Abstract
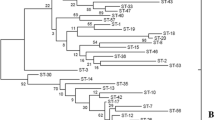
Yogurt, a globally consumed fermented dairy product, is recognized for its taste and potential health benefits attributed to probiotic bacteria, particularly Streptococcus thermophilus. In this study, we employed Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) to investigate the genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships of 13 S. thermophilus isolates from traditional Turkish yogurt samples. We also assessed potential correlations between genetic traits and geographic origins. The isolates were identified as S. thermophilus using VITEK® MALDI-TOF MS, ribotyping, and 16S rRNA analysis methods. MLST analysis revealed 13 different sequence types (STs), with seven new STs for Turkey. The most prevalent STs were ST/83 (n = 3), ST/135 (n = 2), and ST/134 (n = 2). eBURST analysis showed that these isolates mainly were singletons (n = 7) defined as sequence types (STs) that cannot be assigned to any group and differ at two or more alleles from every other ST in the sample. This information suggests that the isolates under study were genetically distinct from the other isolates in the dataset, highlighting their unique genetic profiles within the population. Genetic diversity analysis of ten housekeeping genes revealed polymorphism, with some genes showing higher allelic variation than others. Tajima’s D values suggested that selection pressures differed among these genes, with some being more conserved, likely due to their vital functions. Phylogenetic analysis revealed distinct genetic diversity between Turkish isolates and European and Asian counterparts. These findings demonstrate the genetic diversity of S. thermophilus isolates in Turkish yogurt and highlight their unique evolutionary patterns. This research contributes to our understanding of local microbial diversity associated with yogurt production in Turkey and holds the potential for identifyic strains with enhanced functional attributes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Data and materials used in this study are available upon request. In addition, the data of the isolates used in this study can be found in NCBI BioProject Number PRJNA914520.
References
Alexandraki V, Kazou M, Blom J, Pot B, Papadimitriou K, Tsakalidou E (2019) Comparative genomics of Streptococcus thermophilus support important traits concerning the evolution, biology and technological properties of the species. Front Microbiol 10:2916
Arnold BJ, Huang I-T, Hanage WP (2022) Horizontal gene transfer and adaptive evolution in bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 20(4):206–218
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS et al (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19(5):455–477
Bolotin A, Quinquis B, Renault P, Sorokin A, Ehrlich SD, Kulakauskas S, Lapidus A, Goltsman E, Mazur M, Pusch GD (2004) Complete sequence and comparative genome analysis of the dairy bacterium Streptococcus thermophilus. Nat Biotechnol 22(12):1554–1558
Dan T, Liu W, Sun Z, Lv Q, Xu H, Song Y, Zhang H (2014) A novel multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) protocol for Leuconostoc lactis isolates from traditional dairy products in China and Mongolia. BMC Microbiol 14(1):1–9
Delorme C, Bartholini C, Bolotine A, Ehrlich SD, Renault P (2010) Emergence of a cell wall protease in the Streptococcus thermophilus population. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(2):451–460
Delorme C, Legravet N, Jamet E, Hoarau C, Alexandre B, El-Sharoud WM, Darwish MS, Renault P (2017) Study of Streptococcus thermophilus population on a world-wide and historical collection by a new MLST scheme. Int J Food Microbiol 242:70–81
Demirci T, Akın N, Öztürk Hİ, Oğul A (2022) A metagenomic approach to homemade back-slopped yogurts produced in mountainous villages of Turkey with the potential next-generation probiotics. LWT 154:112860
Dikmen H, Goktas H, Demirbas F, Kayacan S, Ispirli H, Arici M, Turker M, Sagdic O, Dertli E (2023) Multilocus sequence typing of L. bulgaricus and S. thermophilus strains from Turkish traditional yoghurts and characterisation of their techno-functional roles. Food Sci Biotechnol 1–11
Fernandez MA, Marette A (2017) Potential health benefits of combining yogurt and fruits based on their probiotic and prebiotic properties. Adv Nutr 8(1):155S-164S
Francisco AP, Bugalho M, Ramirez M, Carriço JA (2009) Global optimal eBURST analysis of multilocus typing data using a graphic matroid approach. BMC Bioinf 10:1–15
Hafeez Z, Cakir-Kiefer C, Girardet J-M, Jardin J, Perrin C, Dary A, Miclo L (2013) Hydrolysis of milk-derived bioactive peptides by cell-associated extracellular peptidases of Streptococcus thermophilus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9787–9799
Hols P, Hancy F, Fontaine L, Grossiord B, Prozzi D, Leblond-Bourget N, Decaris B, Bolotin A, Delorme C, Dusko Ehrlich S (2005) New insights in the molecular biology and physiology of Streptococcus thermophilus revealed by comparative genomics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29(3):435–463
