao H, Kane DW, Reimers M, Stephens RM, Bryant D, Burt SK et al (2005) High-Throughput GoMiner, an ‘industrial-strength’ integrative gene ontology tool for interpretation of multiple-microarray experiments, with application to studies of Common Variable Immune Deficiency (CVID). BMC Bioinform 6:168
Zhang B, Duan S, Shi J, Jiang S, Feng F, Shi B, Jia Z (2018) Family-based study of association between MAFB gene polymorphisms and NSCL/P among Western Han Chinese population. Adv Clin Exp Med 27:1109–1116
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Hanbert Chen, Alexander Wu, Ashley Smith, Janne Korkalainen, Arja Moilanen, and Virpi Tiihonen for excellent technical assistance and support. Additional thanks to Marc Baumann and staff at the Meilahti Clinical & Basic Proteomics Core Facility. This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research [grant number MOP-57903 to ABO and PCB], the Academy of Finland [grant number 123345 to RP], and with the support of the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research to PCB through funding provided by the Government of Ontario. PCB was supported by a Terry Fox Research Institute New Investigator Award and a Canadian Institutes of Health Research New Investigator Award.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JDW and SDP carried out the sample preparation for transcriptomic analyses. AW, MS and PZ were involved in library preparation and genome sequencing. RS performed proteomics work. AL, SDP, SL and RDB performed statistical and bioinformatics analyses. AL and SDP wrote the first draft of the manuscript. AL, CQY, SDP, RXS and RP generated tools and reagents. ABO, RP and PCB initiated the project. JDM, ABO, RP and PCB supervised the research. All authors approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All study plans were approved by the Finnish National Animal Experiment Board (Eläinkoelautakunta, ELLA; permit code: ESLH-2008-07223/Ym-23). All animal handling and reporting comply with ARRIVE guidelines (Kilkenny et al. 2010).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prokopec, S.D., Lu, A., Lee, S.CE.S. et al. Comparative toxicoproteogenomics of mouse and rat liver identifies TCDD-resistance genes. Arch Toxicol 93, 2961–2978 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02560-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-019-02560-0