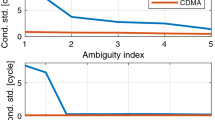
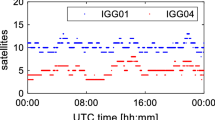
Abstract
As the Chinese BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) has become operational in the Asia-Pacific region, it is of importance to better understand as well as demonstrate the capabilities that a combination of BeiDou with GPS brings to positioning. In this contribution, a formal and empirical analysis is given of the single-epoch RTK positioning capabilities of such a combined system. This will be done for the single- and dual-frequency case, and in comparison with the BDS- and GPS-only performances. It will be shown that with the combined system, when more satellites are available, much larger than the customary cut-off elevations can be used. This is important, as such measurement set-up will significantly increase the GNSS applicability in constrained environments, such as e.g. in urban canyons or when low-elevation multipath is present.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao C, Jing G, Luo M (2008a) COMPASS satellite navigation system development. In: PNT challenges and opportunities symposium. Stanford, California
Cao W, O’Keefe K, Cannon M (2008b) Evaluation of COMPASS ambiguity resolution performance using geometric-based techniques with comparison to GPS and Galileo. In: Proceedings of the ION GNSS, Savannah
Chen H, Huang Y, Chiang K, Yang M, Rau R (2009) The performance comparison between GPS and BeiDou-2/COMPASS: a perspective from Asia. J Chin inst of eng 32(5):679–689
CSNO (2012) BeiDou navigation satellite system signal. In: Space interface control document by China satellite navigation office (CSNO). Open service signal B1I (Version 1.0). Tech. rep., December 2012
Euler HJ, Goad C (1991) On optimal filtering of GPS dual frequency observations without using orbit information. Bull Geod 65:130–143
Gibbons G (2013) GNSS News. Inside GNSS, p 1
Goad C (1998) Short distance GPS models (Chap. 11). In: Teunissen PJG, Kleusberg A (eds) GPS for geodesy, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 457–482
Grelier T, Ghion A, Dantepal J, Ries L, DeLatour A, Issler JL, Avila-Rodriguez J, Wallner S, Hein G (2007) Compass signal structure and first measurements. In: Proceedings of the ION GNSS, Fort Worth, pp 3015–3024
Guo H, He H, Li J, Wang A (2011) Estimation and mitigation of the main errors for centimetre-level COMPASS RTK solutions over medium-long baselines. J Navig 64:S113–S126. doi:10.1017/S0373463311000324
Han C, Yang Y, Cai Z (2011) BeiDou navigation satellite system and its timescales. Metrol 48(4). doi:10.1088/0026-1394/48/4/S13
Huang YS, Tsai ML (2008) The impact of Compass/Beidou-2 on future GNSS: a perspective from Asia. In: Proceedings of the ION GNSS, Savannah, pp 2227–2238
Li W, Teunissen PJG, Zhang B, Verhagen S (2013) Precise point positioning using GPS and Compass observations. In: Sun et al. (eds) Lect Notes in Electr Eng, Chap. 33, vol 2, pp 367–378
Montenbruck O, Hauschild A, Steigenberger P, Hugentobler U, Riley S (2012) A COMPASS for Asia: first experience with the BeiDou-2 regional Navigation System. In: Proceedings of the IGS workshop 2012, Olsztyn, 23–27 July 2012
Montenbruck O, Hauschild A, Steigenberger P, Hugentobler U, Teunissen P, Nakamura S (2013) Initial assessment of the COMPASS/BeiDou-2 regional navigation satellite system. GPS Solut 17(2):211–222. doi:10.1007/s10291-012-0272-x
Nadarajah N, Teunissen PJG, Raziq N (2013) BeiDou inter-satellite-type bias evaluation and calibration for mixed receiver attitude determination. Sensors 13(7):9435–9463
Odijk D, Teunissen PJG (2008) ADOP in closed form for a hierarchy of multi-frequency single-baseline GNSS models. J Geod 82:473
Odijk D, Teunissen PJG (2013) Characterization of between-receiver GPS-Galileo inter-system biases and their effect on mixed ambiguity resolution. GPS Solut 17(4):521–533. doi:10.1007/s10291-012-0298-0
