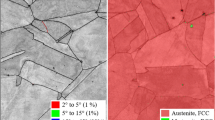
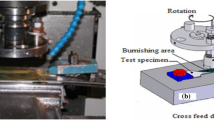
Abstract
In the literature, the most studies conducted on the flat surface ball-burnishing process have been focused on the most important classical factors like burnishing speed, lateral feed, and the ball-burnishing load or pressure on the treated surfaces integrity enhancement. In this research, ball-burnishing strategies are studied as a new ball-burnishing factor. The aim of this research is to show the improvement of the flat surface integrity of 2017A-T451 aluminum alloy using six new ball-burnishing strategies. Ball-burnishing tests were conducted in two passes using the recommended values of the ball-burnishing factors (the penetration depth a b is 40 μm, the linear ball-burnishing speed V b is 500 mm/min and a lateral feed f of 0.2 mm). Two ball-burnishing strategies in two successive and perpendicular passes to the machining direction and four ball-burnishing strategies in two crossed passes have been designed and tested to improve the flat surfaces integrity of the samples. The characterization and the micrographic observations of the ball-burnished surfaces show that using the best ball-burnishing strategy leads to a great enhancement in surface quality. The latter is predicted by a gain in average roughness Ra of 81 %, an improvement in the mean spacing of profile irregularities Sm of 34 %, an enhancement in surface Nano-hardness HIT of 17 %, and sub-layer hardness betterment up to a depth of 500 μm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loh NH, Tam SC (1988) Effects of ball burnishing parameters on surface finish—a literature survey and discussion. Precis Eng 10(4):215–220. doi:10.1016/0141-6359(88)90056-6
Hassan AM, Al-Bsharat AS (1996) Improvements in some properties of non-ferrous metals by the application of the ball-burnishing process. J Mater Process Technol 59:250–256. doi:10.1016/0924-0136(95)02149-3
López de Lacalle LN, Lamikiz A, Sánchez JA, Arana JL (2007) The effect of ball burnishing on heat treated steel and Inconel 718 milled surfaces. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 32(9-10):958–968. doi:10.1007/s00170-005-0402-5
Travieso-Rodríguez JA, Dessein G, González-Rojas HA (2011) Improving the surface finish of concave and convex surfaces using a ball burnishing process. Mater Manuf Process 26(12):1494–1502. doi:10.1080/10426914.2010.544819
Tadic B, Todorovic PM, Luzanin O, Miljanic D, Jeremic BM, Bogdanovic B, Vukelic D (2013) Using specially designed high-stiffness burnishing tool to achieve high-quality surface finish. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 67(1-4):601–611. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4508-2
Sequera A, Fu CH, Guo YB, Wei XT (2014) Surface integrity of inconel 718 by ball burnishing. J Mater Eng Perform 23(9):3347–3353. doi:10.1007/s11665-014-1093-6
López de Lacalle LN, Rodríguez A, Lamikiz A, Celaya A, Alberdi R (2011) Five-axis machining and burnishing of complex parts for the improvement of surface roughness. Mater Manuf Process 26(8):997–1003. doi:10.1080/10426914.2010.529589
El-Axir MH, Othman OM, Abodiena AM (2008) Study on the inner surface finishing of aluminum alloy 2014 by ball burnishing process. J Mater Process Technol 202:435–442. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.10.040
Bouzid W, Tsoumarev O, SaÏ K (2004) An investigation of surface roughness of burnished AISI 1042 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 24:120–125. doi:10.1007/s00170-003-1761-4
Akkurt A (2011) Comparison of roller burnishing method with other hole surface finishing processes applied on AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel. J Mater Eng Perform 20:960–968. doi:10.1007/s11665-010-9718-x
Hassan AM (1997) The effects of ball- and roller-burnishing on the surface roughness and hardness of some non-ferrous metals. J Mater Process Technol 72:385–391. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(97)00199-4
Hassan AM, AI-Wahhab OM (1998) Surface characteristics of some roller burnished non-ferrous components. Mater Manuf Process 13(4):505–515. doi:10.1080/10426919808935272
H Amdouni, H Bouzaiene, A Montagne, M Nasri, A Iost. Modeling and optimization of a ball-burnished aluminum alloy flat surface with a crossed strategy based on response surface methodology. Int J Adv Manuf Technol. 2016; 1–14. DOI 10.1007/s00170–016–8817–8
Shiou F-J, Chen C-H (2003) Freeform surface finish of plastic injection mold by using ball-burnishing process. J Mater Process Technol 140:248–254. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00750-7
Loh NH, Tam SC, Miyazawa S (1989) A study of the effects of ball burnishing parameters on surface roughness using factorial design. J Mech Work Technol 18:53–61. doi:10.1016/0378-3804(89)90109-5
Salahshoor M, Guo YB (2011) Surface integrity of biodegradable magnesium-calcium orthopedic implant by burnishing. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 4(8):1888–1904. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2011.06.006
Prevéy PS, Cammett J (2001) Low cost corrosion damage mitigation and improved fatigue performance of low plasticity burnished 7075-T6. J Mater Eng Perform 10(5):548–555. doi:10.1361/105994901770344692
Hassan AM, Al-Dhifi ZS (1999) Sulieman. Improvement in the wear resistance of brass components by the ball burnishing process. J Mater Process Technol 96(1–3):73–80. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(99)00254-X
Rodríguez A, López de Lacalle LN, Celaya A, Lamikiz A, Albizuri J (2012) Surface improvement of shafts by the deep ball-burnishing technique. Surface & Coatings Technology 206:2817–2824. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.11.045
Rajasekariah R, Vaidyanathan S (1975) Increasing the wear-resistance of steel components by ball burnishing. Wear 34:183–188. doi:10.1016/0043-1648(75)90064-2
Neema ML, Pandey PC (1980) Investigation of the performance characteristics of cold-worked machined surfaces. Wear 60:157–166. doi:10.1016/0043-1648(80)90256-2
Hassan AM, Maqableh AM (2000) The effects of initial burnishing parameters on non-ferrous components. J Mater Process Technol 102:115–121. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(00)00464-7
Shiou F-J, Hsu C-C (2008) Surface finishing of hardened and tempered stainless tool steel using sequential ball grinding, ball burnishing and ball polishing processes on a machining Centre. J Mater Process Technol 205:249–258. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.11.244
Oliver WC, Pharr GM (1992) An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J Mater Res 7:1564–1583. doi:10.1557/JMR.1992.1564
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amdouni, H., Bouzaiene, H., Montagne, A. et al. Experimental study of a six new ball-burnishing strategies effects on the Al-alloy flat surfaces integrity enhancement. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 90, 2271–2282 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9529-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-9529-9