Abstract
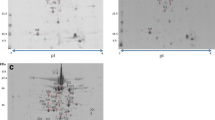
All bacteria can survive and adapt to different stresses, such as fluctuations in temperature, pH oxidative, and osmotic pressure occurring in their surrounding environments. This study aims to evaluate the effects of a variety of stress conditions on the growth, and proteome of Raoultella planticola PTCC 1598. R. planticola cells were exposed to different values of temperatures, sodium chloride, pH, and hydrogen peroxide stresses. Among the stress conditions, oxidative stress, upon exposure to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) at 4000 ppm concentration was selected for proteomics analysis in detail. Approximately, 1400 spots were identified in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE). Among the identified spots, 85 spots were repeatable using 2D-Platinum software and eye confirmation and, nine protein spots were differentially expressed. Among nine proteins, six proteins identified successfully with an MASCOT score greater than 40 (p < 0.05) were 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate-2,3-dehydrogenase (oxidoreductase family), hypothetical protein G787-04832, periplasmic d-galactose-binding protein, uridine phosphorylase (glycosyltransferases), a single peptide match to cysteine-binding periplasmic protein, and NADP(H) nitroreductase. All identified proteins showed decreased level expression. Based on the obtained results, we concluded that hydrogen peroxide as an antiseptic compound could affect cell growth and proteomics of R. planticola. Therefore, we recommend using an antiseptic solution containing H2O2 to prevent the spread of R. planticola as a new emerging pathogen.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baez A, Shiloach J (2013) Escherichia coli avoids high dissolved oxygen stress by activation of SoxRS and manganese-superoxide dismutase. Microb Cell Fact 12(1):23
Bagley ST, Seidler RJ, Brenner DJ (1981) Klebsiella planticola sp. Nov.: a new species of Enterobacteriaceae found primarily in nonclinical environments. Curr Microbiol 6(2):105–109
Bartholomäus A, Fedyunin I, Feist P, Sin C, Zhang G, Valleriani A, Ignatova Z (2016) Bacteria differently regulate mRNA abundance to specifically respond to various stresses. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2015.0069
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Cho YJ, Jung EJ, Seong JS, Woo YM, Jeong BJ, Kang YM, Lee E (2016) A case of pneumonia caused by Raoultella planticola. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul) 79(1):42–45
Daware V, Kesavan S, Patil R, Natu A, Kumar A, Kulkarni M, Gade W (2012) Effects of arsenite stress on growth and proteome of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Biotechnol 158(1–2):8–16
Fager C, Yurteri-Kaplan L (2019) Urinary tract infection with rare pathogen Raoultella planticola: a post-operative case and review. Urol Case Rep 22:76–79
Farahtaj F, Zandi F, Khalaj V, Biglari P, Fayaz A, Vaziri B (2013) Proteomics analysis of human brain tissue infected by street rabies virus. Mol Biol Rep 40(11):6443–6450
Garavito MF, Narváez-Ortiz HY, Zimmermann BH (2015) Pyrimidine metabolism: dynamic and versatile pathways in pathogens and cellular development. J Transl Genet Genom 42(5):195–205
Guo MS, Gross CA (2014) Stress-induced remodeling of the bacterial proteome. Curr Biol 24(10):R424–R434
Hayyan M, Hashim MA, AlNashef IM (2016) Superoxide ion: generation and chemical implications. Chem Rev 116(5):3029–3085
Holden VI, Breen P, Houle S, Dozois CM, Bachman MA (2016) Klebsiella pneumoniae siderophores induce inflammation, bacterial dissemination, and HIF-1α stabilization during pneumonia. MBio 7(5):e01397-e1416
Khalil S, Pawelek PD (2011) Enzymatic adenylation of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate is enhanced by a protein−protein interaction between Escherichia coli 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybenzoate dehydrogenase (EntA) and 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate-AMP ligase (EntE). Biochemistry 50(4):533–545
Kim H-Y, Song H-G (2005) Purification and characterization of NAD (P) H-dependent nitroreductase I from Klebsiella sp. C1 and enzymatic transformation of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68(6):766–773
Lam PW, Salit IE (2014) Raoultella planticola bacteremia following consumption of seafood. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol 25(4):e83–e84
