Abstract
Purpose
Trochlear dysplasia is an important aetiological factor for the development of patellofemoral instability (PFI). The aim of the study was to identify the arthroscopic morphology of trochlear dysplasia that can be helpful when planning operative treatment for PFI.
Methods
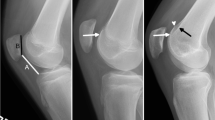
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans and strict lateral radiographs of 46 patients treated for PFI were assigned according to Dejour and matched with arthroscopic views from the lateral superior arthroscopic portal. On arthroscopy, signs of trochlear dysplasia were identified and classified into two types. Intra- and inter-observer agreements of the arthroscopic evaluation were assessed.
Results
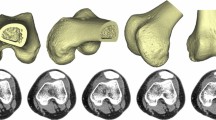
Arthroscopically, 2 major types of trochlear dysplasia could be distinguished. Type I shows a flat trochlear groove with an elevated trochlear floor in relation to the anterior femoral cortex. In type II, the proximal trochlea was convex with a lateral trochlear bump. Arthroscopic evaluation was not consistent with the Dejour’s radiographic and axial MRI classification. Arthroscopic grading showed excellent intra- and inter-observer agreements (81–92 %).
Conclusion
Arthroscopic evaluation can give additional information about the severity of trochlear dysplasia. This additional information can be used as an aid in decision making for the treatment of PFI.
Level of evidence
II.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amis AA, Oguz C, Bull AM, Senavongse W, Dejour D (2008) The effect of trochleoplasty on patellar stability and kinematics: a biomechanical study in vitro. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:864–869
Balcarek P, Ammon J, Frosch S (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of the medial patellofemoral ligament lesion in acute lateral patellar dislocations considering trochlear dysplasia, patella alta and tibial tuberosity-trochlear groove distance. Arthroscopy 26:926–935
Biedert RM, Bachmann M (2009) Anterior-posterior trochlear measurements of normal and dysplastic trochlea by axial magnetic resonance imaging. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 17:1225–1230
Blønd L, Schöttle PB (2010) The arthroscopic deepening trochleoplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18:480–485
Bollier M, Fulkerson JP (2011) The role of trochlear dysplasia in patellofemoral instability. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 19:8–16
Brattstrom H (1964) Shape of the intercondylar groove normally and in recurrent dislocation of patella. A clinical and X-Ray-Anatomical investigation. Acta Orthop Scand 68:1–148
Chhabra A, Subhawong TK, Carrino JA (2010) A systematised MRI approach to evaluating the patellofemoral joint. Skeletal Radiol 40:375–387
Cicchetti DV, Feinstein AR (1990) High agreement but low kappa: II. Resolving the paradoxes. J Clin Epidemiol 43:551–558
Dejour H, Walch G, Neyret PH, Adeleine P (1990) La dysplasie de la trochlèe fèmorale. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 76:45–54
Dejour H, Walch G, Nove-Josserand L, Guier CH (1994) Factors of patellar instability: an anatomic radiographic study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2:19–26
Dejour D, Le Coultre B (2007) Osteotomies in patellofemoral instabilities. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev 15:39–46
Dejour D, Saggin P (2010) The sulcus deepening trochleoplasty—the Lyon’s procedure. Int Orthop 34:311–316
Diederichs G, Issever AS, Scheffler S (2010) MR imaging of patellar instability: injury patterns and assessment of risk factors. Radiographics 30:961–981
Donell ST, Joseph G, Hing CB, Marshall TJ (2006) Modified Dejour trochleoplasty for severe dysplasia: operative technique and early clinical results. Knee 13:266–273
Feinstein AR, Cicchetti DV (1990) High agreement but low kappa: I. The problems of two paradoxes. J Clin Epidemiol 43:543–549
Fucentese SF, Zingg PO, Schmitt J, Pfirrmann CW, Meyer DC, Koch PP (2011) Classification of trochlear dysplasia as predictor of clinical outcome after trochleoplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19:1655–1661
Koeter S, Pakvis D, von Loon CJM, van Kampen A (2007) Trochlear osteotomy for patellar instability: satisfactory minimum 2-year results in patients with dysplasia of the trochlea. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15:228–232
Lippacher S, Dejour D, Elsharkawi M, Dornacher D, Ring C, Dreyhaupt J, Reichel H, Nelitz M (2012) Observer agreement on the Dejour trochlea dysplasia classification. A comparison of true lateral radiographs to axial magnetic resonance images. Am J Sports Med 40:837–843
Nelitz M, Theile M, Dornacher D, Wölfle J, Reichel H, Lippacher S (2012) Analysis of failed surgery for patellar instability in children with open growth plates. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20:822–828
Nelitz M, Dreyhaupt J, Lippacher S (2013) Combined trochleoplasty and patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for recurrent patellar dislocation in severe trochlear dysplasia. A minimum two years follow-up study. Am J Sports Med 41:1005–1012
Pfirrmann CW, Zanetti M, Romero J, Hodler J (2000) Femoral trochlear dysplasia: MR findings. Radiology 216:858–864
Redziniak DE, Diduch DR, Mihalko WM, Fulkerson JP, Novicoff WM, Sheibani-Rad S, Saleh KJ (2009) Patellar instability. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:2264–2275
Salzmann GM, Weber TS, Spang JT, Imhoff AB, Schöttle PB (2010) Comparison of native axial radiographs with axial imaging for the determination of the trochlear morphology in patients with trochlear dysplasia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 130:335–340
Schoettle PB, Fucentese SF, Pfirrmann C, Bereiter H, Romero J (2005) Trochleaplasty for patellar instability due to trochlear dysplasia: a minimum 2 year clinical and radiological follow-up of 19 knees. Acta Orthop 76:693–698
Shih YF, Bull AM, Amis AA (2004) The cartilaginous and osseous geometry of the femoral trochlear groove. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 12:300–306
Tecklenburg K, Feller JA, Whitehead TS, Webster KE, Elzarka A (2010) Outcome of surgery for recurrent patellar dislocation based on the distance of the tibial tuberosity to the trochlear groove. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92:1376–1380
Utting MR, Mulford JS, Eldridge JD (2008) A prospective evaluation of trochleoplasty for the treatment of patellofemoral dislocation and instability. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:180–185
Van Huyssteen AL, Hendrix MRG, Barnett AJ, Wakeley CJ, Eldridge JDJ (2006) Cartilage-bone mismatch in the dysplastic trochlea: an MRI study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88:688–691
Verdonk R, Jansegers E, Stuyts B (2005) Trochleoplasty in dysplastic knee trochlea. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13:529–533
Von Knoch F, Böhm T, Bürgi ML, Von Knoch M, Bereiter H (2006) Trochleaplasty for recurrent patellar dislocation in association with trochlear dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88:1331–1335
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelitz, M., Lippacher, S. Arthroscopic evaluation of trochlear dysplasia as an aid in decision making for the treatment of patellofemoral instability. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22, 2788–2794 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2586-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-013-2586-9