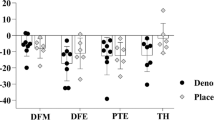
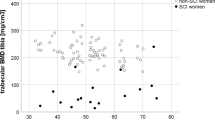
Abstract
Persons with spinal cord injury (SCI) undergo immediate unloading of the skeleton and, as a result, have severe bone loss below the level of lesion associated with increased risk of long-bone fractures. The pattern of bone loss in individuals with SCI differs from other forms of secondary osteoporosis because the skeleton above the level of lesion remains unaffected, while marked bone loss occurs in the regions of neurological impairment. Striking demineralization of the trabecular epiphyses of the distal femur (supracondylar) and proximal tibia occurs, with the knee region being highly vulnerable to fracture because many accidents occur while sitting in a wheelchair, making the knee region the first point of contact to any applied force. To quantify bone mineral density (BMD) at the knee, dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) and/or computed tomography (CT) bone densitometry are routinely employed in the clinical and research settings. A detailed review of imaging methods to acquire and quantify BMD at the distal femur and proximal tibia has not been performed to date but, if available, would serve as a reference for clinicians and researchers. This article will discuss the risk of fracture at the knee in persons with SCI, imaging methods to acquire and quantify BMD at the distal femur and proximal tibia, and treatment options available for prophylaxis against or reversal of osteoporosis in individuals with SCI.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Abbreviations
- SCI:
-
Spinal cord injury
- DXA:
-
Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- QCT:
-
Quantitative computed tomography
- MDCT:
-
Multidetector computed tomography
- pQCT:
-
Peripheral quantitative computerized tomography
- HR-pQCT:
-
High-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography
- mSv:
-
Millisievert
- DF:
-
Distal femur
- PT:
-
Proximal tibia
- LE:
-
Lower extremity
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- RMS-CV%:
-
Root mean square coefficient of variation percent
- LSC:
-
Least significant change
- BMC:
-
Bone mineral content
- aBMD:
-
Areal bone mineral density
- vBMD:
-
Volumetric bone mineral density
- vBMDTb :
-
Trabecular volumetric bone mineral density
- vBMDCt :
-
Cortical volumetric bone mineral density
- App:
-
Apparent
- BV/TV:
-
Bone volume/tissue volume
- Tb.N:
-
Trabecular number
- Tb.Sp:
-
Trabecular spacing
- Tb.Th:
-
Trabecular thickness
- SSIpol :
-
Polar stress strain index
- PI:
-
Polar moment of inertia
- ES:
-
Electrical stimulation
- FES:
-
Functional electrical stimulation
- ZA:
-
Zoledronic acid
- IOF:
-
International Osteoporosis Foundation
- AIS:
-
American Spinal Injury Association Impairment Scale
References
Minaire P, Neunier P, Edouard C, Bernard J, Courpron P, Bourret J (1974) Quantitative histological data on disuse osteoporosis: comparison with biological data. Calcif Tissue Res 17(1):57–73
Bauman WA, Cardozo CP (2015) Osteoporosis in individuals with spinal cord injury. PM & R: the journal of injury, function, and rehabilitation 7(2):188–201 . doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2014.08.948quiz 201
Chantraine A, Nusgens B, Lapiere CM (1986) Bone remodeling during the development of osteoporosis in paraplegia. Calcif Tissue Int 38(6):323–327
Roberts D, Lee W, Cuneo RC, Wittmann J, Ward G, Flatman R, McWhinney B, Hickman PE (1998) Longitudinal study of bone turnover after acute spinal cord injury. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83(2):415–422. doi:10.1210/jcem.83.2.4581
Shields RK, Dudley-Javoroski S, Boaldin KM, Corey TA, Fog DB, Ruen JM (2006) Peripheral quantitative computed tomography: measurement sensitivity in persons with and without spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 87(10):1376–1381. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2006.07.257
Biering-Sorensen F, Bohr HH, Schaadt OP (1990) Longitudinal study of bone mineral content in the lumbar spine, the forearm and the lower extremities after spinal cord injury. Eur J Clin Investig 20(3):330–335
Wilmet E, Ismail AA, Heilporn A, Welraeds D, Bergmann P (1995) Longitudinal study of the bone mineral content and of soft tissue composition after spinal cord section. Paraplegia 33(11):674–677. doi:10.1038/sc.1995.141
