Abstract
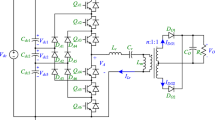
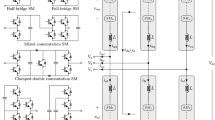
In this paper, a novel high-gain DC–DC converter which is suitable for integrating low-voltage renewable energy source with a common DC bus is presented. The proposed converter is synthesised from a quadratic boost converter (QBC). Two QBC structures are interleaved to reduce the current ripple at the input port (12.9% of input current). The voltage conversion ratio of the proposed interleaved quadratic boost converter (IQBC) is extended by using the voltage lift technique. The energy storage inductors are judiciously coupled to realise a compact IQBC. Experimental results obtained from a 24 to 380 V, 100 W prototype converter validate the novel gain extension method and proposed design concepts. Under full-load condition, the practical efficiency value of the proposed converter is 92.49%. By implementing a simple closed loop, the output voltage of the proposed converter is regulated and maintained constant at 380 V when the input voltage and load current change. Under practical conditions, the percentage voltage regulation and the time response characteristics of the proposed IQBC are extremely satisfactory.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tripathi L, Mishra AK, Dubey AK, Tripathi CB, Baredar P (2016) Renewable energy: an overview on its contribution in current energy scenario of India. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 60:226–233
Kuang Y et al (2016) A review of renewable energy utilization in islands. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 59:504–513
Li W, He X (2011) Review of non-isolated high-step-up DC/DC converters in photovoltaic grid connected applications. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 58(4):1239–1250
Vighetti S, Ferrieux JP, Lembeye Y (2012) Optimization and design of a cascaded DC–DC converter devoted to grid-connected photovoltaic systems. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27(4):2018–2027
Sri Revathi B, Prabhakar M (2016) Non isolated high gain DC–DC converter topologies for PV applications—a comprehensive review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 66:920–933
Ye Y, Cheng KWE (2014) Quadratic boost converter with low buffer capacitor stress. IET Power Electron 7(5):1162–1170
Schmitz L, Martins DC, Coelho RF (2017) Generalized high step-up DC–DC boost-based converter with gain cell. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 64(2):480–493
Forouzesh M, Siwakoti YP, Gorji SA, Blaabjerg F, Lehman B (2017) Step-up DC–DC converters: a comprehensive review of voltage-boosting techniques, topologies, and applications. IEEE Trans Power Electron 32(12):9143–9178
Tofoli FL, de Castro Pereira D, de Paula WJ et al (2015) Survey on nonisolated high-voltage step-up DC–DC topologies based on the boost converter. IET Power Electron 8(10):2044–2057
Zhang X, Green TC (2015) The modular multilevel converter for high step-up ratio DC–DC conversion. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 62(8):4925–4936
Axelrod B, Beck Y, Berkovich Y (2015) High step-up DC–DC converter based on the switched-coupled-inductor boost converter and diode-capacitor multiplier: steady state and dynamics. IET Power Electron 8(8):1420–1428
Girish Ganesan R, Prabhakar M (2014) Non-isolated high step-up interleaved boost converter. Int J Power Electron 6(3):288
Chen Z, Jianping X, Zhou Q (2015) Coupled-inductor boost integrated flyback converter with high-voltage gain and ripple-free input current. IET Power Electron 8(2):213–220
Sri Revathi B, Mahalingam P (2018) Non-isolated high gain DC–DC converter with low device stress and input current ripple. IET Power Electron 11(15):2553–2562
Liu H, Haibing H, Hongfei W, Xing Y, Batarseh I (2016) Overview of high-step-up coupled-inductor boost converters. IEEE J Emerg Sel Top Power Electron 4(2):689–704
Lee S-W, Do H-L (2018) High step-up coupled-inductor cascade boost DC–DC converter with lossless passive snubber. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 65(10):7753–7761
Xuefeng H, Wang J, Wang J, Li Y (2018) A three-winding coupled-inductor DC–DC converter topology with high voltage gain and reduced switch stress. IEEE Trans Power Electron 33(2):1453–1462
Xuefeng H, Gao B, Wang Q, Li L, Chen H (2018) A zero-ripple input current boost converter for high-gain applications. IEEE J Emerg Sel Top Power Electron 6(1):246–254
Sizkoohi HM, Milimonfared J, Taheri M, Salehi S (2015) High step-up soft-switched dual-boost coupled-inductor-based converter integrating multipurpose coupled inductors with capacitor-diode stages. IET Power Electron 8(9):1786–1797
Gang W, Ruan X, Ye Z (2017) Non-isolated high step-up DC–DC converter adopting auxiliary capacitor and coupled inductor. J Mod Power Syst Clean Energy 6(2):384–398
Muhammad M, Armstrong M, Elgendy MA (2017) Analysis and implementation of high-gain non-isolated DC–DC boost converter. IET Power Electron 10(11):1241–1249
Ai J, Lin M (2017) Ultra-large gain step-up coupled-inductor DC–DC converter with an asymmetric voltage multiplier network for a sustainable energy system. IEEE Trans Power Electron 32(9):6896–6903
Andrade AMSS, Mattos E, Schuch L, Hey HL, da Silva Martins ML (2018) Synthesis and comparative analysis of very high step-up DC–DC converters adopting coupled-inductor and voltage multiplier cells. IEEE Trans Power Electron 33(7):5880–5897
Gao W, Zhang Y, Lv X, Lou Q (2017) Non-isolated high-step-up soft switching DC/DC converter with low-voltage stress. IET Power Electron 10(1):120–128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samuel, V.J., Keerthi, G. & Mahalingam, P. Interleaved quadratic boost DC–DC converter with high voltage gain capability. Electr Eng 102, 651–662 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-019-00901-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-019-00901-x