Abstract
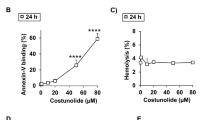
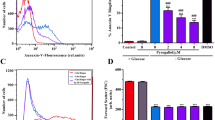
Cordyceps sinensis is a prized traditional Chinese medicine and its major component cordycepin is found to have anti-leukemia activities. However, its cytotoxicity in erythrocytes was unclear. To examine the effect of cordycepin on the induction of eryptosis (an apoptosis-like process in enucleated erythrocytes), flow cytometric assays based on membrane integrity and asymmetry were employed. For comparison, analyses were performed in parallel with two other anti-leukemia agents, indirubin 3′-monoxime (IDM) and As2O3. We found that at the IC50 against leukemia HL-60, cordycepin elicited eryptosis while IDM and As2O3 showed no erythrotoxicity in mouse erythrocytes. Mechanistically, cordycepin increased the [Ca2+]i and activated μ-calpain protease in a dose-dependent manner. Yet, no caspase-3 activation was observed in the cordycepin-treated erythrocytes. When extracellular Ca2+ was depleted, both the cordycepin-induced eryptosis and μ-calpain cleavage were suppressed. Our study therefore demonstrated for the first time that cordycepin induces eryptosis through a calcium-dependent pathway in the absence of mitochondria and caspase-3 activation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- As2O3 :
-
Arsenic trioxide
- [Ca2+]i :
-
Intracellular free calcium concentration
- IDM:
-
Indirubin 3′-monoxime
- PE:
-
Phycoerythrin
- PS:
-
Phosphatidylserine
- RBC:
-
Red blood cell
- STS:
-
Staurosporine
References
Bosman GJ, Willekens FL, Werre JM (2005) Erythrocytes aging: a more than superficial resemblance to apoptosis? Cell Physiol Biochem 16:1–8
Bratosin D, Estaquier J, Petit F, Arnoult D, Quatannens B, Tissier JP, Slomianny C, Sartiaux C, Alonso C, Huart JJ, Montreuil J, Ameisen JC (2001) Programmed cell death in mature erythrocytes: a model for investigating death effector pathways operating in the absence of mitochondria. Cell Death Differ 8:1143–1156
Bratosin D, Mitrofan L, Palii C, Estaquier J, Montreuil J (2005) Novel fluorescence assay using calcein-AM for the determination of human erythrocyte viability and aging. Cytometry A 66:78–84
Dekkers DW, Comfurius P, Bevers EM, Zwaal RF (2002) Comparison between Ca2+-induced scrambling of various fluorescently labelled lipid analogues in red blood cells. Biochem J 362:741–747
Fang J, Chen SJ, Tong JH, Wang ZG, Chen GQ, Chen Z (2002) Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with ATRA and As2O3: a model of molecular target-based cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther 1:614–620
Goll DE, Thompson VF, Li H, Wei W, Cong J (2003) The calpain system. Physiol Rev 83:731–801
Green DR, Kroemer G (2004) The pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science 305:626–629
Hoessel R, Leclerc S, Endicott JA, Nobel ME, Lawrie A, Tunnah P, Leost M, Damiens E, Marie D, Marko D, Niederberger E, Tang W, Eisenbrand G, Meijer L (1999) Indirubin, the active constituent of a Chinese antileukaemia medicine, inhibits cyclin-dependent kinases. Nat Cell Biol 1:60–67
Koc Y, Urbano AG, Sweeney EB, McCaffrey R (1996) Induction of apoptosis by cordycepin in ADA-inhibited TdT-positive leukemia cells. Leukemia 10:1019–1024
Kodama EN, McCaffrey RP, Yusa K, Mitsuya H (2000) Antileukemic activity and mechanism of action of cordycepin against terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-positive (TdT+) leukemic cells. Biochem Pharmacol 59:273–281
Lang PA, Kempe DS, Myssina S, Tanneur V, Birka C, Laufer S, Lang F, Wieder T, Huber SM (2005) PGE(2) in the regulation of programmed erythrocyte death. Cell Death Differ 12:415–428
Lang F, Lang KS, Lang PA, Huber SM, Wieder T (2006) Mechanisms and significance of eryptosis. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1183–1192
Lui JC, Kong SK (2007) Heat shock protein 70 inhibits the nuclear import of apoptosis-inducing factor to avoid DNA fragmentation in TF-1 cells during erythropoiesis. FEBS Lett 581:109–117
Mandal D, Mazumder A, Das P, Kundu M, Basu J (2005) Fas-, caspase 8-, and caspase 3-dependent signaling regulates the activity of the aminophospholipid translocase and phosphatidylserine externalization in human erythrocytes. J Biol Chem 280:39460–39467
Nakamura K, Yoshikawa N, Yamaguchi Y, Kagota S, Shinozuka K, Kunitomo M (2006) Antitumor effect of cordycepin (3’-deoxyadenosine) on mouse melanoma and lung carcinoma cells involves adenosine A3 receptor stimulation. Anticancer Res 26:43–47
Ng TB, Wang HX (2005) Pharmacological actions of Cordyceps, a prized folk medicine. J Pharm Pharmacol 57:1509–1519
Niemoeller OM, Akel A, Lang PA, Attanasio P, Kempe DS, Hermle T, Sobiesiak M, Wieder T, Lang F (2006) Induction of eryptosis by cyclosporine. Naunyn-schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 374:41–49
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reutelingsperger C (1995) A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods 184:39–51
Zhu JS, Halpern GM, Jones K (1998a) The scientific rediscovery of an ancient Chinese herbal medicine: Cordyceps sinensis: part I. J Altern Complement Med 4:289–303
Zhu JS, Halpern GM, Jones K (1998b) The scientific rediscovery of a precious ancient Chinese herbal regimen: Cordyceps sinensis: part II. J Altern Complement Med 4:429–457
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a direct grant from CUHK, earmarked grants from SHARF and Research Grants Council, Hong Kong, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lui, J.C.K., Wong, J.W.Y., Suen, Y.K. et al. Cordycepin induced eryptosis in mouse erythrocytes through a Ca2+-dependent pathway without caspase-3 activation. Arch Toxicol 81, 859–865 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-007-0214-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-007-0214-5