Abstract
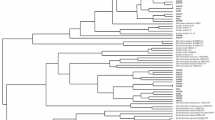
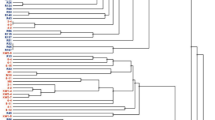
Seventy-three isolates of rhizobia sampled from root nodules of Medicago truncatula were analyzed by restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) of DNA regions amplified by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) targeting the symbiotic plasmid (nifD-K, nodD1, and nodD2 genes) and the chromosome (16S rDNA plus intergenic spacer). Two genotypic groups were found, regardless of the DNA region targeted. These two groups were given the status of genomic species based on results of DNA/DNA hybridization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 August 1995 / Accepted: 13 October 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rome, S., Brunel, B., Normand, P. et al. Evidence that two genomic species of Rhizobium are associated with Medicago truncatula. Arch Microbiol 165, 285–288 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030050328
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030050328