Abstract
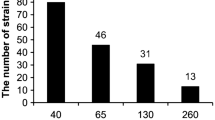
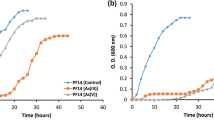
The study of arsenic (As)-resistant microorganisms with high As removal capacity is fundamental for the development of economically sustainable technologies used for the treatment of water contaminated with metalloid. In the current study, four bacterial strains were isolated from As-contaminated water samples of the Xichu region, Mexico. Based on 16S rRNA gene sequencing and phylogenetic analysis of the isolated strains, Rhodococcus gordoniae, Microbacterium hydrocarbonoxydans, Exiguobacterium indicum, and Pseudomonas kribbensis were identified as potential As removal strains. R. gordoniae shows the highest growth capacity in both As(III) and As(V). R. gordoniae, M. hydrocarbonoxydans, and E. indicum removed approximately 81.6, 79.9, and 61.7% of As(III), as well as 77.2, 68.9, and 74.8% of As(V), respectively. P. kribbensis removed only about 80.2% of As(V). This study contributes to the possible detoxification mechanisms employed by these bacteria. Such insight could be crucial in the successful implementation of in situ bioremediation programs using these little-known bacteria.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar NC, Faria MCS, Pedron T, Batista BL, Mesquita JP, Bomfeti CA, Rodrigues JL (2020) Isolation and characterization of bacteria from a brazilian gold mining area with a capacity of arsenic bioaccumulation. Chemosphere 240:124871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124871
Alka S, Shahir S, Ibrahim N, Ndejiko MJ, Vo D-VN, Abd Manan F (2021) Arsenic removal technologies and future trends: A mini review. J Clean Prod 278:123805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123805
Andreasen R, Li Y, Rehman Y, Ahmed M, Meyer RL, Sabri AN (2018) Prospective role of indigenous Exiguobacterium profundum PT 2 in arsenic biotransformation and biosorption by planktonic cultures and biofilms. J Appl Microb 124(2):431–443. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13636
Andres J, Bertin PN (2016) The microbial genomics of arsenic. FEMS Microb Rev 40(2):299–322. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuv050
Arroyo YR, Muñoz AH, Barrientos EY, Huerta IR, Wrobel K (2013) Natural decrease of dissolved arsenic in a small stream receiving drainages of abandoned silver mines in Guanajuato, Mexico. Bull Env Contam Toxicol 91(5):539–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1091-7
Arroyo-Herrera I, Román-Ponce B, Reséndiz-Martínez AL, Estrada-de Los Santos P, Wang ET, Vásquez-Murrieta MS (2021) Heavy-metal resistance mechanisms developed by bacteria from Lerma-Chapala basin. Arch Microb. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-02140-2
Cai X, Wang P, Li Z, Li Y, Yin N, Du H, Cui Y (2020) Mobilization and transformation of arsenic from ternary complex OM-Fe(III)-As(V) in the presence of As(V)-reducing bacteria. J Hazard Mater 381:120975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120975
Cartwright AC, Matthews BR (eds) International pharmaceutical product registration, 2nd edn. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.3109/9781420081831
Castrejón UER, Muñoz AHS, Jimenez GC, Canchoa CC, Vargas AA, Ortega NG, Puga LEM (2020) Characterization of arsenite oxidizing bacteria for wastewater treatment. Jóvenes En La Ciencia 8:1–4
Cavalca L, Corsini A, Zaccheo P, Andreoni V, Muyzer G (2013) Microbial transformations of arsenic: perspectives for biological removal of arsenic from water. Future Microb 8(6):753–768. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb.13.38
Chang J-S, Yoon I-H, Lee J-H, Kim K-R, An J, Kim K-W (2010) Arsenic detoxification potential of aox genes in arsenite-oxidizing bacteria isolated from natural and constructed wetlands in the Republic of Korea. Env Geochem Health 32(2):95–105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-009-9268-z
Chang DH, Rhee MS, Kim JS, Lee Y, Park M, Kim H, Kim BC (2016) Pseudomonas kribbensis sp. nov, isolated from garden soils in Daejeon, Korea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek Int J Gen Mol Microb 109(11):1433–1446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-016-0743-0
Chaturvedi P, Shivaji S (2006) Exiguobacterium indicum sp. nov, a psychrophilic bacterium from the Hamta glacier of the Himalayan mountain ranges of India. Int J Syst Evol Microb 56(Pt 12):2765–2770. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64508-0
Corsini A, Zaccheo P, Muyzer G, Andreoni V, Cavalca L (2014) Arsenic transforming abilities of groundwater bacteria and the combined use of Aliihoeflea sp. strain 2WW and goethite in metalloid removal. J Hazard Mater 269:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.12.037
Edgell, KW (1989) USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) method study 35. SW method 3005. Acid digestion of waters for total recoverable or dissolved metals for analyses by flame atomic absorption spectroscopy. Report for September 1986-December 1987 (Final) (No. PB-89-190573/XAB). Bionetics Corp., Cincinnati, OH (USA). https://www.osti.gov/biblio/5632197
