Abstract
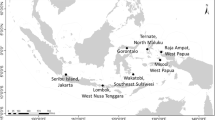
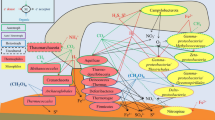
Halophilic Archaea are widely distributed globally in hypersaline environments. However, little is known of how dominant halophilic archaeal genera are distributed across environments and how they may co-associate across ecosystems. Here, the archaeal community composition and diversity from hypersaline environments (> 300 g/L salinity; total of 33 samples) in the Qaidam Basin of China were investigated using high-throughput Illumina sequencing of 16S rRNA genes. The archaeal communities (total of 3,419 OTUs) were dominated by the class Halobacteria (31.7–99.6% relative abundances) within the phylum Euryarchaeota (90.8–99.9%). Five predominant taxa, including Halorubrum, Halobacterium, Halopenitus, Methanothrix, and Halomicrobium, were observed across most samples. However, several distinct genera were associated with individual samples and were inconsistently distributed across samples, which contrast with previous studies of hypersaline archaeal communities. Additionally, co-occurrence network analysis indicated that five network clusters were present and potentially reflective of interspecies interactions among the environments, including three clusters (clusters II, III, and IV) comprising halophilic archaeal taxa within the Halobacteriaceae and Haloferacaceae families. In addition, two other clusters (clusters I and V) were identified that comprised methanogens. Finally, salinity comprising ionic concentrations (in the order of Na+ > Ca2+ > Mg2+) and pH were most correlated with taxonomic distributions across sample sites.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah MB, Karray F, Mhiri N, Mei N, Quéméneur M, Cayol JL, Erauso G, Tholozan JL, Alazard D, Sayadi S (2016) Prokaryotic diversity in a Tunisian hypersaline lake, Chott El Jerid. Extremophiles 20:125–138
Abdallah MB, Karray F, Kallel N, Armougom F, Mhiri N, Quéméneur M, Cayol JL, Erauso G, Sayadi S (2018) Abundance and diversity of prokaryotes in ephemeral hypersaline lake Chott El Jerid using Illumina Miseq sequencing, DGGE and qPCR assays. Extremophiles 22:811–823
Adhikari NP, Adhikari S, Liu XB, Shen L, Gu Z (2019) Bacterial diversity in alpine lakes: a review from the third pole region. J Earth Sci 30:387–396
Andrei AS, Robeson MS, Baricz A, Coman C, Muntean V, Ionescu A, Etiope G, Alexe M, Sicora CI, Podar M, Banciu HL (2015) Contrasting taxonomic stratification of microbial communities in two hypersaline meromictic lakes. ISME J 9:2642–2656
Asnicar F, Weingart G, Tickle TL, Huttenhower C, Segata N (2015) Compact graphical representation of phylogenetic data and metadata with GraPhlAn. Peer J 3:e1029
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) Qiime allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Chen S, Xu Y, Helfant L (2020) Geographical isolation, buried depth, and physicochemical traits drive the variation of species diversity and prokaryotic community in three typical hypersaline environments. Microorganisms 8:120
Çınar S, Mutlu MB (2016) Comparative analysis of prokaryotic diversity in solar salterns in eastern Anatolia (Turkey). Extremophiles 20:589–601
Couto-Rodríguez RL, Montalvo-Rodríguez R (2019) Temporal analysis of the microbial community from the crystallizer ponds in Cabo Rojo, Puerto Rico, using metagenomics. Genes 10:422
de la Haba RR, Sánchez-Porro C, Marquez MC, Ventosa A (2010) Extremophiles halophiles: taxonomy of halophiles. In: Horikoshi K, Antranikian G, Bull AT, Robb FT, Stetter KO (eds) Extremophiles Handbook. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, pp 255–308
Deng Y, Liu Y, Dumont M, Conrad R (2017) Salinity affects the composition of the aerobic Methanotroph community in alkaline lake sediments from the Tibetan Plateau. Microb Ecol 73:101–110
Dillon JG, Carlin M, Gutierrez A, NguyenV, and Mclain N, (2013) Patterns of microbial diversity along a salinity gradient in the Guerrero Negro solar saltern, Baja CA Sur. Mexico Front Microbiol 4:399
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) Uchime improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200