Dauty M, Perrouin Verbe B, Maugars Y, Dubois C, Mathe JF (2000) Supralesional and sublesional bone mineral density in spinal cord-injured patients. Bone 27(2):305–309
Morse LR, Battaglino RA, Stolzmann KL, Hallett LD, Waddimba A, Gagnon D, Lazzari AA, Garshick E (2009) Osteoporotic fractures and hospitalization risk in chronic spinal cord injury. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 20(3):385–392. doi:10.1007/s00198-008-0671-6
Ingram RR, Suman RK, Freeman PA (1989) Lower limb fractures in the chronic spinal cord injured patient. Paraplegia 27(2):133–139. doi:10.1038/sc.1989.20
Ragnarsson KT, Sell GH (1981) Lower extremity fractures after spinal cord injury: a retrospective study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 62(9):418–423
Carbone LD, Chin AS, Burns SP, Svircev JN, Hoenig H, Heggeness M, Weaver F (2013) Morbidity following lower extremity fractures in men with spinal cord injury. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 24(8):2261–2267. doi:10.1007/s00198-013-2295-8
Akhigbe T, Chin AS, Svircev JN, Hoenig H, Burns SP, Weaver FM, Bailey L, Carbone L (2015) A retrospective review of lower extremity fracture care in patients with spinal cord injury. J Spinal cord Med 38(1):2–9. doi:10.1179/2045772313Y.0000000156
Frey-Rindova P, de Bruin ED, Stussi E, Dambacher MA, Dietz V (2000) Bone mineral density in upper and lower extremities during 12 months after spinal cord injury measured by peripheral quantitative computed tomography. Spinal Cord 38(1):26–32
de Bruin ED, Vanwanseele B, Dambacher MA, Dietz V, Stussi E (2005) Long-term changes in the tibia and radius bone mineral density following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 43(2):96–101. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.3101685
Warden SJ, Bennell KL, Matthews B, Brown DJ, McMeeken JM, Wark JD (2002) Quantitative ultrasound assessment of acute bone loss following spinal cord injury: a longitudinal pilot study. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 13(7):586–592. doi:10.1007/s001980200077
Frotzler A, Berger M, Knecht H, Eser P (2008) Bone steady-state is established at reduced bone strength after spinal cord injury: a longitudinal study using peripheral quantitative computed tomography (pQCT). Bone 43(3):549–555. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2008.05.006
Eser P, Frotzler A, Zehnder Y, Wick L, Knecht H, Denoth J, Schiessl H (2004) Relationship between the duration of paralysis and bone structure: a pQCT study of spinal cord injured individuals. Bone 34(5):869–880. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2004.01.001
Bauman WA, Spungen AM, Wang J, Pierson RN Jr, Schwartz E (1999) Continuous loss of bone during chronic immobilization: a monozygotic twin study. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 10(2):123–127
Modlesky CM, Majumdar S, Narasimhan A, Dudley GA (2004) Trabecular bone microarchitecture is deteriorated in men with spinal cord injury. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 19(1):48–55. doi:10.1359/JBMR.0301208
Recker R, Lappe J, Davies K, Heaney R (2000) Characterization of perimenopausal bone loss: a prospective study. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 15(10):1965–1973. doi:10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.10.1965
Leblanc AD, Schneider VS, Evans HJ, Engelbretson DA, Krebs JM (1990) Bone mineral loss and recovery after 17 weeks of bed rest. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 5(8):843–850. doi:10.1002/jbmr.5650050807
Vico L, Collet P, Guignandon A, Lafage-Proust MH, Thomas T, Rehaillia M, Alexandre C (2000) Effects of long-term microgravity exposure on cancellous and cortical weight-bearing bones of cosmonauts. Lancet 355(9215):1607–1611
Khoo BC, Brown K, Cann C, Zhu K, Henzell S, Low V, Gustafsson S, Price RI, Prince RL (2009) Comparison of QCT-derived and DXA-derived areal bone mineral density and T scores. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 20(9):1539–1545. doi:10.1007/s00198-008-0820-y
Li N, Li XM, Xu L, Sun WJ, Cheng XG, Tian W (2013) Comparison of QCT and DXA: osteoporosis detection rates in postmenopausal women. Int J Endocrinol 2013:895474. doi:10.1155/2013/895474
del Puente A, Pappone N, Mandes MG, Mantova D, Scarpa R, Oriente P (1996) Determinants of bone mineral density in immobilization: a study on hemiplegic patients. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 6(1):50–54
