Abstract
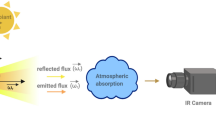
Many experimental techniques and many commercial solutions have been proposed to realize non-contact 3D digitization of industrial objects. Unfortunately, the performances of active 3D scanners depend on the optical properties of the surface to digitize. That is why the results obtained by active 3D triangulation on specular or transparent surfaces are not as good as those obtained on diffuse surfaces. In this paper, we present the developments we have realized to address highly reflective metallic surfaces. These developments are based on the extension of a technique, called “Scanning from heating” and initially dedicated to glass material. In comparison to conventional active triangulation techniques that measure the reflection of visible radiation, we measure here the thermal emission of a surface, which is locally heated by a laser source. We describe in this paper the successive steps we have followed to adapt Scanning From Heating to metallic materials, to evaluate the performances and finally to develop an operational prototype.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blais, F.: Review of 20 years of range sensor development. J. Electron. Imaging 13, 231–240 (2004)
Sansoni, G., Trebeschi, M., Docchio, F.: State-of-The-Art and applications of 3D imaging sensors in industry, cultural heritagen medicine, and criminal investigation. Sensors 9, 568–601 (2009)
Ihrke, I., Kutulakos, K.N., Lensch, H.P.A., Magnor, M., Heidrich, W.: Transparent and specular object reconstruction. Comput. Graph. Forum 29(8), 1–27 (2010)
Park, J., Kak, A.C.: 3D modeling of optically challenging objects. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 14, 246–262 (2008)
Wolff, L.B., Boult, T.E.: Constraining object features using a polarization reflectance model. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 13(7), 635–657 (1991)
Rahmann, S., Canterakis, N.: Reconstruction of specular surfaces using polarization imaging. In: IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 149–155. Kauai, USA (2001)
Morel, O., Stolz, C., Meriaudeau, F., Gorria, P.: Active lighting applied to 3D reconstruction of specular metallic surfaces by polarization imaging. Appl. Opt. 45(17), 4062–4068 (2006)
Tarini, M., Lensch, H.P.A., Goesele, M., Seidel, H.-P.: 3D acquisition of mirroring objects. Graph. Model. 67(4), 233–259 (2005)
Bonfort, T., Sturm, P., Gargallo, P.: General specular surface triangulation. In: Asian Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 872–881 (2006)
Zheng, J.Y., Murata, A.: Acquiring a complete 3D model from specular motion under the illumination of circular-shaped light sources. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22(8), 913–920 (2000)
Bhat, D.N., Nayar, S.K.: Stereo and specular reflection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 26(2), 91–106 (1998)
Gupta, M., Agrawal, A., Veeraraghavan, A.: Structured light 3D scanning in the presence of global illumination. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 713–720. RI, Providence (2011)
Rantoson, R.: Numérisation 3D d’objets transparents par polarisation dans l’IR & par triangulation dans l’UV. Université de Bourgogne, Thèse (2011)
Tiziani, H.J., Uhde, H.M.: Three-dimensional image sensing by chromatic confocal microscopy. Appl. Opt. 33(10), 1838–1843 (1994)
Boverie, S., Devy, M., Lerasle, F.: “3D Perception for New Airbag Generation”, 15th IFAC world Congress on Automatic Control. Barcelona, Spain (2002)
Romain, O., Ea, T., Gastaud, C., Garda, P.: “Un Capteur Multispectral de vision Panoramique 3D” Actes des Journées Francophones Des Chjercheurs En Ananlyse d’Images et Perception Visuelle (ORASIS’2001). Cahors, France, Juin (2001)
Orteu, J.-J., Rotrou, Y., Sentenac, T., Robert, L.: An innovative method for 3-D shape, strain and temperature full-field measurement using a single type of camera: principle and preliminary results. Exp. Mech. 48(2), 163–179 (2008)
Rantonson, R., Stolz, C., Fofi, D., Meriaudeau, F.: Optimization of transparent objects digitization from visible fluorescence UV-induced. Opt. Eng. 51(2), 033601 (2012)
Bodnar, J.L., Egée, M.: Wear crack characterization by photothermal radiometry. WEAR 196, 54–59 (1996)
Pelletier, J.-F., Maldague, X.: Shape from heating: a two-dimensional approach for shape extraction in infrared images. Opt. Eng. 36(2), 370–375 (1997)
Eren, G., Aubreton, O., Meriaudeau, F., Fofi, D., Naskali, A.T., Truchetet, F., Erçil, A.: Scanning from heating: 3D shape estimation of transparent objects from local surface heating. Opt. Express 17(14), 11457–11468 (2009)
Eren, G. (2010) 3D scanning of transparent objects. Université de Bourgogne–Sabancı Universitesi, Thèse de doctorat
Eyglunent, B: Manuel de Thermique.: Hermès Science, Publication, 2000
Paschotta, R.: Gaussian beams. Encyclopedia of Laser Physics and Technology (2011)
Bajard, A., Aubreton, O., Eren, G., Sallamand, P., Truchetet, F.: 3D Digitization of Metallic Surfaces Using Scanning From Heating Method Approach. SPIE Electronic Imaging San Francisco. Proceedings SPIE 7864, 786413 (2011)
Palik, Edward D.: Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids. Academic Press, Boston (1985)
Ordal, M.A., Long, L.L., Bell, R.J., Bell, R.R., Alexander, R.W., Ward, C.A.: Optical properties of the metals Al, Co., Cu, Au, Fe, Pb, Ni, Pd, Pt, Ag, TI, and W in the infrared and far infrared. Appl. Opt. 22(7), (1983)
Bajard, A., Aubreton, O., Bokhabrine, Y., Verney, B., Eren, G., Erçil, A., Truchetet, F.: 3D Scanning of specular and diffuse metallic surfaces using an infrared technique. Opt. Eng. 51, 06 (2012):0091–3286 (2012)
Marzani, F., Voisin, Y., Diou, A.: Calibration of a three-dimensional reconstruction system using a structured light source. Opt. Eng. 41(2), 484–492 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aubreton, O., Bajard, A., Verney, B. et al. Infrared system for 3D scanning of metallic surfaces. Machine Vision and Applications 24, 1513–1524 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-013-0487-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-013-0487-z