Abstract
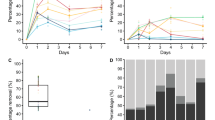
The widespread use of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) has attracted much attention and the impact of PPCPs on indigenous microbial communities has become increasingly important in recent days. Five common PPCPs, including doxycycline (DOX), ciprofloxacin (CIP), triclocarban (TCC), carbamazepine (CBZ), and sulfadimidine (SMZ), were selected and their effects on soil microbial respiration were studied at concentrations of 0, 0.2, 1, 5, 25 and 50 mg/kg. The results of this study indicate that the effect of five common PPCPs on soil microbial respiration was dose- and time- dependent. At low concentrations (0.2 and 1 mg/kg), CBZ and SMZ exhibited an activation effect on microbial soil respiration at 1 day (58.02%, 26.39% and 1.54%, 1.76% at 0.2 and 1 mg/kg respectively), while DOX showed inhibition for all tested concentrations at 1 day of incubation. At high concentrations (25 and 50 mg/kg) CIP and SMZ showed an inhibitory effect (− 69.13%, − 80.86% for 25 and 50 mg/kg, respectively), while TCC and CBZ exhibited stimulatory effect (38.07%, 9.64% and 4.06%, 12.18% at 25 and 50 mg/kg, respectively) at 1 day of incubation. Our findings indicate that the effect of tested PPCPs on soil microbial respiration had an inhibitory or stimulatory effect based on the dose and extent of time.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accinelli C, Koskinen WC, Becker JM, Sandowsky MJ (2007) Environmental fate of two sulfonamide antimicrobial agents in Soil. J Agric Food Chem 55:2677–2682
Aldén L, Demoling F, Bååth E (2001) Rapid method of determining factors limiting bacterial growth in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1830–1838
Butler E, Whelan MJ, Ritz K, Sakrabani R, Van Egmond R (2011) Effects of triclosan on soil microbial respiration. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:360–366
Chen F, Ying GG, Kong LX, Wang L, Zhao JL, Zhou LJ, Zhang LJ (2011) Distribution and accumulation of endocrine-disrupting chemicals and pharmaceuticals in wastewater irrigated soils in Hebei, China. Environ Pollut 159:1490–1498
Cizmas L, Sharma VK, Gray CM, McDonald TJ (2015) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in waters: occurrence, toxicity, and risk. Environ Chem Lett 13:381–394
Conkle JL, White JR (2012) An initial screening of antibiotic effects on microbial respiration in wetland soils. J Environ Sci Health A 47:1381–1390
Cui H, Wang SP, Fu J, Zhou ZQ, Zhang N, Guo L (2014) Influence of ciprofloxacin on microbial community structure and function in soils. Biol Fertil Soils 50:939–947
Fernández C, Alonso C, Babı́n MM, Pro J, Carbonell G, Tarazona JV (2004) Ecotoxicological assessment of doxycycline in aged pig manure using multispecies soil systems. Sci Total Environ 323:63–69
Fu QG, Sanganyado E, Ye QF, Gan J (2016) Meta-analysis of biosolid effects on persistence of triclosan and triclocarban in soil. Environ Pollut 210:137–144
Ge GF, Li ZJ, Zhang J et al (2009) Geographical and climatic differences in long-term effect of organic and inorganic amendments on soil enzymatic activities and respiration in field experimental stations of China. Ecol Complex 6:421–431
Gougoulias C, Clark JM, Shaw LJ (2014) The role of soil microbes in the global carbon cycle: Tracking the below-ground microbial processing of plant-derived carbon for manipulating carbon dynamics in agricultural systems. J Sci Food Agric 94:2362–2371
Guo PP, Zhu LS, Wang JH, Wang J, Xie H, Lv DD (2015) Enzymatic activities and microbial biomass in black soil as affected by azoxystrobin. Environ Earth Sci 74:1353–1361
Jager T, Fleuren RH, Hogendoorn EA, De Korte G (2003) Elucidating the routes of exposure for organic chemicals in the earthworm, Eisenia andrei (Oligochaeta). Environ Sci Technol 37:3399–3404
Jutkina J, Rutgersson C, Flach CF, Larsson DGJ (2016) An assay for determining minimal concentrations of antibiotics that drive horizontal transfer of resistance. Sci Total Environ 548–549:131–138
Kang D, Zhao Q, Wud Y, Wua C, Xiang W (2018) Removal of nutrients and pharmaceuticals and personal care products from wastewater using periphyton photobioreactors. Bioresour Technol 248:113–119