Troy KL, Morse LR (2015) Measurement of bone: diagnosis of SCI-induced osteoporosis and fracture risk prediction. Topics in spinal cord injury rehabilitation 21(4):267–274. doi:10.1310/sci2104-267
Edwards WB, Schnitzer TJ, Troy KL (2014) Bone mineral and stiffness loss at the distal femur and proximal tibia in acute spinal cord injury. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 25(3):1005–1015. doi:10.1007/s00198-013-2557-5
Biering-Sorensen F, Bohr H, Schaadt O (1988) Bone mineral content of the lumbar spine and lower extremities years after spinal cord lesion. Paraplegia 26(5):293–301
Garland DE, Adkins RH, Stewart CA (2005) Fracture threshold and risk for osteoporosis and pathologic fractures in individuals with spinal cord injury. Top Spinal Cord Inj 11(1):61–69
Garland DE, Adkins RH, Stewart CA, Ashford R, Vigil D (2001) Regional osteoporosis in women who have a complete spinal cord injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83-A(8):1195–1200
Shields RK, Schlechte J, Dudley-Javoroski S, Zwart BD, Clark SD, Grant SA, Mattiace VM (2005) Bone mineral density after spinal cord injury: a reliable method for knee measurement. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86(10):1969–1973. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2005.06.001
Lala D, Craven BC, Thabane L, Papaioannou A, Adachi JD, Popovic MR, Giangregorio LM (2014) Exploring the determinants of fracture risk among individuals with spinal cord injury. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 25(1):177–185. doi:10.1007/s00198-013-2419-1
Garland DE, Adkins RH, Scott M, Singh H, Massih M, Stewart C (2004) Bone loss at the os calcis compared with bone loss at the knee in individuals with spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med 27(3):207–211
Garland DE, Adkins RH, Stewart CA (2008) Five-year longitudinal bone evaluations in individuals with chronic complete spinal cord injury. The journal of spinal cord medicine 31(5):543–550
Baim S, Wilson CR, Lewiecki EM, Luckey MM, Downs RW Jr, Lentle BC (2005) Precision assessment and radiation safety for dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry: position paper of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry. Journal of clinical densitometry: the official journal of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry 8(4):371–378
Diez-Perez A, Adachi JD, Agnusdei D, Bilezikian JP, Compston JE, Cummings SR, Eastell R, Eriksen EF, Gonzalez-Macias J, Liberman UA, Wahl DA, Seeman E, Kanis JA, Cooper C, Group ICIRW (2012) Treatment failure in osteoporosis. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 23(12):2769–2774. doi:10.1007/s00198-012-2093-8
Murphy E, Bresnihan B, FitzGerald O (2001) Validated measurement of periarticular bone mineral density at the knee joint by dual energy x ray absorptiometry. Ann Rheum Dis 60(1):8–13
Bohr HH, Schaadt O (1987) Mineral content of upper tibia assessed by dual photon densitometry. Acta Orthop Scand 58(5):557–559
Li MG, Nilsson KG, Nivbrant B (2004) Decreased precision for BMD measurements in the prosthetic knee using a non-knee-specific software. Journal of clinical densitometry: the official journal of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry 7(3):319–325
McPherson JG, Edwards WB, Prasad A, Troy KL, Griffith JW, Schnitzer TJ (2014) Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry of the knee in spinal cord injury: methodology and correlation with quantitative computed tomography. Spinal Cord 52(11):821–825. doi:10.1038/sc.2014.122
Forrest G, Harkema S, Angeli C, Faghri P, Kirshblum S, Cirnigliaro C, Garbarinin E, Bauman W (2013) Preliminary results on the differential effect on bone of applying multi-muscle electrical stimulation to the leg while supine or standing in patients with SCI: the importance of combining a mechanical intervention with gravitational loading. J Spinal Cord Med Accepted for Publication
Bauman W, Cirnigliaro C, LaFountaine M, Martinez L, Kirshblum S, Spungen A (2014) Zoledronic acid administration failed to prevent bone loss at the knee in persons with acute spinal cord injury: an observational cohort study. J Bone Miner Metab Accepted for Publication
Bakkum AJ, Janssen TW, Rolf MP, Roos JC, Burcksen J, Knol DL, de Groot S (2014) A reliable method for measuring proximal tibia and distal femur bone mineral density using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Med Eng Phys 36(3):387–390. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2013.08.010