Element CAS (2007) Method 3015A microwave assisted acid digestion of aqueous samples and extracts. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Escudero LV, Casamayor EO, Chong G, Pedrós-Alió C, Demergasso C (2013) Distribution of microbial arsenic reduction, oxidation and extrusion genes along a wide range of environmental arsenic concentrations. PLoS ONE 8(10):e78890. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0078890
Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (1994) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for microbiology, Washington, DC, Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM, p 607654
Gu Y, Wang Y, Sun Y, Zhao K, Xiang Q, Yu X, Chen Q (2018) Genetic diversity and characterization of arsenic-resistant endophytic bacteria isolated from Pteris vittata, an arsenic hyperaccumulator. BMC Microb 18(1):42. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-018-1184-x
Jones AL, Brown JM, Mishra V, Perry JD, Steigerwalt AG, Goodfellow M (2004) Rhodococcus gordoniae sp. nov, an actinomycete isolated from clinical material and phenol-contaminated soil. Int J Systematic Evolut Microb 54(2):407–411. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.02756-0
Kao A-C, Chu Y-J, Hsu F-L, Liao VH-C (2013) Removal of arsenic from groundwater by using a native isolated arsenite-oxidizing bacterium. J Contam Hydrol 155:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2013.09.001
Kenny QY (2003) Indicator function and its application in two-level factorial designs. Ann Stat 31(3):984–994. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1056562470
Kirchman D, Sigda J, Kapuscinski R, Mitchell R (1982) Statistical analysis of the direct count method for enumerating bacteria. Appl Env Microb 44(2):376–382. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.44.2.376-382.1982
Kruger MC, Bertin PN, Heipieper HJ, Arsène-Ploetze F (2013) Bacterial metabolism of environmental arsenic–mechanisms and biotechnological applications. Appl Microb Biotechnol 97(9):3827–3841. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4838-5
Kumari N, Rana A, Jagadevan S (2019) Arsenite biotransformation by Rhodococcus sp.: Characterization, optimization using response surface methodology and mechanistic studies. Sci Total Env 687:577–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.077
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Lopez R (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23(21):2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
LeBlanc MS, McKinney EC, Meagher RB, Smith AP (2013) Hijacking membrane transporters for arsenic phytoextraction. J Biotechnol 163(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.10.013
Lee Y, Um I-H, Yoon J (2003) Arsenic (III) oxidation by iron (VI)(ferrate) and subsequent removal of arsenic (V) by iron (III) coagulation. Env Sci Technol 37(24):5750–5756. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034203
Loredo-Portales R, Castillo-Michel H, Aquilanti G, De La Rosa-Álvarez MG, Rocha-Amador DO, Vogel-Mikus K, Cruz-Jiménez G (2017) Synchrotron based study of As mobility and speciation in tailings from a mining site in Mexico. J Env Chem Eng 5(1):1140–1149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.01.019
Macur RE, Jackson CR, Botero LM, McDermott TR, Inskeep WP (2004) Bacterial populations associated with the oxidation and reduction of arsenic in an unsaturated soil. Env Sci Technol 38(1):104–111. https://doi.org/10.1021/es034455a
Men AE, Wilson P, Siemering K, Forrest S (2008) Sanger DNA sequencing. Next Gener Genome Seq: towards Personalized Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527625130
Mirza BS, Sorensen DL, Dupont RR, McLean JE (2017) New arsenate reductase gene (arrA) PCR primers for diversity assessment and quantification in environmental samples. Appl Env Microb. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02725-16
Mudzielwana R, Gitari MW, Akinyemi SA, Talabi AO, Ndungu P (2020) Hydrogeochemical characteristics of arsenic rich groundwater in greater Giyani municipality, Limpopo province South Africa. Groundw Sustain Dev 10:100336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100336
Muñoz AHS, García MGM, García FAV, Luna BN, Molina AZ, Li Y, Castrejón UER (2016) Uso potencial de pellets para el tratamiento de aguas contaminadas con arsénico en comunidades de Xichú, Gto, México. Acta Universitaria 26(2):22–32. https://doi.org/10.15174/au.2016.1502
NOM-127-SSA. (2019) Proyecto de norma oficial mexicana, agua para uso y consumo humano Límites permisibles de la calidad del agua. PROY-NOM-127-SSA1-2017
Nordstrom DK (2002) Public health Worldwide occurrences of arsenic in ground water. Science 296(5576):2143–2145. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1072375
