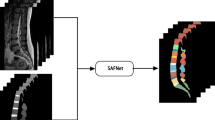
Abstract
Spine segmentation is necessary for the clinical quantitative analysis of computed tomography (CT) images and plays an important role in the early diagnosis and treatment of spine diseases. However, because of the different fields of view of sagittal CT, these images show different shapes and sizes of vertebrae, unclear vertebral boundaries, and different image scales which greatly complicate the segmentation of the spine. To solve this problem, we propose a new deep learning method for segmenting the spine. For this algorithm, we first proposed a residual feature pyramids block for capturing and fusing multi-scale information. For fusing shallow and deep features, we then propose an attention skip layer structure for suppressing the reuse of redundant information. Finally, we use a joint loss function to optimize the segmentation results and achieve the effect of clear segmentation edges. Through the combination of these three techniques, our method achieves efficient and accurate spinal segmentation. The experimental results show that our model has a good performance in spine segmentation. In particular, our achieve the Dice of 0.8973, the Hausdorff distance of 77.6277 on the VerSe 2019 dataset and the Dice of 0.8626, the Hausdorff distance of 82.6170 on the VerSe 2020 dataset.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslan, M.S., Ali, A., Rara, H., Farag, A.A.: An automated vertebra identification and segmentation in CT images. pp. 233–236, 10 (2010)
Chen, L.C., Papandreou, G., Kokkinos, I., Murphy, K., Yuille, A.L.: DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(4), 834–848 (2018)
Chen, S., Tan, X., Wang, B., Hu, X.: Reverse attention for salient object detection. In: Vittorio, F., Martial, H., Cristian, S., Yair, W. (eds.), Computer Vision—ECCV 2018, pp. 236–252. Springer, Cham (2018)
De Guio, F., Shevroja, E., Lamy, O., Michelet, F., Hans, D.: Deep learning spine segmentation to get accurate and relevant BMD and TBS values: the OsteoLaus study. Bone Rep. 13, 100355 (2020)
Forsberg, D.: Atlas-based registration for accurate segmentation of thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in CT data. In: Jianhua, Y., Ben, G., Tobias, K., Shuo, L. (eds.), Recent Advances in Computational Methods and Clinical Applications for Spine Imaging, Lecture Notes in Computational Vision and Biomechanics, vol. 20. Springer, pp. 49–59 (2015)
Forsberg, D.: Atlas-based segmentation of the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae. In: Jianhua, Y., Ben, G., Tobias, K., Shuo, L. (eds.), Recent Advances in Computational Methods and Clinical Applications for Spine Imaging, Lecture Notes in Computational Vision and Biomechanics, vol. 20. Springer, pp. 215–220
Fu, H., Xu, Y., Lin, S., Kee Wong, D.W., Liu, J.: DeepVessel: retinal vessel segmentation via deep learning and conditional random field. In: Sebastien, O., Leo J., Mert, R.S., Gozde, U., William, W. (eds.), Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 9901. Springer, pp. 132–139 (2016)
Gu, Z., Cheng, J., Fu, H., Zhou, K., Hao, H., Zhao, Y., Zhang, T., Gao, S., Liu, J.: CE-net: context encoder network for 2d medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 38(10), 2281–2292 (2019)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hou, Q., Cheng, M.M., Hu, X., Borji, A., Tu, Z., Torr, P.H.: Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp. 5300–5309 (2017)
Ibtehaz, N., Rahman, M.S.: Multiresunet: rethinking the u-net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw. 121, 74–87 (2020)
Iglovikov, V., Shvets, A.: Ternausnet: U-net with vgg11 encoder pre-trained on imagenet for image segmentation. 01 (2018)
Ito, M., Ikeda, K., Nishiguchi, M., Shindo, H., Uetani, M., Hosoi, T., Orimo, H.: Multi-detector row CT imaging of vertebral microstructure for evaluation of fracture risk. J. Bone Miner. Res. 20(10), 1828–1836 (2005)
Janssens, R., Zeng, G., Zheng, G.: Fully automatic segmentation of lumbar vertebrae from CT images using cascaded 3d fully convolutional networks. pp. 893–897 (2018)
Joutard, S., Dorent, R., Isaac, A., Ourselin, S., Vercauteren, T., Modat, M.: Permutohedral attention module for efficient non-local neural networks. In: Dinggang, S., Tianming, L., Terry,M.P., Lawrence H.S., Caroline, E., Sean, Z., Pew-Thian, Y., Ali, K. (eds.), Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2019, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 11769. Springer, Cham, pp. 393–401 (2019)
Kim, Y.J., Ganbold, B., Kim, K.G.: Web-based spine segmentation using deep learning in computed tomography images. Healthc. Inform. Res. 26(1), 61 (2020)
Klinder, T., Ostermann, J., Ehm, M., Franz, A., Kneser, R., Lorenz, C.: Automated model-based vertebra detection, identification, and segmentation in CT images. Med. Image Anal. 13(3), 471–482 (2009)
