Abstract
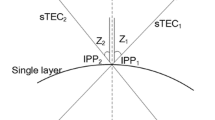
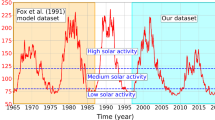
This work aims to contribute to the understanding of the influence of the ionospheric layer height (ILH) on the thin layer ionospheric model (TLIM) used to retrieve ionospheric information from the GNSS observations. Particular attention is paid to the errors caused on the estimation of the vertical total electron content (vTEC) and the GNSS satellites and receivers inter-frequency biases (IFB), by the use of an inappropriate ILH. The work relies upon numerical simulations performed with an empirical model of the Earth’s ionosphere: the model is used to create realistic but controlled ionospheric scenarios and the errors are evaluated after recovering those scenarios with the TLIM. The error assessment is performed in the Central and the northern part of the South American continents, a region where large errors are expected due to the combined actions of the Appleton Anomaly of the ionosphere and the South-Atlantic anomaly of the geomagnetic field. According to this study, there does not exist a unique ILH that cancels the vTEC error for the whole region under consideration. The ILH that cancels the regional mean vTEC error varies with the solar activity and season. The latitude-dependent conversion error propagates to the parameters of the model used to represent the latitudinal variation on the vTEC on the ionospheric layer, and to the IFB, when these values are simultaneously estimated from the observed sTEC. Besides, the ILH that cancels the regional mean vTEC error is different from the one that cancels the IFB error and the difference between both ILH varies with the solar activity and season.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdu MA, Batista IS, Carrasco AJ, Brum CGM (2005) South Atlantic magnetic anomaly ionization: a review and a new focus on electrodynamic effects in the equatorial ionosphere. J Atmos Sol-Terr Phys 67: 1643–1657
Appleton EV (1946) Two anomalies in the ionosphere. Nature 157: 691
Azpilicueta F, Brunini C (2011) A new concept regarding the cause of ionosphere semiannual and annual anomalies. J. Geophys. Res. 116:A01307. doi:10.1029/2010JA015977
Birch MJ, Hargreaves JK, Bailey GJ (2002) On the use of an effective ionospheric height in electron content measurement by GPS reception. Radio Sci 37(1): 1015. doi:10.1029/2000RS002601
Brunini C, Azpilicueta F (2010) GPS slant total electron content accuracy using the single layer model under different geomagnetic regions and ionospheric conditions. J Geod 84(5):239–304. doi:10.1007/s00190-010-0367-5
Ciraolo L, Spalla P (1997) Comparison of ionospheric total electron content from the Navy Navigation Satellite System and the GPS. Radio Sci 32(3): 1071–1080
Coïsson P, Radicella SM, Leitinger R, Nava B (2006) Topside electron density in IRI and NeQuick: features and limitations. Adv Space Res 37: 937–942
Di Giovanni G, Radicella SM (1990) An analytical model of the electron density profile in the ionosphere. Adv Space Res 10(11): 27–30
Davies K, Hartmann GK (1997) Studying the ionosphere with the Global Positioning System. Radio Sci 32(4): 1695–1703
Enge P, Walter T, Pullen S, Kee C, Chao YC, Tsai Y-J (1996) Wide area augmentation of the global positioning system. Proc IEEE 84: 1063–1088
Hernández-Pajarez M, Juan JM, Sanz J, Orus R, Garcia-Rigo A, Feltens J, Komjathy A, Schaer SC, Krankowski A (2009) The IGS VTEC map: a reliable source of ionospheric information since 1998. J. Geod. 83:263–275
Hochegger G, Nava B, Radicella SM, Leitinger R (2000) A family of ionospheric models for different uses Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part C: Solar. Terr Planet Sci 25(4): 307–310
ITU (2003) Ionospheric propagation data and prediction methods required for the design of satellite services and systems. Recommendation, Geneva, pp 531–537
Kalton G (1983) Introduction to survey sampling, SAGE University Paper 35. ISBN 0-8039-2126-8
Klobuchar JA (1987) Ionospheric time-delay algorithm for single-frequency GPS users. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 23(1): 325–331
Klobuchar JA (1996) Ionospheric effects on GPS, Chapter 12. In: Parkinson BW, Spilker JJ (eds) Global positioning system: theory and applications, vol I, progress in astronautics and aeronautics, vol 163. AIAA Inc, Washington DC
Komjathy A, Langley RB (1996) The effect of shell height on high precision ionospheric modelling using GPS. In: Proceedings of the international GPS service for geodynamics (IGS) workshop in Silver Spring, MD, 19–21 March 1996, pp 193–203
Leitinger R, Zhang ML, Radicella SM (2005) An improved bottomside for the ionospheric electron density model NeQuick. Ann Geophys 48(3): 525–534
Li X, Yu T (2003) Annual and semi-annual variations of the observed foF2 in a high solar activity year. Terr Atmos Oceanic Sci 14(1): 41–62
Mannucci AJ, Wilson BD, Edwards CD (1993) A new method for monitoring the Earth’s ionospheric total electron content using the GPS global network. In: Proceedings of the Institute of Navigation GPS Meeting, pp 1113–1122, Institute of Navigation, Fairfax
Mannucci AJ, Wilson BD, Yuan DN, Ho CH, Lindqwister UJ, Runge TF (1998) A global mapping technique for GPS derived ionospheric total electron content measurements. Radio Sci 33: 565–582
Mendillo M, Huang C, Pi X, Rishbeth H, Meier R (2005) The global ionospheric asymmetry in total electron content. J Atmos Sol Terr Phys 67: 1377–1387
Nava B, Radicella SM, Leitinger R, Coïsson P (2007) Use of total electron content data to analyze ionosphere electron density gradients. Adv Space Res 39(8): 1292–1297
Nava B, Coïsson P, Radicella SM (2008) pp 1856–1862. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2008.01.015
Radicella SM, Leitinger R (2001) The evolution of the DGR approach to model electron density profiles. Adv Space Res 27(1): 35–40
Radicella SM, Nava B, Coïsson P, Kersley L, Bailey G (2004) Effects of gradients of the electron density on Earthspace communications. Ann Geophys 47(suppl): 1227
Rishbeth H (2000) The equatorial F-layer: progress and puzzles. Ann Geophysicae 18: 730–739
Sardon E, Rius A, Zarraoa N (1994) Estimation of the transmitter and receiver differential biases and the ionospheric total electron content from Global Positioning System observations. Radio Sci 29: 577–586
Schaer S. (1999) Mapping and predicting the Earth’s ionosphere using the Global Positioning System. PhD thesis, Bern University
Smith DA, Araujo-Pradere EA, Minter C, Fuller-Rowell T (2008) A comprehensive evaluation of the errors inherent in the use of a two-dimensional shell for modeling the ionosphere. Radio Sci. 43:RS6008. doi:10.1029/2007RS003769
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brunini, C., Camilion, E. & Azpilicueta, F. Simulation study of the influence of the ionospheric layer height in the thin layer ionospheric model. J Geod 85, 637–645 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-011-0470-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00190-011-0470-2