Ono FB, Tappero R, Sparks D, Guilherme LRG (2016) Investigation of arsenic species in tailings and windblown dust from a gold mining area. Env Sci Pollut Res 23(1):638–647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5304-y
Osuna-Martínez CC, Armienta MA, Bergés-Tiznado ME, Páez-Osuna F (2020) Arsenic in waters, soils, sediments, and biota from Mexico: an environmental review. Sci Total Env. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142062
Pandey N, Bhatt R (2015) Exiguobacterium mediated arsenic removal and its protective effect against arsenic induced toxicity and oxidative damage in freshwater fish, Channa striata. Toxicol Rep 2:1367–1375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2015.10.002
Pandey N, Bhatt R (2016a) Arsenic removal and biotransformation potential of Exiguobacterium isolated from an arsenic-rich soil of Chhattisgarh, India. Clean–soil, Air, Water 44(2):211–218. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201500095
Pandey N, Bhatt R (2016b) Role of soil associated Exiguobacterium in reducing arsenic toxicity and promoting plant growth in Vigna radiata. Eur J Soil Biol 75:142–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2016.05.007
Prasad KS, Srivastava P, Subramanian V, Paul J (2011) Biosorption of As(III) Ion on Rhodococcus sp. WB-12: biomass characterization and kinetic studies. Sep Sci Technol 46(16):2517–2525. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2011.597040
PROY-NMX-AA-121/1-SCFI-2008 (2008) Análisis de agua-aguas naturales epicontinentales, costeras y marinas. México: Secretaria de Comercio y Fomento Industrial. Accessed June 2019. In
Rio DC, Ares M, Hannon GJ, Nilsen TW (2010) Purification of RNA using TRIzol (TRI reagent). Cold Spring Harbor Protoc 2010(6):pdb-prot5439. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot5439
Rodríguez UE, Serafín AH, Cano MC, Gutierrez NL, Alvarez A (2019) Isolation and molecular identification of arsenic resistant microorganisms coming from xichu river, Gto Mexico. Chem Eng. https://doi.org/10.3303/CET1974255
Saiki RK (1990) Amplification of genomic DNA. PCR Protoc: Guide Methods Appl 2:13–20
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Sayers EW, Beck J, Bolton EE, Bourexis D, Brister JR, Canese K, Klimke W (2021a) Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res 49(D1):D10. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa892
Sayers EW, Cavanaugh M, Clark K, Pruitt KD, Schoch CL, Sherry ST, Karsch-Mizrachi I (2021b) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 49(D1):D92–D96. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa1023
Schippers A, Bosecker K, Spröer C, Schumann P (2005) Microbacterium oleivorans sp. nov and Microbacterium hydrocarbonoxydans sp. nov, novel crude-oil-degrading gram-positive bacteria. Int J Syst Evol Microb 55(Pt 2):655–660. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63305-0
Schwartz S, Zhang Z, Frazer KA, Smit A, Riemer C, Bouck J, Miller W (2000) PipMaker—a web server for aligning two genomic DNA sequences. Genome Res 10(4):577–586. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.10.4.577
Thompson F, de Oliveira BC, Cordeiro MC, Masi BP, Rangel TP, Paz P, Cabral AS (2020) Severe impacts of the Brumadinho dam failure (Minas Gerais, Brazil) on the water quality of the Paraopeba River. Sci Total Env 705:135914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135914
Tsuchiya T, Ehara A, Kasahara Y, Hamamura N, Amachi S (2019) Expression of genes and proteins involved in arsenic respiration and resistance in dissimilatory arsenate-reducing Geobacter sp. strain OR-1. Appl Env Microb. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00763-19
Tuzen M, Citak D, Mendil D, Soylak M (2009) Arsenic speciation in natural water samples by coprecipitation-hydride generation atomic absorption spectrometry combination. Talanta 78(1):52–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2008.10.035
Wang L, Yin Z, Jing C (2020) Metagenomic insights into microbial arsenic metabolism in shallow groundwater of Datong basin. China Chemosphere 245:125603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125603
Weerasundara L, Ok Y-S, Bundschuh J (2021) Selective removal of arsenic in water: a critical review. Env Pollut 268:115668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115668
World Health O. (2018). A global overview of national regulations and standards for drinking-water quality
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT) and the University of Guanajuato (Engineering Division and Directorate for Research and Postgraduate Support).
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with humans or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez-Castrejón, U.E., Serafin-Muñoz, A.H., Alvarez-Vargas, A. et al. Isolation and molecular identification of native As-resistant bacteria: As(III) and As(V) removal capacity and possible mechanism of detoxification. Arch Microbiol 204, 191 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02794-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02794-0