Gilchrist N, Hooper G, Frampton C, Maguire P, Heard A, March RL, Maxwell R, Penny I (2013) Measurement of bone density around the Oxford medial compartment knee replacement using iDXA. A precision study. Journal of clinical densitometry: the official journal of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry 16(2):178–182. doi:10.1016/j.jocd.2012.02.015
Morse LR, Lazzari AA, Battaglino R, Stolzmann KL, Matthess KR, Gagnon DR, Davis SA, Garshick E (2009) Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry of the distal femur may be more reliable than the proximal tibia in spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 90(5):827–831. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2008.12.004
Bauman WA, Cirnigliaro CM, La Fountaine MF, Martinez L, Kirshblum SC, Spungen AM (2014) Zoledronic acid administration failed to prevent bone loss at the knee in persons with acute spinal cord injury: an observational cohort study. J Bone Miner Metab. doi:10.1007/s00774-014-0602-x
Schnitzer TJ, Kim K, Marks J, Yeasted R, Simonian N, Chen D (2016) Zoledronic acid treatment after acute spinal cord injury: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled pilot trial. PM & R: the journal of injury, function, and rehabilitation. doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2016.01.012
Lauer R, Johnston TE, Smith BT, Mulcahey MJ, Betz RR, Maurer AH (2007) Bone mineral density of the hip and knee in children with spinal cord injury. J Spinal cord Med 30(Suppl 1):S10–S14
Prentice A, Parsons TJ, Cole TJ (1994) Uncritical use of bone mineral density in absorptiometry may lead to size-related artifacts in the identification of bone mineral determinants. Am J Clin Nutr 60(6):837–842
Tothill P, Avenell A, Reid DM (1994) Precision and accuracy of measurements of whole-body bone mineral: comparisons between Hologic, Lunar and Norland dual-energy X-ray absorptiometers. Br J Radiol 67(804):1210–1217. doi:10.1259/0007-1285-67-804-1210
Pors Nielsen S, Barenholdt O, Diessel E, Armbrust S, Felsenberg D (1998) Linearity and accuracy errors in bone densitometry. Br J Radiol 71(850):1062–1068. doi:10.1259/bjr.71.850.10211067
Craven R, McGillivray A (2009) Detection and treatment of sublesional osteoporosis among patients with chronic spinal cord injury. Topics in spinal cord injury rehabilitation 14(4):1–22. doi:10.1310/sci1404-1
Rittweger J, Goosey-Tolfrey VL, Cointry G, Ferretti JL (2010) Structural analysis of the human tibia in men with spinal cord injury by tomographic (pQCT) serial scans. Bone 47(3):511–518. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2010.05.025
Coupaud S, McLean AN, Purcell M, Fraser MH, Allan DB (2015) Decreases in bone mineral density at cortical and trabecular sites in the tibia and femur during the first year of spinal cord injury. Bone 74:69–75. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2015.01.005
Burghardt AJ, Link TM, Majumdar S (2011) High-resolution computed tomography for clinical imaging of bone microarchitecture. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(8):2179–2193. doi:10.1007/s11999-010-1766-x
Ito M, Ikeda K, Nishiguchi M, Shindo H, Uetani M, Hosoi T, Orimo H (2005) Multi-detector row CT imaging of vertebral microstructure for evaluation of fracture risk. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 20(10):1828–1836. doi:10.1359/JBMR.050610
Lee SY, Kwon SS, Kim HS, Yoo JH, Kim J, Kim JY, Min BC, Moon SJ, Sung KH (2015) Reliability and validity of lower extremity computed tomography as a screening tool for osteoporosis. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 26(4):1387–1394. doi:10.1007/s00198-014-3013-x
Giangregorio LM, Gibbs JC, Craven BC (2016) Measuring muscle and bone in individuals with neurologic impairment; lessons learned about participant selection and pQCT scan acquisition and analysis. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 27(8):2433–2446. doi:10.1007/s00198-016-3572-0
Engelke K, Lang T, Khosla S, Qin L, Zysset P, Leslie WD, Shepherd JA, Schousboe JT (2015) Clinical use of quantitative computed tomography (QCT) of the hip in the management of osteoporosis in adults: the 2015 ISCD official positions—part I. Journal of clinical densitometry: the official journal of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry 18(3):338–358. doi:10.1016/j.jocd.2015.06.012