Korez, R., Ibragimov, B., Likar, B., Pernuš, F., Vrtovec, T.: A framework for automated spine and vertebrae interpolation-based detection and model-based segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 34(8), 1649–1662 (2015)
Lee, C.Y., Xie, S., Gallagher, P., Zhang, Z., Tu, Z.: Deeply-supervised nets. In: Guy, L., Vishwanathan, S.V.N. (eds.), Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, vol. 38. PMLR, San Diego, pp. 562–570 (2015)
Lessmann, N., van Ginneken, B., de Jong, P.A., Isgum, I.: Iterative fully convolutional neural networks for automatic vertebra segmentation and identification. Med. Image Anal. 53, 142–155 (2019)
Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, E., Chen, Y., Wang, Q., Liu, K., Yu, H.J., Yuan, H., Lang, N., Su, M.Y.: Differential diagnosis of benign and malignant vertebral fracture on CT using deep learning. Eur. Radiol. 202131(12), 9612–9619 (2021)
Lin, T.Y., Dollar, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp. 936–944 (2017)
Liskowski, P., Krawiec, K.: Segmenting retinal blood vessels with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(11), 2369–2380 (2016)
Liu, Z., Chen, G., Shan, Z., Xueqin, J.: Segmentation of spine CT image based on deep learning. Comput. Appl. Softw. (2018)
Lu, Z., Chen, Y.: Dense u-net for super-resolution with shuffle pooling layer. 11 (2020)
Luo, X., Wang, G., Song, T., Zhang, J., Aertsen, M., Deprest, J., Ourselin, S., Vercauteren, T., Zhang, S.: MIDeepSeg: minimally interactive segmentation of unseen objects from medical images using deep learning. Med. Image Anal. 72, 102102 (2021)
Ma, J., Le, L.: Hierarchical segmentation and identification of thoracic vertebra using learning-based edge detection and coarse-to-fine deformable model. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 117(9), 1072–1083 (2013)
Maccauro, G., Spinelli, M.S., Mauro, S., Perisano, C., Graci, C., Rosa, M.A.: Physiopathology of spine metastasis. Int. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 1–8 (2011)
Masuzawa, N., Kitamura, Y., Nakamura, K., Iizuka, S., Simo-Serra, E.: Automatic segmentation, localization, and identification of vertebrae in 3d CT images using cascaded convolutional neural networks. In: Anne, L.M., Purang, A., Danail, S., Diana, M., Maria, A.Z., Kevin Zhou, S., Daniel, R., Leo, J., (eds.), Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI (2020), Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 12266. Springer, pp. 681–690 (2020)
Moeskops, P., Wolterink, J.M., van der Velden, B.H., Gilhuijs, K.G., Leiner, T., Viergever, M.A., Išgum, I.: Deep learning for multi-task medical image segmentation in multiple modalities. In: Sebastien, O., Leo, J., Mert, R.S., Gozde, U., William, W. (eds.), Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2016, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 9901. Springer, pp. 478–486 (2016)
Obaid, W., Obaidat, M.S.: Automatic spine bone segmentation and feature extraction in computed tomography images for biometric recognition. In: 2020 International Conference on Computer, Information and Telecommunication Systems (CITS). IEEE, pp. 1–5 (2020)
Oktay, O., Schlemper, J., Folgoc, L.L., Lee, M., Heinrich, M., Misawa, K., Mori, K., McDonagh, S., Hammerla, N.Y., Kainz, B., Glocker, B.: Attention U-net: learning where to look for the pancreas. 04 (2018)
Peng, W., Li, L., Liang, L., Ding, H., Zang, L., Yuan, S., Wang, G.: A convenient and stable vertebrae instance segmentation method for transforaminal endoscopic surgery planning. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 16(8), 1263–1276 (2021)
Qin, X., Zhang, Z., Huang, C., Gao, C., Dehghan, M., Jagersand, M.: Basnet: boundary-aware salient object detection. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7471–7481 (2019)
Qiu, Y., Liu, Y., Li, S., Xu, J.: MiniSeg: an extremely minimum network for efficient COVID-19 segmentation. In: AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 4846–4854 (2021)
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 39(6), 1137–1149 (2017)
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., Brox, T.: U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Nassir, N., Joachim, H., William, M.W., Alejandro F.F. (eds.), Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 9351. Springer, pp. 234–241 (2015)
Ruiz-Espana, S., Diaz-Parra, A., Arana, E., Moratal, D.: A fully automated level-set based segmentation method of thoracic and lumbar vertebral bodies in computed tomography images. In: 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE, pp. 3049–3052 (2015)
Seitel, A., Rasoulian, A., Rohling, R., Abolmaesumi, P.: Lumbar and Thoracic Spine Segmentation Using a Statistical Multi-object Shape+Pose Model, vol. 20, pp. 221–225 (2015)