Liu X, Sun X, Wu Y, Xie C, Zhang W, Wang D et al (2013) Oxidation-sensing regulator AbfR regulates oxidative stress responses, bacterial aggregation, and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Biol Chem 288(6):3739–3752
McDonnell G (2014) The Use of Hydrogen Peroxide for Disinfection and Sterilization ApplicationsPeroxides.https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470682531.pat0885
Montero IG, Dolata KM, Schlüter R, Malherbe G, Sievers S, Zühlke D et al (2019) Comparative proteome analysis in an Escherichia coli CyDisCo strain identifies stress responses related to protein production, oxidative stress and accumulation of misfolded protein. Microb Cell Fact 18(1):1–15
Nandakumar M, Shen J, Raman B, Marten MR (2003) Solubilization of trichloroacetic acid (TCA) precipitated microbial proteins via NaOH for two-dimensional electrophoresis. J Proteome Res 2(1):89–93
Nathan C, Ding A (2010) SnapShot: reactive oxygen intermediates (ROI). Cell 140(6):951
Niedergethmann M, Alves F, Neff J, Heidrich B, Aramin N, Li L et al (2007) Gene expression profiling of liver metastases and tumour invasion in pancreatic cancer using an orthotopic SCID mouse model. Br J Cancer 97(10):1432–1440
O'Connell K, Kelly J , NiRiain U (2010) A rare case of soft-tissue infection caused by Raoultella planticola. J Med Case Rep 2010
Ohtsu I, Kawano Y, Suzuki M, Morigasaki S, Saiki K, Yamazaki S et al (2015) Uptake of l-cystine via an ABC transporter contributes defense of oxidative stress in the l-cystine export-dependent manner in Escherichia coli. PLoS ONE 10(4):e0120619
Olson D, Asare K, Lyons M, Hofinger D (2013) A novel case of Raoultella planticola urinary tract infection. Infection 41(1):259–261
Pan S, Rodriguez D, Thirumavalavan N, Gross MS, Eid JF, Mulcahy J, Munarriz R (2019) The use of antiseptic solutions in the prevention and management of penile prosthesis infections: a review of the cytotoxic and microbiological effects of common irrigation solutions. J Sex Med 16(6):781–790
Siauciunaite R, Foulkes NS, Calabrò V, Vallone D (2019) Evolution shapes the gene expression response to oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci 20(12):3040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20123040
Tang P, Liu JK, Chou SM, Hor LI, Chen WJ, Chen SC (2008) A proteomic analysis of Klebsiella oxytoca after exposure to succinonitrile. Process Biochem 43(7):753–757
Tantasuttikul A, Mahakarnchanakul W (2019) Growth parameters and sanitizer resistance of Raoultella ornithinolytica and Raoultella terrigena isolated from seafood processing plant. Cogent Food Agric 5(1):1569830. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311932.2019.1569830
Van Meurs S, Gawlitta D, Heemstra K, Poolman R, Vogely H, Kruyt M (2014) Selection of an optimal antiseptic solution for intraoperative irrigation: an in vitro study. JBJS 96(4):285–291
Westerveld D, Hussain J, Aljaafareh A, Ataya A (2017) A rare case of Raoultella planticola pneumonia: an emerging pathogen. Respir Med Case Rep 21:69–70
Young I, Gibson F (1969) Regulation of the enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid in Aerobacter aerogenes and Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 177(3):401–411
Acknowledgements
The laboratory facilities of microbial experiments were provided by Lahijan Branch, Islamic Azad University, Lahijan, Iran. The authors are grateful to Dr. Behrouz Vaziri and Mrs. Bahareh Azarian at Protein Chemistry Unit, Biotechnology Research Center, Pasteur Institute of Iran and ProteomicsTechnology Facility, Department of Biology, the University of York UK for their helpful assistance in proteomics analysis.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific Grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors and the authors financially supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This study was performed based on a Master of Science (MSc) thesis addressed to Zeynab Hajian. ZH, MFG, and FEA contributed almost equally to this study. MFG¸ designed the study, ZH and FEA did the experiments and performed research; MFG analyzed all data and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hajian, Z., Ghasemi, M.F. & Alikhani, F.(. The study of stress conditions on growth and proteome of Raoultella planticola: a new emerging pathogen. Arch Microbiol 203, 3269–3278 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02312-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02312-8