Cervinka T, Sievanen H, Hyttinen J, Rittweger J (2014) Bone loss patterns in cortical, subcortical, and trabecular compartments during simulated microgravity. J Appl Physiol 117(1):80–88. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00021.2014
Dudley-Javoroski S, Amelon R, Liu Y, Saha PK, Shields RK (2014) High bone density masks architectural deficiencies in an individual with spinal cord injury. J Spinal cord Med 37(3):349–354. doi:10.1179/2045772313Y.0000000166
Bouxsein ML, Boyd SK, Christiansen BA, Guldberg RE, Jepsen KJ, Muller R (2010) Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 25(7):1468–1486. doi:10.1002/jbmr.141
Krug R, Burghardt AJ, Majumdar S, Link TM (2010) High-resolution imaging techniques for the assessment of osteoporosis. Radiol Clin N Am 48(3):601–621. doi:10.1016/j.rcl.2010.02.015
Dudley-Javoroski S, Shields RK (2012) Regional cortical and trabecular bone loss after spinal cord injury. J Rehabil Res Dev 49(9):1365–1376
Coupaud S, McLean AN, Allan DB (2009) Role of peripheral quantitative computed tomography in identifying disuse osteoporosis in paraplegia. Skelet Radiol 38(10):989–995. doi:10.1007/s00256-009-0674-1
Frotzler A, Cheikh-Sarraf B, Pourtehrani M, Krebs J, Lippuner K (2015) Long-bone fractures in persons with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 53(9):701–704. doi:10.1038/sc.2015.74
Pop LC, Sukumar D, Tomaino K, Schlussel Y, Schneider SH, Gordon CL, Wang X, Shapses SA (2015) Moderate weight loss in obese and overweight men preserves bone quality. Am J Clin Nutr 101(3):659–667. doi:10.3945/ajcn.114.088534
Giangregorio L, Lala D, Hummel K, Gordon C, Craven BC (2013) Measuring apparent trabecular density and bone structure using peripheral quantitative computed tomography at the tibia: precision in participants with and without spinal cord injury. Journal of clinical densitometry: the official journal of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry 16(2):139–146. doi:10.1016/j.jocd.2012.02.003
Edwards WB, Schnitzer TJ, Troy KL (2014) The mechanical consequence of actual bone loss and simulated bone recovery in acute spinal cord injury. Bone 60:141–147. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2013.12.012
Rajapakse CS, Magland J, Zhang XH, Liu XS, Wehrli SL, Guo XE, Wehrli FW (2009) Implications of noise and resolution on mechanical properties of trabecular bone estimated by image-based finite-element analysis. Journal of orthopaedic research: official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society 27(10):1263–1271. doi:10.1002/jor.20877
Wehrli FW, Gomberg BR, Saha PK, Song HK, Hwang SN, Snyder PJ (2001) Digital topological analysis of in vivo magnetic resonance microimages of trabecular bone reveals structural implications of osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 16(8):1520–1531. doi:10.1359/jbmr.2001.16.8.1520
Chesnut CH 3rd, Majumdar S, Newitt DC, Shields A, Van Pelt J, Laschansky E, Azria M, Kriegman A, Olson M, Eriksen EF, Mindeholm L (2005) Effects of salmon calcitonin on trabecular microarchitecture as determined by magnetic resonance imaging: results from the QUEST study. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 20(9):1548–1561. doi:10.1359/JBMR.050411
Slade JM, Bickel CS, Modlesky CM, Majumdar S, Dudley GA (2005) Trabecular bone is more deteriorated in spinal cord injured versus estrogen-free postmenopausal women. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 16(3):263–272. doi:10.1007/s00198-004-1665-7
Lazo MG, Shirazi P, Sam M, Giobbie-Hurder A, Blacconiere MJ, Muppidi M (2001) Osteoporosis and risk of fracture in men with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 39(4):208–214. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.3101139
Vestergaard P, Krogh K, Rejnmark L, Mosekilde L (1998) Fracture rates and risk factors for fractures in patients with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 36(11):790–796
Parsons KC, Lammertse DP (1991) Rehabilitation in spinal cord disorders. 1. Epidemiology, prevention, and system of care of spinal cord disorders. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 72(4-S):S293–S294
Freehafer AA (1995) Limb fractures in patients with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 76(9):823–827
Garland DE, Adkins RH, Kushwaha V, Stewart C (2004) Risk factors for osteoporosis at the knee in the spinal cord injury population. J Spinal Cord Med 27(3):202–206