Odolinski R, Teunissen PJG, Odijk D (2013) An analysis of combined COMPASS/BeiDou-2 and GPS single- and multiple-frequency RTK positioning. In: Proceedings of the ION Pacific PNT, Honolulu, pp 69–90
Qu J, Yuan H, Zhang X, Ouyang G (2012) Single-epoch COMPASS carrier-phase ambiguous resolution using three civil frequencies and special constellations. In: Proceedings of the ION GNSS, Nashville
Shi C, Zhao Q, Li M, Tang W, Hu Z, Lou Y, Zhang H, Niu X, Liu J (2012) Precise orbit determination of Beidou Satellites with precise positioning. Sci China Earth Sci 55:1079–1086. doi:10.1007/s11430-012-4446-8
Shi C, Zhao Q, Hu Z, Liu J (2013) Precise relative positioning using real tracking data from COMPASS GEO and IGSO satellites. GPS Solut 17(1):103–119. doi:10.1007/s10291-012-0264-x
Steigenberger P, Hauschild A, Hugentobler U, Montenbruck O (2012) Performance analysis of Compass orbit and clock determination and Compass only PPP. In: Proceedings of the IGS Workshop 2012, Olsztyn, 23–27 July 2012
Steigenberger P, Hugentobler U, Hauschild A, Montenbruck O (2013) Orbit and clock analysis of COMPASS GEO and IGSO satellites. J Geod. doi:10.1007/s00190-013-0625-4
Teunissen PJG (1995) The least squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: a method for fast GPS integer estimation. J Geod 70:65–82
Teunissen PJG (1997) A canonical theory for short GPS baselines. Part I: The baseline precision, Part II: The ambiguity precision and correlation, Part III: The geometry of the ambiguity search space, Part IV: Precision versus reliability. J Geod 71(6): 320–336, 71(7): 389–401, 71(8): 486–501, 71(9): 513–525
Teunissen PJG (1998) Success probability of integer GPS ambiguity rounding and bootstrapping. J Geod 72:606–612
Teunissen PJG (1999) An optimality property of the integer least-squares estimator. J Geod 73:587–593
Teunissen PJG, de Jonge P, Tiberius C (1996) The volume of the GPS ambiguity search space and its relevance for integer ambiguity resolution In:Proceedings of the ION GPS, vol 9, pp 889–898
Verhagen S, Teunissen PJG (2013) Ambiguity resolution performance with GPS and BeiDou for LEO formation flying. J Adv Space Res. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2013.03.007
Verhagen S, Li B, Teunissen PJG (2013) Ps-LAMBDA: ambiguity success rate evaluation software for interferometric applications. Comput Geosci 54:361–376
Yang Y, Li J, Xu J, Tang J, Guo H, He H (2011) Contribution of the compass satellite navigation system to global PNT users. Chinese Sci Bull 56(26):2813–2819
Zhang S, Guo J, Li B, Rizos C (2010) An analysis of satellite visibility and relative positioning precision of COMPASS. In: Proceedings of the symposium for Chinese professionals in GPS, pp 41–46. Singhai, 18–20 August 2010
Acknowledgments
This work has been executed in the framework of the Positioning Program of the Cooperative Research Centre for Spatial Information (CRC–SI). The first author is the recipient of an Australian Research Council (ARC) Federation Fellowship (Project number FF0883188). All this support is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Proof of Theorem (Combined-system ADOP) The ambiguity variance matrix of the combined system can be expressed in the single-system variance matrices as
Upon taking the determinant, we get
where we made use of the determinant property \(|I_{m}-BC|=|I_{n}-CB|\) for \(m \times n\) matrices \(B\) and \(C^{T}\). With the use of
we can then finally write
from which the expression (12) for the combined ADOP follows. \(\square \)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teunissen, P.J.G., Odolinski, R. & Odijk, D. Instantaneous BeiDou+GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles. J Geod 88, 335–350 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-013-0686-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-013-0686-4