Abstract
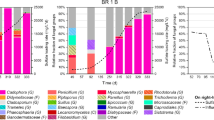
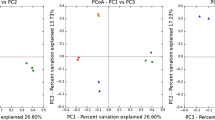
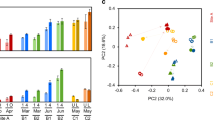
Anaerobic technology has a wide scope of application in different areas such as manufacturing, food industry, and agriculture. Nowadays, it is mainly used to produce electrical and thermal energy from crop processing, solid waste treatment or wastewater treatment. More intensively, trend nowadays is usage of this technology biodegradable and biomass waste processing and biomethane or hydrogen production. In this paper, the diversities of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) under different imputed raw material to the bioreactors were characterized. These diversities at the beginning of sampling and after cultivation were compared. Desulfovibrio, Desulfobulbus, and Desulfomicrobium genus as dominant among sulfate reducers in the bioreactors were detected. The Desulfobulbus species were dominant among other SRB genera before cultivation, but these bacteria were detected only in three out of the seven bioreactors after cultivation dominant.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410
Azabou S, Mechichi T, Patel BK, Sayadi S (2007) Isolation and characterization of a mesophilic heavy-metals-tolerant sulfate-reducing bacterium Desulfomicrobium sp. from an enrichment culture using phosphogypsum as a sulfate source. J Hazard Mater 140:264–270
Barton LL, Hamilton WA (2010) Sulphate-reducing bacteria. Environmental and engineered systems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK et al (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M, Sturrock S (2012) Geneious Basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28:1647–1649
Koschorreck M (2008) Microbial sulphate reduction at a low pH. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 64:329–342
Krich K, Augenstein D, Batmale JP, Benemann J, Rutledge B, Salour D (2005) Biomethane from dairy waste. A sourcebook for the production and use of renewable natural gas in California. USDA Rural Development, California
Kushkevych IV (2015b) Kinetic properties of pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase of intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio piger Vib-7 and Desulfomicrobium sp. Rod-9. Pol J Microbiol 64:107–114
Kushkevych IV (2015d) Activity and kinetic properties of phosphotransacetylase from intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria. Acta Bioch Polonica 62:1037–1108
Kushkevych I (2016b) Dissimilatory sulfate reduction in the intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria. Stud Biol 10:197–228
Kushkevych I, Kollar P, Suchy P, Parak K, Pauk K, Imramovsky A (2015a) Activity of selected salicylamides against intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria. Neuroendocrinol Lett 36:106–113
Kushkevych I, Fafula R, Parak T, Bartos M (2015c) Activity of Na+/K+-activated Mg2+-dependent ATP hydrolase in the cell-free extracts of the sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio piger Vib-7 and Desulfomicrobium sp. Rod-9. Acta Vet Brno 84:3–12
Kushkevych I, Kollar P, Ferreira AL, Palma D (2016a) Antimicrobial effect of salicylamide derivatives against intestinal sulfate-reducing bacteria. J Appl Biomed 14:125–130
Kushkevych I, Vítězová M, Vítěz T, Bartoš M (2017a) Production of biogas: relationship between methanogenic and sulfate-reducing microorganisms. Open Life Sci 12:82–91
Kushkevych I, Vítězová M, Fedrová M, Vochyanová Z, Paráková L, Hošek J (2017b) Kinetic properties of growth of intestinal sulphate-reducing bacteria isolated from healthy mice and mice with ulcerative colitis. Acta Vet Brno 86:405–411
Kushkevych I, Vítězová M, Kos J, Kollár P, Jampílek J (2018) Effect of selected 8-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxanilides on viability and sulfate metabolism of Desulfovibrio piger. J App Biomed 16:1–6
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H (2007) Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Lien T, Madsen M, Steen IH, Gjerdevik K (1998) Desulfobulbusrhabdoformis sp. nov., a sulfate reducer from a water-oil separation system. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:469–474
Lovley DR (1985) Minimum threshold for hydrogen metabolism in methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:1530–1531
Lovley DR, Ferry JG (1985) Production and consumption of H2 during growth of Methanosarcina spp. on acetate. Appl Environ Microbiol 49:247–249
McCarty PL, Smith DP (1986) Anaerobic wastewater treatment. Env Sci Tech 20:1200–1206
Nossa CW, Oberdorf WE, Yang L, Aas JA, Paster BJ, Desantis TZ et al (2010) Design of 16S rRNA gene primers for 454 pyrosequencing of the human foregut microbiome. World J Gastroenterol 16(33):4135–4144
Oremland RS, Polcin S (1982) Methanogenesis and sulfate reduction: competitive and noncompetitive substrates in estuarine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:1270–1276
Postgate JR (1984) The sulfate-reducing bacteria. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
van Houten BHGW., Meulepas RJW, van Doesburg W, Smidt H, Muyzer G, Stams AJM (2009) Desulfovibrio paquesii sp. nov., a hydrogenotrophic sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from a synthesis gas-fed bioreactor treating zinc- and sulfate-rich wastewater. Int J Sys Evol Microbiol 59:229–233
Wawer C, Jetten MSM, Muyzer G (1997) Genetic diversity and expression of the [NiFe] hydrogenase large subunit gene of Desulfovibrio spp. in environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4360–4369
Weijma J (2001) Methanol conversion in high-rate anaerobic reactors. Water Sci Technol 44:7–14
Wilkie A (2008) Biomethane from biomass. In: Harwood C, Demain A (eds) Biowaste and biofuels. ASM, Washington, pp 195–205
Zeikus JG (1977) The biology of methanogenic bacteria. Bact Rev 41:514–541
Zellner G, Messner P, Kneifel H, Winter J (1989) Desulfovibrio simplex sp. nov., a new sulfate-reducing bacterium from a sour whey digester. Arch Microbiol 152:329–334
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grant Agency of the Masaryk University (MUNI/A/0906/2017). The authors wish to acknowledge the institutional support of the Faculty of AgriSciences, Mendel University in Brno funded by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Communicated by Harald Huber.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kushkevych, I., Kováč, J., Vítězová, M. et al. The diversity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in the seven bioreactors. Arch Microbiol 200, 945–950 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1510-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-018-1510-6