Martinez A, Cuenca J, Herrera A, Domingo J (2002) Late lower extremity fractures in patients with paraplegia. Injury 33(7):583–586
Gifre L, Vidal J, Carrasco J, Portell E, Puig J, Monegal A, Guanabens N, Peris P (2014) Incidence of skeletal fractures after traumatic spinal cord injury: a 10-year follow-up study. Clin Rehabil 28(4):361–369. doi:10.1177/0269215513501905
Comarr AE, Hutchinson RH, Bors E (1962) Extremity fractures of patients with spinal cord injuries. Am J Surg 103:732–739
Zehnder Y, Luthi M, Michel D, Knecht H, Perrelet R, Neto I, Kraenzlin M, Zach G, Lippuner K (2004) Long-term changes in bone metabolism, bone mineral density, quantitative ultrasound parameters, and fracture incidence after spinal cord injury: a cross-sectional observational study in 100 paraplegic men. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 15(3):180–189. doi:10.1007/s00198-003-1529-6
Freehafer AA, Mast WA (1965) Lower extremity fractures in patients with spinal-cord injury. J Bone Joint Surg Am 47:683–694
Garland DE, Maric Z, Adkins RH, Stewart CA (1993) Bone mineral density about the knee in spinal cord injured patients with pathologic fractures. Contemp Orthop 26:375–379
Mazess RB (1990) Bone densitometry of the axial skeleton. Orthopedic Clinic North Am 21(1):51–63
Eser P, Frotzler A, Zehnder Y, Denoth J (2005) Fracture threshold in the femur and tibia of people with spinal cord injury as determined by peripheral quantitative computed tomography. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86(3):498–504. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2004.09.006
Frost HM (1987) The mechanostat: a proposed pathogenic mechanism of osteoporosis and the bone mass effects of mechanical and nonmechanical agents. Bone Min 2(2):73–85
Isaacson J, Brotto M (2014) Physiology of mechanotransduction: how do muscle and bone “talk” to one another? Clin Rev Bone Min metab 12(2):77–85. doi:10.1007/s12018-013-9152-3
Dolbow DR, Gorgey AS, Gater DR, Moore JR (2014) Body composition changes after 12 months of FES cycling: case report of a 60-year-old female with paraplegia. Spinal Cord 52(Suppl 1):S3–S4. doi:10.1038/sc.2014.40
Pacy PJ, Hesp R, Halliday DA, Katz D, Cameron G, Reeve J (1988) Muscle and bone in paraplegic patients, and the effect of functional electrical stimulation. Clin Sci 75(5):481–487
Biering-Sorensen F, Hansen B, Lee BS (2009) Non-pharmacological treatment and prevention of bone loss after spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Spinal Cord 47(7):508–518. doi:10.1038/sc.2008.177
Guertin PA (2009) Recovery of locomotor function with combinatory drug treatments designed to synergistically activate specific neuronal networks. Curr Med Chem 16(11):1366–1371
de Bruin ED, Frey-Rindova P, Herzog RE, Dietz V, Dambacher MA, Stussi E (1999) Changes of tibia bone properties after spinal cord injury: effects of early intervention. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 80(2):214–220
Giangregorio LM, Hicks AL, Webber CE, Phillips SM, Craven BC, Bugaresti JM, McCartney N (2005) Body weight supported treadmill training in acute spinal cord injury: impact on muscle and bone. Spinal Cord 43(11):649–657. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.3101774
Bloomfield SA, Mysiw WJ, Jackson RD (1996) Bone mass and endocrine adaptations to training in spinal cord injured individuals. Bone 19(1):61–68
Frotzler A, Coupaud S, Perret C, Kakebeeke TH, Hunt KJ, Donaldson Nde N, Eser P (2008) High-volume FES-cycling partially reverses bone loss in people with chronic spinal cord injury. Bone 43(1):169–176. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2008.03.004
Lai CH, Chang WH, Chan WP, Peng CW, Shen LK, Chen JJ, Chen SC (2010) Effects of functional electrical stimulation cycling exercise on bone mineral density loss in the early stages of spinal cord injury. J Rehabil Med 42(2):150–154. doi:10.2340/16501977-0499
Eser P, de Bruin ED, Telley I, Lechner HE, Knecht H, Stussi E (2003) Effect of electrical stimulation-induced cycling on bone mineral density in spinal cord-injured patients. Eur J Clin Investig 33(5):412–419
Dudley-Javoroski S, Saha PK, Liang G, Li C, Gao Z, Shields RK (2012) High dose compressive loads attenuate bone mineral loss in humans with spinal cord injury. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 23(9):2335–2346. doi:10.1007/s00198-011-1879-4
