Abstract
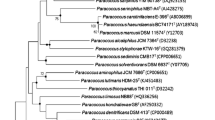
A Gram-stain-negative, non-motile and coccoid bacterial strain, designated XHP0099T, was isolated from the coastal water of the Yellow Sea, China. Growth occurred at 20–37 ℃ (optimum, 28 ℃), pH 5.0–9.0 (optimum, pH 7.0–8.0), and with 0–7.0% NaCl (optimum, 2.0–3.0%). Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showed that strain XHP0099T was related to members of the genus Paracoccus and shared the highest sequence similarity with “P. siganidrum” M26 (98.2%), followed by P. alkanivorans 4-2 T (97.6%) and P. alkenifer DSM 11593 T (97.4%). The average nucleotide identity, amino acid identity, and digital DNA–DNA hybridization values of strain XHP0099T against related members in the genus Paracoccus were below the cut-off points proposed for the delineation of a novel species. The major cellular fatty acids (> 10%) were summed feature 8 (C18:1 ω7c/C18:1 ω6c), and C18:0. The major isoprenoid quinone was Q-10 and the polar lipids contained diphosphatidylglycerol (DPG), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylcholine (PC), aminolipid (AL) and unidentified polar lipids (L). The G + C content of the genomic DNA of strain XHP0099T was 66.0%. Genomic analysis suggested that strain XHP0099T harbored gene clusters for formaldehyde and the XoxF-type methanol oxidation and type 1 Calvin cycle, which could confer the methylotrophy pathway. Based on the phenotypic, phylogenetic, biochemical and chemotaxonomic analysis, strain XHP0099T represents a novel species of the genus Paracoccus, for which the name Paracoccus marinaquae sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is XHP0099T (= JCM 34661 T = GDMCC 1.2414 T = MCCC 1K05846T).


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers of strain XHP0099T are ON329670 (16S rRNA gene) and JAHKNG000000000 (genome), respectively. Other datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Athayle M, Schaal A, Parlett J (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Meth 2:233241. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-7012(84)90018-6
Carbon S et al (2019) The gene ontology resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D330–D338. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1055
Chen S et al (2020) Nitrate reduction by Paracoccus thiophilus strain LSL 251 under aerobic condition: Performance and intracellular central carbon flux pathways. Bioresour Technol 308:123301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123301
Coulthurst S (2019) The type VI secretion system: a versatile bacterial weapon. Microbiology 165:503–515. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.000789
Czarnecki J, Bartosik D (2019) Diversity of methylotrophy pathways in the genus Paracoccus (Alphaproteobacteria). Curr Issues Molr Biol. 33:117–132. https://doi.org/10.21775/cimb.033.117
Davis DH, Doudoroff M, Stanier RY, Mandel M (1969) Proposal to reject the genus Hydrogenomonas: taxonomic implications. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 19:375–390. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-19-4-375
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01734359
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Biol 20:406–416. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/20.4.406
Galperin MY, Makarova KS, Wolf YI, Koonin EV (2015) Expanded microbial genome coverage and improved protein family annotation in the COG database. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D261–D269. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1223
Hiraishi A, Ueda Y, Ishihara J, Mori T (1996) Comparative lipoquinone analysis of influent sewage and activated sludge by high-performance liquid chromatography and photodiode array detection. J Gen Appl Microbiol 42:457–469. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.42.457
Huerta-Cepas J, Forslund K, Coelho LP, Szklarczyk D, Jensen LJ, Von Mering C, Bork P (2017) Fast genome-wide functional annotation through orthology assignment by eggNOG-mapper. Mol Biol Evol 34:2115–2122. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx148
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M (2016) KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D457–D462. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1070
Katayama Y, Hiraishi A, Kuraishi H (1995) Paracoccus thiocyanatus sp. nov., a new species of thiocyanate-utilizing facultative chemolithotroph, and transfer of Thiobacillus versutus to the genus Paracoccus as Paracoccus versutus comb. nov. with emendation of the genus. Microbiology 141:1469–1477. https://doi.org/10.1099/13500872-141-6-1469
Kelly DP, Rainey FA, Wood AP (2006) The genus Paracoccus. Springer, New York, pp 232–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-387-30745-1_12
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731581
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Lee M, Woo S-G, Park G, Kim MK (2011) Paracoccus caeni sp. nov., isolated from sludge. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1968–1972. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.017897-0
Lee J-Y, Hyun D-W, Yun J-H, Jung M-J, Shin N-R, Bae J-W (2019) Paracoccus tegillarcae sp. nov., isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of a blood cockle (Tegillarca granosa). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 69:2815–2822. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003561
Liu Z-P, Wang B-J, Liu X-Y, Dai X, Liu Y-H, Liu S-J (2008) Paracoccus halophilus sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment of the South China Sea, China, and emended description of genus Paracoccus Davis 1969. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:257–261. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65237-0
Liu Y et al (2013) Paracoccus siganidrum sp. nov., isolated from fish gastrointestinal tract. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103:1133–1139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9894-4