García-Maldonado JQ, Alejandra EZ, Luciana R, Bebout BM, Alejandro SF, Alejandro LC (2018) Bacterial and archaeal profiling of hypersaline microbial mats and endoevaporites, under natural conditions and methanogenic microcosm experiments. Extremophiles 22:903–916
Ghai R, Pašić L, Fernández AB, Martin-Cuadrado AB, Mizuno CM, McMahon KD, Papke RT, Stepanauskas R, Rodriguez-Brito B, Rohwer F, Sánchez-Porro C, Ventosa A, Rodríguez-Valera F (2011) New abundant microbial groups in aquatic hypersaline environments. Sci Rep 1:135
Haferburg G, Janosch AD, Schmidt GN, Kummer NA, Erquicia JC, Schlömann M (2017) Microbial diversity of the hypersaline and lithium-rich Salar de Uyuni, Bolivia. Microbiol Res 199:19–28
Hamm JN, Erdmann S, Eloe-Fadrosh EA, Angeloni A, Zhong L, Brownlee C, Williams TJ, Barton K, Carswell S, Smith MA, Brazendale S, Hancock AM, Allen MA, Raftery MJ, Cavicchioli R (2019) Unexpected host dependency of Antarctic Nanohaloarchaeota. PNAS 116:14661–14670
Han R, Zhang X, Liu J, Long Q, Chen L, Liu D, Zhu D (2017) Microbial community structure and diversity within hypersaline Keke Salt Lake environments. Can J Microbiol 63:895–908
Hayden CJ, Beman JM (2016) Microbial diversity and community structure along a lake elevation gradient in Yosemite National Park, California, USA. Environ Microbiol 18:1782–1791
Hu A, Yao DD, Jiao NZ, Liu YQ, Yang Z, Liu XB (2010) Community structures of ammonia-oxidising Archaea and Bacteria in high-altitude lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Freshwater Biol 55:2375–2390
Jacob JH, Hussein EI, Shakhatreh MAK, Cornelison CT (2017) Microbial community analysis of the hypersaline water of the Dead Sea using high-throughput amplicon sequencing. Microbiologyopen 6:e00500
Jiang H, Dong H, Yu B, Liu X, Li Y, Ji S, Zhang CL (2007) Microbial response to salinity change in Lake Chaka, a hypersaline lake on Tibetan plateau. Environ Microbiol 9:2603–2621
Jiang H, Dong H, Deng S, Yu B, Huang Q, Wu Q (2009) Response of archaeal community structure to environmental changes in lakes on the Tibetan Plateau, northwestern China. Geomicrobiol J 26:289–297
Jiang H, Huang Q, Deng S, Dong H, Yu B (2010) Planktonic actinobacterial diversity along a salinity gradient of a river and five lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Extremophiles 14:367–376
Letunic I, Bork P (2015) Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: an online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res 44:242–245
Liu Y, Yao T, Zhu L, Jiao N, Liu X, Zeng Y, Jiang HC (2009) Bacterial diversity of freshwater alpine lake Puma Yumco on the Tibetan Plateau. Geomicrobiol J 26:131–145
Liu Y, Priscu JC, Yao T, Vick-Majors TJ, Michaud AB, Jiao N, Hou J, Tian L, Hu A, Chen ZQ (2014) A comparison of pelagic, littoral, and riverine bacterial assemblages in lake Bangongco, Tibetan Plateau. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 89:211–221
Liu K, Liun Y, JiaoN ZhuL, Wang J, Hu A, Liu X (2016a) Vertical variation of bacterial community in Nam Co, a large stratified lake in central Tibetan Plateau. Anton Leeuw 109:1323–1335
Liu Y, Priscu JC, Xiong J, Conrad R, Vick-Majors T, Chu H, Hou J (2016a) Salinity drives archaeal distribution patterns in high altitude lake sediments on the Tibetan Plateau. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 92:fiw033.
Liu W, Jiang H, Jian Y, Wu G (2018a) Gammaproteobacterial diversity and carbon utilization in response to salinity in the lakes on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Geomicrobiol J 35:392–403
Liu X, Li M, Castelle CJ, Probst AJ, Zhou Z, Pan J, Liu Y, Banfield JF, Gu J (2018b) Insights into the ecology, evolution, and metabolism of the widespread Woesearchaeotal lineages. Microbiome 6:102
Ma B, Wang Y, Ye S, Liu S, Stirling E, Gilbert JA, Faust K, Knight R, Jansson JK, Cardona C, Röttjers L, Xu J (2020) Earth microbial co-occurrence network reveals interconnection pattern across microbiomes. Microbiome 8:82
Martin M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J 17:10–12
Mateu MS, Ontiveros VJ, Xavier TM, David A, Casamayor EO (2020) Dynamics and ecological distributions of the Archaea microbiome from inland saline lakes (monegros desert, Spain). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 96:fiaa019.