Belanger M, Stein RB, Wheeler GD, Gordon T, Leduc B (2000) Electrical stimulation: can it increase muscle strength and reverse osteopenia in spinal cord injured individuals? Arch Phys Med Rehabil 81(8):1090–1098
Chen SC, Lai CH, Chan WP, Huang MH, Tsai HW, Chen JJ (2005) Increases in bone mineral density after functional electrical stimulation cycling exercises in spinal cord injured patients. Disabil Rehabil 27(22):1337–1341. doi:10.1080/09638280500164032
Mohr T, Podenphant J, Biering-Sorensen F, Galbo H, Thamsborg G, Kjaer M (1997) Increased bone mineral density after prolonged electrically induced cycle training of paralyzed limbs in spinal cord injured man. Calcif Tissue Int 61(1):22–25
Shields RK, Dudley-Javoroski S (2007) Musculoskeletal adaptations in chronic spinal cord injury: effects of long-term soleus electrical stimulation training. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 21(2):169–179. doi:10.1177/1545968306293447
Dudley-Javoroski S, Shields RK (2013) Active-resisted stance modulates regional bone mineral density in humans with spinal cord injury. J spinal cord Med 36(3):191–199. doi:10.1179/2045772313Y.0000000092
Forrest G, Harkema SJ, Angeli CA, Faghri PD, Kirshblum SC, Cirnigliaro CM, LaFountaine, Garbarini E, Bauman WA. (2014) Preliminary results on the differential effect on bone of applying multi-muscle electrical stimulation to the leg while supine or standing in patients with SCI: the importance of combining a mechanical intervention with gravitational loading. The journal of spinal cord medicine In Preparation
Ben M, Harvey L, Denis S, Glinsky J, Goehl G, Chee S, Herbert RD (2005) Does 12 weeks of regular standing prevent loss of ankle mobility and bone mineral density in people with recent spinal cord injuries? Australian J physiother 51(4):251–256
Warden SJ, Bennell KL, Matthews B, Brown DJ, McMeeken JM, Wark JD (2001) Efficacy of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in the prevention of osteoporosis following spinal cord injury. Bone 29(5):431–436
Wuermser LA, Beck LA, Lamb JL, Atkinson EJ, Amin S (2014) The effect of low-magnitude whole body vibration on bone density and microstructure in men and women with chronic motor complete paraplegia. J Spinal cord Med. doi:10.1179/2045772313Y.0000000191
Bultink IE, Baden M, Lems WF (2013) Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: an update on current pharmacotherapy and future directions. Expert Opin Pharmacother 14(2):185–197. doi:10.1517/14656566.2013.761975
Chappard D, Minaire P, Privat C, Berard E, Mendoza-Sarmiento J, Tournebise H, Basle MF, Audran M, Rebel A, Picot C et al (1995) Effects of tiludronate on bone loss in paraplegic patients. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 10(1):112–118. doi:10.1002/jbmr.5650100116
Pearson EG, Nance PW, Leslie WD, Ludwig S (1997) Cyclical etidronate: its effect on bone density in patients with acute spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 78(3):269–272
Nance PW, Schryvers O, Leslie W, Ludwig S, Krahn J, Uebelhart D (1999) Intravenous pamidronate attenuates bone density loss after acute spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 80(3):243–251
Gilchrist NL, Frampton CM, Acland RH, Nicholls MG, March RL, Maguire P, Heard A, Reilly P, Marshall K (2007) Alendronate prevents bone loss in patients with acute spinal cord injury: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(4):1385–1390. doi:10.1210/jc.2006-2013
Bauman WA, Wecht JM, Kirshblum S, Spungen AM, Morrison N, Cirnigliaro C, Schwartz E (2005) Effect of pamidronate administration on bone in patients with acute spinal cord injury. J Rehabil Res Dev 42(3):305–313
Bubbear JS, Gall A, Middleton FR, Ferguson-Pell M, Swaminathan R, Keen RW (2011) Early treatment with zoledronic acid prevents bone loss at the hip following acute spinal cord injury. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 22(1):271–279. doi:10.1007/s00198-010-1221-6
Shapiro J, Smith B, Beck T, Ballard P, Dapthary M, BrintzenhofeSzoc K, Caminis J (2007) Treatment with zoledronic acid ameliorates negative geometric changes in the proximal femur following acute spinal cord injury. Calcif Tissue Int 80(5):316–322. doi:10.1007/s00223-007-9012-6
Gifre L, Vidal J, Carrasco JL, Muxi A, Portell E, Monegal A, Guanabens N, Peris P (2016) Denosumab increases sublesional bone mass in osteoporotic individuals with recent spinal cord injury. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 27(1):405–410. doi:10.1007/s00198-015-3333-5
