Abstract
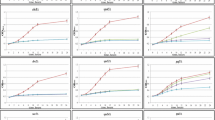
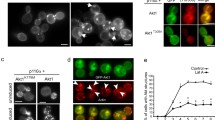
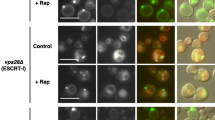
We previously reported that double disruption of protein phosphatase (PPase) genes PTP2 (phosphotyrosine-specific PPase) and MSG5 (phosphotyrosine and phosphothreonine/serine-PPase) causes Ca2+ sensitive growth, whereas the single disruptions do not. This finding suggests that Ptp2p and Msg5p are involved in Ca2+-induced stress response in a redundant manner. To gain insight into the molecular mechanism causing calcium sensitivity of the ∆ptp2 ∆msg5 double disruptant, we performed fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis and found a delayed G1 phase. This delayed G1 was consistent with the defect in bud emergence, and reduced CLN2 transcription upon addition of CaCl2. We also found that Slt2p is hyper-phosphorylated in the Δptp2 Δmsg5 double disruptant and that the vacuole of the Δptp2 Δmsg5 double disruptant is fragmented even in the absence of Ca2+. These findings suggest that both Ptp2p and Msg5p are involved in the G1 to S transition and vacuole morphogenesis possibly through their regulation of Slt2 pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PPase:
-
Protein phosphatase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- Cas :
-
Calcium sensitive
- CWI:
-
Cell wall integrity
References
An X, Zhang Z, Yang K, Huang M (2006) Cotransport of the heterodimer small subunit of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ribonucleotide reductase between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Genetics 173:63–73
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1989) Current protocols in molecular biology, vol 2. Wiley, Boston
Batiza AF, Schulz T, Masson PH (1996) Yeast response to hypotonic shock with a calcium pulse. J Biol Chem 271:23357–23362
Denis V, Cyert MS (2002) Internal Ca2+ release in yeast is triggered by hypertonic shock and mediated by a TRP channel homologue. J Cell Biol 156:29–34
Doi K, Gartner A, Ammerer G, Errede B, Shinkawa H, Sugimoto K, Matsumoto K (1994) MSG5, a novel protein phosphatase promotes adaptation to pheromone response in S. cerevisiae. EMBO J 13:61–70
Flandez M, Cosano IC, Nombela C, Martin H, Molina M (2004) Reciprocal regulation between Slt2 MAPK and isoforms of Msg5 dual-specificity protein phosphatase modulates the yeast cell integrity pathway. J Biol Chem 279:11027–11034
Guan KL, Deschenes RJ, Dixon JE (1992) Isolation and characterization of a second protein tyrosine phosphatase gene, PTP2, from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 267:10024–10030
Gustin MC, Albertyn J, Alexander M, Davenport K (1998) MAP kinase pathways in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70:177–191
Haase SB, Lew DJ (1997) Flow cytomerotic analysis of DNA content in budding yeast. Methods Enzymol 283:322–332
Hoffman-Sommer M, Migdalski A, Rytka J, Kucharczyk R (2005) Multiple function of the vacuolar sorting protein Ccz1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 329(1):197–204
Huang KN, Odinsky SA, Cross FR (1997) Structure-function analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae G1 Cyclin Cln2. Mol Cel Biol 17:4654–4666
Kane PM (2006) The where, when, and how of organelle acidification by the yeast vacuolar H+-ATPase. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70:177–191
Kellermayer R, Aiello DP, Miseta A, Bedwell DM (2003) Extracellular Ca2+ sensing contributes to excess Ca2+ accumulation and vacuolar fragmentation in a pmr1Δ mutant of S. cerevisiae. J Cell Sci 116:1637–1646
Kim KY, Truman AW, Levin DE (2008) Yeast Mpk1 mitogen-activated protein kinase actives transcription through Swi4/Swi6 by a noncatalytic mechanism that requires upstream signal. Mol Cell Biol 28:2579–2589
Kitada K, Yamaguchi E, Arisawa M (1995) Cloning of the candida glabrata TRP1 and HIS3 genes, and construction of their disruptant strains by sequential integrative transformation. Gene 165:203–206
Madden K, Sheu YJ, Baetz K, Andrews B, Snyder M (1997) SBF cell cycle regulator as a target of the yeast PKC-MAP kinase pathway. Science 275:1781–1784
Martin H, Rodriguez-Pachon JM, Ruiz C, Nombela C, Molina M (2000) Regulatory mechanism for modulation of signaling through the cell integrity Slt2-mediated pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 18:1511–1519
Mattison CP, Spencerm SS, Kresge KA, Lee J, Ota IM (1999) Differential regulation of the cell wall integrity mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in the budding yeast by the protein tyrosine phosphatase Ptp2 and Ptp3. Mol Cell Biol 19:7651–7660
Mizunuma M, Hirata D, Miyakawa T (2005) Implication of Pkc1p protein kinase C in sustaining Cln2p level and polarized bud growth in response to calcium signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci 118:4219–4229
Muller EM, Locke EG, Cunningham KW (2001) Differential regulation of two Ca2+ influx systems by pheromone signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 159:1527–1538
Queralt E, Igual JC (2004) Functional distinction between Cln1p and Cln2p cyclins in the control of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitotic cycle. Genetics 168:129–140
Sakumoto N, Mukai Y, Uchida K, Kouchi T, Kuwajima J, Nakagawa Y, Sugioka S, Yamamoto E, Furuyama T, Mizubuchi H, Ohsugi N, Sakuno T, Kikuchi K, Matsuoka I, Ogawa N, Kaneko Y, Harashima S (1999) A series of protein phosphatase gene disruptants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 15:1669–1679
Sakumoto N, Matsuoka I, Mukai Y, Ogawa N, Kaneko Y, Harashima S (2002) A series of double disruptants for protein phosphatase genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and their phenotypic analysis. Yeast 19:587–599
Seeley ES, Kato N, Margolis N, Wickner W, Eitzen G (2002) Genomic analysis of homotypic vacuole fusion. Mol Bio Cell 13:782–794
Sherman F, Hicks J (1991) Micromanipulation and dissection of Asci. Methods Enzymol 194:21–37 Guide to yeast genetics and molecular biology
Vida TA, Emr SD (1995) A new stain for visualizing vacuolar membrane dynamics and endocytosis in yeast. J Cell Biol 128:779–792
Watanabe Y, Irie K, Matsumoto K (1995) Yeast RLM1 encodes a serum response factor-like protein that may function downstream of the Mpk1 (Slt2) mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Mol Cell Biol 15:5740–5749
Winston F, Dollard C, Ricupero-Hovasse SL (1995) Construction of a set of convenient Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains that are isogenic to S288C. Yeast 11:53–55
Wittenberg C, Sugimoto K, Reed SI (1990) G1-specific cyclins of S. cerevisiae: cell cycle periodicity, regulation by mating pheromone, and association with the p34CDC28 protein kinase. Cell 62:225–237
Zarzov P, Mazzoni C, Mann C (1996) The SLT2 (MPK1) MAP kinase is activated during periods of polarized cell growth in yeast. EMBO J 15:83–91
Zolnierowicz S, Bollen M (2000) Protein phosphorylation and protein phosphatases. EMBO J 19:483–488
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research B, 2007 to 2009, to S.H. from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Axel Brakhage.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hermansyah, Sugiyama, M., Kaneko, Y. et al. Yeast protein phosphatases Ptp2p and Msg5p are involved in G1–S transition, CLN2 transcription, and vacuole morphogenesis. Arch Microbiol 191, 721–733 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-009-0498-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-009-0498-3