Kemper N (2008) Veterinary antibiotics in the aquatic and terrestrial environment. Ecol Indic 8:1–13
Kotzerke A, Sharma S, Schauss K, Heuer H, Thiele-Bruhn S, Smalla K, Schloter M (2008) Alterations in soil microbial activity and N-transformation processes due to sulfadiazine loads in pig-manure. Environ Pollut 153:315–322
Li JY, Dodgen L, Ye QF, Gan J (2013) Degradation kinetics and metabolites of carbamazepine in soil. Environ Sci Technol 47:3678–3684
Liu SY, Saul N, Pan B, Menzel R, Steinberg CEW (2013) The non-target organism Caenorhabditis elegans withstands the impact of sulfamethoxazole. Chemosphere 93:2373–2380
Liu LY, Mi JD, Wang Y et al (2018) Different methods of incorporating ciprofloxacin in soil affect microbiome and degradation of ciprofloxacin residue. Sci Total Environ 619–620:1673–1681
Maeng SK, Sharma SK, Abel CD, Magic-Knezev A, Amy GL (2011) Role of biodegradation in the removal of pharmaceutically active compounds with different bulk organic matter characteristics through managed aquifer recharge: batch and column studies. Water Res 45:4722–4736
Nguyen F, Starosta AL, Arenz S, Sohmen D, Dönhöfer A, Wilson DN (2014) Tetracycline antibiotics and resistance mechanisms. Biol Chem 395:559–575
Pusceddu FH, Choueri RB, Pereira CDS et al (2018) Environmental risk assessment of triclosan and ibuprofen in marine sediments using individual and sub-individual endpoints. Environ Pollut 232:274–283
Qin Q, Chen XJ, Zhuang J (2015) The fate and impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in agricultural soils irrigated with reclaimed water. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 45:1379–1408
Sidhu H, Connor GO, Ogram A, Kumar K (2019) Bioavailability of biosolids-borne ciprofloxacin and azithromycin to terrestrial organisms: microbial toxicity and earthworm responses. Sci Total Environ 650:18–26
Srinivasan P, Sarmah AK (2014) Dissipation of sulfamethoxazole in pasture soils as affected by soil and environmental factors. Sci Total Environ 479–480:284–291
Szatmári I, Barcza T, Körmöczy PS, Laczay P (2012) Ecotoxicological assessment of doxycycline in soil. J Environ Sci Heal B 47:129–135
Vasiliadou IA, Molina R, Martinez F, Melero JA, Stathopoulou PM, Tsiamis G (2018) Toxicity assessment of pharmaceutical compounds on mixed culture from activated sludge using respirometric technique: the role of microbial community structure. Sci Total Environ 630:809–819
Villalaín J, Mateo CR, Aranda FJ, Shapiro S, Micol V (2001) Membranotropic effects of the antibacterial agent Triclosan. Arch Biochem Biophys 390:128–136
Walker CW, Watson JE, Williams C (2012) Occurrence of carbamazepine in soils under different land uses receiving wastewater. J Environ Qual 41:1263–1267. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2011.0193
Walters E, Mcclellan K, Halden RU (2010) Occurrence and loss over three years of 72 pharmaceuticals and personal care products from biosolids-soil mixtures in outdoor mesocosms. Water Res 44:6011–6020
Wang LJ, Wang JH, Zhu LS, Wang J (2018) Toxic effects of oxytetracycline and copper, separately or combined, on soil microbial biomasses. Environ Geochem Health 40:763–776
Zhang YJ, Hu HW, Gou M, Wang JT, Chen D, He JZ (2017) Temporal succession of soil antibiotic resistance genes following application of swine, cattle and poultry manures spiked with or without antibiotics. Environ Pollut 231:1621–1632
Zhu D, An XL, Chen QL, Yang XR, Christie P, Ke X, Wu LH, Zhu YG (2018) Antibiotics disturb the microbiome and increase the incidence of resistance genes in the gut of a common soil collembolan. Environ Sci Technol 52:3081–3090
Acknowledgements
The present study was supported by grants from the National Science and Technology Major Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China [No. 2016YFD0201203].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Wenjie Zhang and Jun Wang are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Wang, J., Wang, J. et al. New Insights into Dose- and Time-Dependent Response of Five Typical PPCPs on Soil Microbial Respiration. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 103, 193–198 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02655-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02655-5