Schousboe JT (2014) ISCD in 2014: state of the society. Journal of clinical densitometry: the official journal of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry 17(3):328–329. doi:10.1016/j.jocd.2014.04.118
Krueger D (2015) ISCD in 2015: state of the society. Journal of clinical densitometry: the official journal of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry 18(3):445–446. doi:10.1016/j.jocd.2015.06.004
Qin W, Li X, Peng Y, Harlow LM, Ren Y, Wu Y, Li J, Qin Y, Sun J, Zheng S, Brown T, Feng JQ, Ke HZ, Bauman WA, Cardozo CP (2015) Sclerostin Antibody Preserves the Morphology and Structure of Osteocytes and Blocks the Severe Skeletal Deterioration After Motor-Complete Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. J Bone Miner Res 30(11):1994–2004
Qin W, Zhao W, Li X, Peng Y, Harlow LM, Li J, Qin Y, Pan J, Wu Y, Ran L, Ke HZ, Cardozo CP, Bauman WA. Mice with sclerostin gene deletion are resistant to the severe sublesional bone loss induced by spinal cord injury. Osteoporos Int. 2016 20. [Epub ahead of print])
Battaglino RA, Sudhakar S, Lazzari AA, Garshick E, Zafonte R, Morse LR (2012) Circulating sclerostin is elevated in short-term and reduced in long-term SCI. Bone 51(3):600–605. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2012.04.019
Doherty AL, Battaglino RA, Donovan J, Gagnon D, Lazzari AA, Garshick E, Zafonte R, Morse LR (2014) Adiponectin is a candidate biomarker of lower extremity bone density in men with chronic spinal cord injury. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 29(1):251–259. doi:10.1002/jbmr.2020
Moreno C (2001) Protocol for using dual photon absorptiometry software to measure BMD of distal femur and proximal tibia. Master’s thesis, McMaster University, Hamilton
Morse LR, Sudhakar S, Danilack V, Tun C, Lazzari A, Gagnon DR, Garshick E, Battaglino RA (2012) Association between sclerostin and bone density in chronic spinal cord injury. J Bone Miner Res Off J Am Soc Bone Miner Res 27(2):352–359. doi:10.1002/jbmr.546
Morse LR, Sudhakar S, Lazzari AA, Tun C, Garshick E, Zafonte R, Battaglino RA (2013) Sclerostin: a candidate biomarker of SCI-induced osteoporosis. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 24(3):961–968. doi:10.1007/s00198-012-2072-0
McCarthy ID, Bloomer Z, Gall A, Keen R, Ferguson-Pell M (2012) Changes in the structural and material properties of the tibia in patients with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 50(4):333–337. doi:10.1038/sc.2011.143
Tan CO, Battaglino RA, Doherty AL, Gupta R, Lazzari AA, Garshick E, Zafonte R, Morse LR (2014) Adiponectin is associated with bone strength and fracture history in paralyzed men with spinal cord injury. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 25(11):2599–2607. doi:10.1007/s00198-014-2786-2
Dudley-Javoroski S, Shields RK (2010) Longitudinal changes in femur bone mineral density after spinal cord injury: effects of slice placement and peel method. Osteoporosis international: a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA 21(6):985–995. doi:10.1007/s00198-009-1044-5
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the James J. Peters Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Bronx, NY, the Department of Veterans Affairs Rehabilitation Research & Development Service, and the Kessler Institute for Rehabilitation, West Orange, NJ, for their support to perform this work. The authors would also like to thank the Department of Physical Therapy, School of Health Related Professions, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, NJ, USA and Alex T. Lombard for his assistance completing the comprehensive literature review necessary to complete this review article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Grant sources
Veterans Affairs Rehabilitation Research and Development Service (#B9212-C, B2020-C) and the James J. Peters VA Medical Center.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cirnigliaro, C.M., Myslinski, M.J., La Fountaine, M.F. et al. Bone loss at the distal femur and proximal tibia in persons with spinal cord injury: imaging approaches, risk of fracture, and potential treatment options. Osteoporos Int 28, 747–765 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-016-3798-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-016-3798-x