Ludwig W, Mittenhuber G, Friedrich CG (1993) Transfer of Thiosphaera pantotropha to Paracoccus denitrificans. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 43:363–367. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-43-2-363
Lyu L, Lai Q, Li J, Yu Z, Shao Z (2021) Paracoccus amoyensis sp. nov., isolated from the surface seawater along the coast of Xiamen Island. China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 71:004685. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004685
Makarova KS et al (2020) Evolutionary classification of CRISPR-Cas systems: a burst of class 2 and derived variants. Nat Rev Microbiol 18:67–83. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-019-0299-x
Ohara M, Katayama Y, Tsuzaki M, Nakamoto S, Kuraishi H (1990) Paracoccus kocurii sp. nov., a tetramethylammonium-assimilating bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 40:292–296. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-40-3-292
Parks DH et al (2018) Recovery of nearly 8,000 metagenome-assembled genomes substantially expands the tree of life. Nat Microbiol 3:253–253. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0083-5
Parte AC, Carbasse JS, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Reimer LC, Göker M (2020) List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) moves to the DSMZ. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:5607. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004332
Rai A, Smita N, Suresh G, Shabbir A, Deepshikha G, Ch S (2020) Paracoccus aeridis sp. nov., an indole-producing bacterium isolated from the rhizosphere of an orchid, Aerides maculosa. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:1720–1728. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003962
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. P Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19126–19131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906412106
Robertson LA, Kuenen JG (1984) Aerobic denitrification: a controversy revived. Arch Microbiol 139:351–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00408378
Rodriguez-R LM, Konstantinidis KT (2014) Bypassing cultivation to identify bacterial species. Microbe 9(3):111–118. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbe.9.111.1
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sanjeevkumar S et al (2013) Paracoccus denitrificans SD1 mediated augmentation with indigenous mixed cultures for enhanced removal of N, N-dimethylformamide from industrial effluents. Biochem Eng J 79:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2013.06.016
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids, MIDI Technical Note 101. Microbial ID Inc, Newark
Sun X, Luo P, Li M (2015) Paracoccus angustae sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:3469–3475. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000440
Wang Y et al (2009) Paracoccus saliphilus sp. nov., a halophilic bacterium isolated from a saline soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1924–1928. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.005918-0
Wayne L et al (1987) Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 37:463–464. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-37-4-463
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.173.2.697-703.1991
Xue H, Piao C-g, Guo M-w, Wang L-f, Li Y (2017) Paracoccus aerius sp. nov., isolated from air. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2586–2591. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001976
Ye J, Lin D, Zhang M, Lin T-H, Sun J, Wang D, Tang K (2020) Paracoccus aurantiacus sp. nov., isolated from shallow-sea hydrothermal systems off Kueishantao Island. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:2554–2559. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004068
Zhang J et al (2011) Biodegradation of chloroacetamide herbicides by Paracoccus sp. FLY-8 in vitro. J Agr Food Chem 59:4614–4621. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf104695g
Zhang G, Jiao K, Xie F, Pei S, Jiang L (2019) Paracoccus subflavus sp. nov., isolated from Pacific Ocean sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 69:1472–1476. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003344
Zhang D-F, Cui X-W, Zhao Z, Zhang A-H, Huang J-K, Li W-J (2020a) Sphingomonas hominis sp. nov., isolated from hair of a 21-year-old girl. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 113:1523–1530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-020-01460-z
Zhang Y-X et al (2020b) Paracoccus alkanivorans sp. nov., isolated from a deep well with oil reservoir water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:2312–2317. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.004036
Zhu S, Zhao Q, Zhang G, Jiang Z, Sheng H, Feng H, An L (2013) Paracoccus tibetensis sp. nov., isolated from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau permafrost. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1902–1905. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.041905-0
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31900001), the Innovation Project for Marine Science and Technology of Jiangsu Province (JSZRHYKJ202209), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (B210202140).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31900001). Innovation Project for Marine Science and Technology of Jiangsu Province (JSZRHYKJ202209). Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (B210202140).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HPX and DFZ: designed research and project outline. LW: provided the three type strains. HPX: performed isolation, deposition and polyphasic taxonomy. HPX, and ZYF: performed genome analysis. ZYF: drafted the manuscript. DFZ, WH, WJL, AHZ, JKH and CL: revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, HP., Fu, ZY., He, W. et al. Paracoccus marinaquae sp. nov., isolated from coastal water of the Yellow Sea. Arch Microbiol 205, 58 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03402-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03402-5