McArdle BH, Anderson MJ (2001) Fitting multivariate models to community data: a comment on distance-based redundancy analysis. Ecology 82:290–297
Mikhailov IS, Zakharova YR, Bukin YS, Galachyants YP, Petrova DP, Sakirko MV, Likhoshway YV (2019) Co-occurrence networks among bacteria and microbial eukaryotes of Lake Baikal during a spring phytoplankton bloom. Microb Ecol 77:96–109
Milici M, Deng ZL, Tomasch J, Decelle J, Wos-Oxley ML, Wang H, Jáuregui R, Plumeier I, Giebel HA, Badewien TH, Wurst M, Pieper DH, Simon M, Wagner-Döbler I (2016) Co-occurrence analysis of microbial taxa in the Atlantic Ocean reveals high connectivity in the free-living bacterioplankton. Front Microbiol 7:649
Mora-Ruiz MR, Cifuentes A, Font-Verdera F, Pérez-Fernández C, Farias ME, González B, Orfila A, Rosselló-Móra R (2018) Biogeographical patterns of bacterial and archaeal communities from distant hypersaline environments. Syst Appl Microbiol 41:139–150
Naghoni A, Emtiazi G, Amoozegar MA, Cretoiu MS, Stal LJ, Etemadifar Z, Fazeli SAS, Bolhuis H (2017) Microbial diversity in the hypersaline Lake Meyghan. Iran Sci Rep 7:11522
Najjari A, Elshahed MS, Cherif A, Youssef NH (2015) Patterns and determinants of halophilic Archaea (class Halobacteria) diversity in Tunisian endorheic salt lakes and sebkhet systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:4432–4441
Oren A (2013) Life at high salt and low oxygen: how do the halobacteriaceae cope with low oxygen concentrations in their environment. In: Seckbach J, Oren A, Stan-Lotter H (eds) Polyextremophiles: life under multiple forms of stress. Springer, Dordrecht, Netherlands, pp 531–548
Oren A (2014) Halophilic Archaea on earth and in space: growth and survival under extreme conditions. Philos Trans R Soc A 372:20140194
Oren A (2018) Halorubrum. In: Rainey F, Kämpfer P, Trujillo M, Chun J, DeVos P, Hedlund B, Dedysh S (eds) Whitman WB. Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Chichester, pp 1–48
Oren A (2019) Euryarchaeota. In: Gemmell RT, Grant WD, Stan-Lotter H (eds) McGenity TJ. Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria. John Wiley & Sons Ltd, Chichester, pp 1–15
Oren A, Ventosa A (2016) International committee on systematic of prokaryotes subcommittee on the taxonomy of Halobacteriaceae and subcommittee on the taxonomy of Halomonadaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:4291–4295
Ortiz-Alvarez R, Casamayor EO (2016) High occurrence of Pacearchaeota and Woesearchaeota (Archaea superphylum DPANN) in the surface waters of oligotrophic high-altitude lakes. Environ Microbiol Rep 8:210–217
Plominsky AM, Henríquez-Castillo C, Delherbe N, Podell S, Ramirez-Flandes S, Ugalde JA, Santibañez JF, van den Engh G, Hanselmann K, Ulloa O, De la Iglesia R, Allen EE, Trefault N (2018) Distinctive archaeal composition of an artisanal crystallizer pond and functional insights into salt-saturated hypersaline environment adaptation. Front Microbiol 9:1800
Qin H, Wang S, Feng K, He Z, Virta MPJ, Hou W, Dong H, Ye D (2019) Unraveling the diversity of sedimentary sulfate-reducing prokaryotes (SRP) across Tibetan saline lakes using epicPCR. Microbiome 7:71
Qu X, Zhang M, Yang Y, Xie Y, Ren Z, Peng W, Du X (2019) Taxonomic structure and potential nitrogen metabolism of microbial assemblage in a large hypereutrophic steppe lake. Environ Sci Pollut R 26:21151–21160
Ren Z, Wang F, Qu X, Elser JJ, Liu Y, Chu L (2017) Taxonomic and functional differences between microbial communities in Qinghai Lake and its input streams. Front Microbiol 8:2319
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, Van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Schmidt TS, Matias Rodrigues JF, Mering CV (2017) A family of interaction-adjusted indices of community similarity. ISME J 11:791–807
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolskyn L, Garrett WS, Huttenhower C (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 12:R60
Shi Y, Fan K, Li Y, Yang T, Chu H (2019) Archaea enhance the robustness of microbial co-occurrence networks in Tibetan Plateau soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 83:1093–1099