Sekuboyina, A., Bayat, A., Husseini, M.E., Löffler, M., Rempfler, M., Kukačka, J., Tetteh, G., Valentinitsch, A., Payer, C., Urschler, M., Chen, M., Cheng, D., Nikolas, L., Yujin, H., Tianfu, W., Dong, Y., Daguang, X., Felix, A., Stefan, Z., Tao, J., Xinjun, M., Christoph, A., Xin, W., Qingyue, W., Kevin, B., Matthias, W., Alexandre, K., Élodie, P., Börn, H.M., Jan S.K.: Verse: a vertebrae labelling and segmentation benchmark (2020)
Sekuboyina, A., Kukačka, J., Kirschke, J.S., Menze, B.H., Valentinitsch, A.: Attention-driven deep learning for pathological spine segmentation. In: Ben, G., Jianhua, Y., Tomaž V., Alejandro, F., Guoyan, Z., (eds.), Computational Methods and Clinical Applications in Musculoskeletal Imaging, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 10734. Springer, Cham, pp. 108–119 (2018)
Shi, D., Pan, Y., Liu, C., Wang, Y., Cui, D., Lu, Y.: Automatic localization and segmentation of vertebral bodies in 3d CT volumes with deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Image Computing and Digital Medicine—ISICDM 2018. ACM Press, pp. 42–46 (2018)
Wang, K.C., Jeanmenne, A., Weber, G.M., Thawait, S., Carrino, J.A.: An online evidence-based decision support system for distinguishing benign from malignant vertebral compression fractures by magnetic resonance imaging feature analysis. J. Digit. Imaging 24(3), 507–515 (2011)
Wang, R., Voon, Y., Hui, J., Ma, D., Dabiri, S., Popuri, K., Beg, M.F.: Vertebra segmentation for clinical CT images using mask R-CNN. In: Tomaz, J., Aleksandra, C., Samo, M.-K., Damijan, M. (eds.), 8th European Medical and Biological Engineering Conference, IFMBE Proceedings, vol. 80. Springer, Cham, pp. 1156–1165 (2021)
Wu, X.: An iterative convolutional neural network algorithm improves electron microscopy image segmentation. 06 (2015)
Xian, L.I., Jie. H.E.: Application of 3d fully convolution network in spine segmentation. Electronic Science and Technology (2018)
Xiao, X., Lian, S., Luo, Z., Li, S.: Weighted res-UNet for high-quality retina vessel segmentation. In: 2018 9th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME). IEEE, pp. 327–331 (2018)
Xie, S., Tu, Z.: Holistically-Nested Edge Detection. Int. J. Comput. Vision 125
Yang, D., Xiong, T., Xu, D., Huang, Q., Liu, D., Zhou, S.K., Xu, Z., Park, J., Chen, M., Tran, T.D., Chin, S.P., Dimitris, M., Dorin, C.: Automatic vertebra labeling in large-scale 3d CT using deep image-to-image network with message passing and sparsity regularization. In: Marc, N., Martin, S., Stephen, A., Hongtu, Z., Ipek, O., Pew-Thian, Y., Dinggang, S. (eds.), Information Processing in Medical Imaging, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 10265. Springer, pp. 633–644 (2017)
Yang, D., Xiong, T., Xu, D., Zhou, S.K., Xu, Z., Chen, M., Park, J., Grbic, S., Tran T, Rac, D., Chin, S.P., Dimitris, M., Dorin, C.: Deep image-to-image recurrent network with shape basis learning for automatic vertebra labeling in large-scale 3d CT volumes. In: Maxime, D., Lena, M.-H., Alfred, F., Pierre, J., Louis Collins, D., Simon, D. (eds.), Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2017, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 10435. Springer, pp. 498–506 (2017)
Zamzmi, G., Sachdev, V., Antani, S.: Trilateral attention network for real-time medical image segmentation. 06 (2021)
Zareie, M., Parsaei, H., Amiri, S., Awan, M.S., Ghofrani, M.: Automatic segmentation of vertebrae in 3d CT images using adaptive fast 3d pulse coupled neural networks. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 41(4), 1009–1020 (2018)
Zhang, Z., Chengdong, W., Coleman, S., Kerr, D.: DENSE-INception u-net for medical image segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 192, 105395 (2020)
Zhao, H., Shi, J., Qi, X., Wang, X., Jia, J.: Pyramid scene parsing network. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE, pp. 6230–6239 (2017)
Zhou, W., Lin, L., Ge, G.: N-net: 3d fully convolution network-based vertebrae segmentation from CT spinal images. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 33(6), 1957003 (2019)
Zhou, Z., Siddiquee, M.M., Tajbakhsh, N., Liang, J.: UNet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39(6), 1856–1867 (2020)
Zhu, H.T., Zhang, X.Y., Shi, Y.J., Li, X.T., Sun, Y.S.: Automatic segmentation of rectal tumor on diffusion-weighted images by deep learning with U-net. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 22(9), 324–331 (2021)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 62106237), Science and Technology Innovation Project of Colleges and Universities in Shanxi Province (Grant No. 2019L0533), and Shanxi Province Science Foundation for Youths (Grant No. 201901D211237).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Wang, Q., Zeng, J. et al. RAU-Net: U-Net network based on residual multi-scale fusion and attention skip layer for overall spine segmentation. Machine Vision and Applications 34, 10 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-022-01360-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-022-01360-4