Abstract
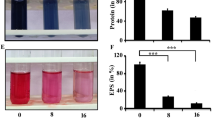
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a potent biofilm forming organism causing several diseases on host involving biofilm. Several natural and synthetic molecules have been explored towards inhibiting the biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In the current report, the role of a natural molecule namely caffeine was examined against the biofilm forming ability of P. aeruginosa. We have observed that caffeine shows substantial antimicrobial activity against P. aeruginosa wherein the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of caffeine was found to be 200 μg/mL. The antibiofilm activity of caffeine was determined by performing a series of experiments using its sub-MIC concentrations (40 and 80 μg/mL). The results revealed that caffeine can significantly inhibit the biofilm development of P. aeruginosa. Caffeine has been found to interfere with the quorum sensing of P. aeruginosa by targeting the swarming motility. Molecular docking analysis further indicated that caffeine can interact with the quorum sensing proteins namely LasR and LasI. Thus, the result indicated that caffeine could inhibit the formation of biofilm by interfering with the quorum sensing of the organism. Apart from biofilm inhibition, caffeine has also been found to reduce the secretion of virulence factors from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Taken together, the results revealed that in addition to biofilm inhibition, caffeine can also decrease the spreading of virulence factors from Pseudomonas aeruginosa.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharyya P, Agarwal B, Goswami M, Maiti D, Baruah S, Tribedi P (2017) Zinc oxide nanoparticle inhibits the biofilm formation of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 111(1):89–99
Bordi C, de Bentzmann S (2011) Hacking into bacterial biofilms: a new therapeutic challenge. Ann Intensive Care 1(1):19
Bothe H, Cammenga HK (1980) Composition, properties, stability and thermal dehydration of crystalline caffeine hydrate. Thermochim Acta 40(1):29–39
Chakraborty P, Joardar S, Ray S, Biswas P, Maiti D, Tribedi P (2018) 3, 6-Di (pyridin-2-yl)-1, 2, 4, 5-tetrazine (pytz)-capped silver nanoparticles (TzAgNPs) inhibit biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a potential approach toward breaking the wall of biofilm through reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Folia Microbiol 63(6):763–772
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2005) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: fifteenth informational supplement M100–S15. CLSI, Wayne
Cortes ME, Consuegra J, Sinisterra RD (2011) Biofilm formation, control and novel strategies for eradication. Sci Against Microbial Pathog Commun Curr Res Technol Adv 2:896–905
Daniels R, Vanderleyden J, Michiels J (2004) Quorum sensing and swarming migration in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28(3):261–289
Das MC, Paul S, Gupta P, Tribedi P, Sarkar S, Manna D, Bhattacharjee S (2016) 3-Amino-4-aminoximidofurazan derivatives: small molecules possessing antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Appl Microbiol 120(4):842–859
Das A, Das MC, Sandhu P, Das N, Tribedi P, De UC, Akhter Y, Bhattacharjee S (2017) Antibiofilm activity of Parkia javanica against Pseudomonas aeruginosa: a study with fruit extract. RSC Adv 7(9):5497–5513
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Essar DW, Eberly L, Hadero A, Crawford IP (1990) Identification and characterization of genes for a second anthranilate synthase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: interchangeability of the two anthranilate synthases and evolutionary implications. J Bacteriol 172:884–900
Gokulakrishnan S, Chandraraj K, Gummadi SN (2005) Microbial and enzymatic methods for the removal of caffeine. Enzyme Microb Technol 37(2):225–232
Goossens H (2003) Susceptibility of multi-drug-resistant pseudomonas aeruginosa in intensive care units: results from the European MYSTIC Study Group. Clin Microbiol Infect 9:980–983
Gupta P, Sarkar S, Das B, Bhattacharjee S, Tribedi P (2016) Biofilm, pathogenesis and prevention-a journey to break the wall: a review. Arch Microbiol 198(1):1–15
Hall-Stoodley L, Stoodley P (2009) Evolving concepts in biofilm infections. Cell Microbiol 11:1034–1043
Kiratisin P, Tucker KD, Passador L (2002) LasR, a transcriptional activator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes, functions as a multimer. J Bacteriol 184(17):4912–4919
Kumar L, Chhibber S, Harjai K (2013) Zingerone inhibit biofilm formation and improve antibiofilm efficacy of ciprofloxacin against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Fitoterapia 90:73–78
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Michel F, Sanner MF (1999) Python: a programming language for software integration and development. J Mol Graph Mod 17:57–61
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ (2009) AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Computl Chem 30(16):2785–2791
Mukherjee K, Tribedi P, Mukhopadhyay B, Sil AK (2013) Antibacterial activity of long-chain fatty alcohols against Mycobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 338:177–183
Oldak E, Trafny EA (2005) Secretion of proteases by Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms exposed to ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:3281–3288
Parsek MR, Greenberg EP (2000) Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: a signaling mechanism involved in associations with higher organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(16):8789–8793
Passador L, Cook JM, Gambello MJ, Rust L, Iglewski BH (1993) Expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes requires cell-to cell communication. Science 260(5111):1127–1130
Ramanavičienė A, Mostovojus V, Bachmatova I, Ramanavičius A (2003) Antibacterial effect of caffeine on Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Acta Med Litu. 10(4):185–188
Saeed ME, Kadioglu O, Seo EJ, Greten HJ, Brenk R, Efferth T (2015) Quantitative structure-activity relationship and molecular docking of artemisinin derivatives to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor. Anticancer Res 35(4):1929–1934
Sharma BK, Saha A, Rahaman L, Bhattacharjee S, Tribedi P (2015) Silver inhibits the biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Adv Microbiol 5(10):677
Tribedi P, Sil AK (2013) Cell surface hydrophobicity: a key component in the degradation of polyethylene succinate by Pseudomonas sp. AKS2. J Appl Microbiol 116:295–303
Tribedi P, Gupta AD, Sil AK (2015) Adaptation of Pseudomonas sp. AKS2 in biofilm on low-density polyethylene surface: an effective strategy for efficient survival and polymer degradation. Bioresour Bioprocess 2(1):1–10
Wagner VE, Iglewski BH (2008) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in CF infection. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 35:124–134
Whiteley M, Bangera MG, Bumgarner RE, Parsek MR (2001) Gene expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Nature 413:860–864
Yakandawala N, Gawande PV, Madhyastha LK (2006) Effect of ovotransferrin, protamine sulfate and EDTA combination on biofilm formation by catheter-associated bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 102:722–727
Zhu H, Bandara R, Conibear TC, Thuruthyil SJ, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S, Givskov M, Willcox MD (2004) Pseudomonas aeruginosa with lasI quorum-sensing deficiency during corneal infection. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45(6):1897–1903
Acknowledgements
PC, DD, PP, SD, DB, SS, SB, RS performed the experiments, analyzed the results and wrote the manuscript. AS, AS designed the experiments, analyzed the results and wrote the manuscript. PT conceived the idea, designed the experiments, analyzed the results and wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, P., Dastidar, D.G., Paul, P. et al. Inhibition of biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by caffeine: a potential approach for sustainable management of biofilm. Arch Microbiol 202, 623–635 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01775-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01775-0