Takai K, Horikoshi K (2000) Rapid detection and quantification of members of the archaeal community by quantitative PCR using fluorogenic probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5066–5072
Vavourakis CD, Andrei AS, Mehrshad M, Ghai R, Sorokin DY, Muyzer G (2018) A metagenomics roadmap to the uncultured genome diversity in hypersaline soda lake sediments. Microbiome 6:168
Ventosa A, Fernández AB, León MJ, Sánchez-Porro C, Rodriguez-Valera F (2014) The Santa Pola Saltern as a model for studying the microbiota of hypersaline environments. Extremophiles 18:811–824
Xiong J, Liu Y, Lin X, Zhang H, Zeng J, Hou J, Yang Y, Yao T, Knight R, Chu H (2012) Geographic distance and pH drive bacterial distribution in alkaline lake sediments across Tibetan Plateau. Environ Microbiol 14:2457–2466
Yang J, Jiang H, Dong H, Wang H, Wu G, Hou W, Liu W, Zhang C, Sun Y, Lai Z (2013) Amoza-encoding Archaea and thaumarchaeol in the lakes on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. China Front Microbiol 4:329
Yang J, Jiang H, Wu G, Liu W (2018) Phylum-level archaeal distributions in the sediments of Chinese lakes with a large range of salinity. Geomicrobiol J 35:404–410
Yang J, Jiang H, Wang LW, B, (2018) Benthic algal community structures and their response to geographic distance and environmental variables in the Qinghai-Tibetan lakes with different salinity. Front Microbiol 9:578
Yang J, Jiang H, Dong H, Liu Y (2019) A comprehensive census of lake microbial diversity on a global scale. Sci China Life Sci 62:1320–1331
Youssef NH, Ashlock-Savage KN, Elshahed MS (2011) Phylogenetic diversities and community structure of members of the extremely halophilic Archaea (Order Halobacteriales) in multiple saline sediment habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:1332–1344
Zhe M, Zhang X, Wang B, Sun R, Zheng D (2017) Hydrochemical regime and its mechanism in Yamzhog Yumco Basin, south Tibet. J Geogr Sci 27:1111–1122
Zheng M, Liu X (2009) Hydrochemistry of salt lakes of the Qinghai-tibet Plateau, China. Aquat Geochem 15:293–320
Zhong ZP, Liu Y, Miao LL, Wang F, Chu LM, Wang JL, Liu ZP (2016) Prokaryotic community structure driven by salinity and ionic concentrations in plateau lakes of the Tibetan Plateau. Appl Environ Microbiol 82:1846–1858
Zhong H, Lehtovirta-Morley L, Liu J, Zheng Y, Lin H, Song D, Todd JD, Tian J, Zhang XH (2020) Novel insights into the Thaumarchaeota in the deepest oceans: their metabolism and potential adaptation mechanisms. Microbiome 8:78
Zhu D, Han R, Long Q, Gao X, Xing J, Shen G, Li Y, Wang R (2020) An evaluation of the core bacterial communities associated with hypersaline environments in the Qaidam Basin, China. Arch Microbiol 202:2093–2103
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China grant numbers 31760034, 31860030, and 21967018, in addition to the Key Research Foundation of Development and Transformation of Qinghai Province grant number 2019SF121, the Applied Basic Research Program of Qinghai Province grant numbers 2020ZJ767, and 2018ZJ930Q, as well as the Team’s Research Program of Microbial Resources in Salt-lakes of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau grant number 2018KYT1. We would like to thank LetPub (www.letpub.com) for providing linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DZ performed most of the experiments, and wrote the manuscript. GS and RW supervised the execution of the experiments, and analyzed the data. ZW, QH, QL, and XG performed the sample collection. JX, GS, and YL provided the bioinformatics technical assistance, and evaluated the data. All authors read and approved the final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Beblo-Vranesevic.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, D., Shen, G., Wang, Z. et al. Distinctive distributions of halophilic Archaea across hypersaline environments within the Qaidam Basin of China. Arch Microbiol 203, 2029–2042 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-02181-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-020-02181-7