Hu T, Cui Y, Zhang Y, Qu X, Zhao C (2020) Genome analysis and physiological characterization of four Streptococcus thermophilus strains isolated from Chinese traditional fermented milk. Front Microbiol 11:184
Jolley KA, Bray JE, Maiden MC (2018) Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res 3:124
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (1994) MEGA: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software for microcomputers. Bioinformatics 10(2):189–191
Letunic I, Bork P (2011) Interactive Tree Of Life v2: online annotation and display of phylogenetic trees made easy. Nucleic Acids Res 39(suppl_2):W475–W478
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25(11):1451–1452
Linares DM, O’Callaghan TF, O’Connor PM, Ross RP, Stanton C (2016) Streptococcus thermophilus APC151 strain is suitable for the manufacture of naturally GABA-enriched bioactive yogurt. Front Microbiol 7:1876
Liu W, Su X, Duo N, Yu J, Song Y, Sun T, Zha M, Menghe B, Zhang H, Sun Z (2019) A survey of the relationship between functional genes and acetaldehyde production characteristics in Streptococcus thermophilus by multilocus sequence typing. J Dairy Sci 102(11):9651–9662
Madslien EH, Olsen JS, Granum PE, Blatny JM (2012) Genotyping of B. licheniformisbased on a novel multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) scheme. BMC Microbiol 12(1):1–8
Maiden MC, Van Rensburg MJJ, Bray JE, Earle SG, Ford SA, Jolley KA, McCarthy ND (2013) MLST revisited: the gene-by-gene approach to bacterial genomics. Nat Rev Microbiol 11(10):728–736
Mora D, Fortina M, Parini C, Ricci G, Gatti M, Giraffa G, Manachini P (2002) Genetic diversity and technological properties of Streptococcus thermophilus strains isolated from dairy products. J Appl Microbiol 93(2):278–287
Nagaoka S (2019) Yogurt production. Lactic acid bacteria: Methods and protocols, 45–54.
Nascimento M, Sousa A, Ramirez M, Francisco AP, Carriço JA, Vaz C (2017) PHYLOViZ 2.0: providing scalable data integration and visualization for multiple phylogenetic inference methods. Bioinformatics 33(1):128–129
National Dairy Council (2019) Dünya ve Türkiye’de Süt Sektörü İstatistikleri 2019. Ulusal Süt Konseyi Yayınları 1. Basım, Ankara http://www.ulusalsutkonseyi.org.tr/wp-content/uploads/Ulusal-Sut-Konseyi-Sut-Raporu-2019.pdf. Accessed January 2024
Pichler M, Coskun ÖK, Ortega-Arbulú AS, Conci N, Wörheide G, Vargas S, Orsi WD (2018) A 16S rRNA gene sequencing and analysis protocol for the Illumina MiniSeq platform. Microbiologyopen 7(6):e00611
Roux E, Nicolas A, Valence F, Siekaniec G, Chuat V, Nicolas J, Le Loir Y, Guédon E (2022) The genomic basis of the Streptococcus thermophilus health-promoting properties. BMC Genomics 23(1):210
Somerville V, Berthoud H, Schmidt RS, Bachmann H-P, Meng YH, Fuchsmann P, von Ah U, Engel P (2022) Functional strain redundancy and persistent phage infection in Swiss hard cheese starter cultures. ISME J 16(2):388–399
Tajima F (1989) Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123(3):585–595
Usui Y, Kimura Y, Satoh T, Takemura N, Ouchi Y, Ohmiya H, Kobayashi K, Suzuki H, Koyama S, Hagiwara S (2018) Effects of long-term intake of a yogurt fermented with Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus 2038 and Streptococcus thermophilus 1131 on mice. Int Immunol 30(7):319–331
Vendramin V, Treu L, Campanaro S, Lombardi A, Corich V, Giacomini A (2017) Genome comparison and physiological characterization of eight Streptococcus thermophilus strains isolated from Italian dairy products. Food Microbiol 63:47–57
Weller C, Wu M (2015) A generation-time effect on the rate of molecular evolution in bacteria. Evolution 69(3):643–652
Xu H, Liu W, Zhang W, Yu J, Song Y, Menhe B, Zhang H, Sun Z (2015) Use of multilocus sequence typing to infer genetic diversity and population structure of Lactobacillus plantarum isolates from different sources. BMC Microbiol 15(1):1–10
Yu J, Sun Z, Liu W, Xi X, Song Y, Xu H, Lv Q, Bao Q, Menghe B, Sun T (2015) Multilocus sequence typing of Streptococcus thermophilus from naturally fermented dairy foods in China and Mongolia. BMC Microbiol 15(1):1–13
Funding
This study was carried out using the data obtained from the academic career project numbered TAGEM/HSGYAD/A/21/A3/P1/2311 by the General Directorate of Agricultural Research and Policy under the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DK research design, data collection and analysis, and writing and editing of the manuscript. AÖ literature review, data analysis, interpretation of results, and revision of the manuscript. AY statistical analysis, design of methods, and proofreading of the manuscript. ED supervision, guiding the research process, and final revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
There is no ethical concern in this study.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kiraz, D., Özcan, A., Yibar, A. et al. Genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationships of Streptococcus thermophilus isolates from traditional Turkish yogurt: multilocus sequence typing (MLST). Arch Microbiol 206, 121 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-024-03850-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-024-03850-7