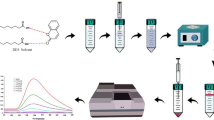
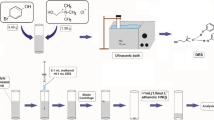
Abstract
In this study, a deep eutectic solvent (DES) based on air-assisted ligandless emulsification liquid–liquid microextraction method (DES-AA-LL-ELLME) was considered for preconcentration and extraction of some metals (Cd, Ni, Pb and Cu). A 1:1 mixture of the synthesized DES and triethylamine was added as an extractant to extract metal ions in the absence of chelating agent. Tetrahydrofuran as the aprotic solvent provided a turbid state. To disperse the aggregated DES droplets into the aqueous phase, air-assisted was performed. The influence of several effective parameters was monitored. Under optimum conditions, limits of detection were found in the range of 0.31–0.99 µg L−1 with preconcentration factor from 67 to 69. The relative standard deviation (n = 10) was in the range of 2.1%–3.1% for all analytes. This procedure was applied to determine some metals in both biological and environmental samples with appropriate recoveries about 98.7%–106%.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez SM, Llamas NE, Lista AG, Mónica B, DominiCE (2017) Ionic liquid mediated extraction, assisted by ultrasound energy, of available/mobilizable metals from sediment samples. Ultrason Sonochem 34:239–245
Biata R, Nyaba L, Ramontja J, Mketo N, Nomngongo PN (2017) Determination of antimony and tin in beverages using inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry after ultrasound-assisted ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid phase microextraction. Food Chem 237:904–911
Farajzadeh MA, Afshar Mogaddam MR, Aghanassa M (2016) Deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Anal Methods 82:576–2583
Galbeiro R, Garcia S, Gaubeur I (2014) Agreen and efficient procedure for the preconcentration and determination of cadmium, nickel and zinc from fresh water, hemodialysis solutions and tuna fish samples by cloud point extraction and flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Trace Elem J Med Biol 2:160–165
Gouda AA (2016) A new coprecipitation method without carrier element for separation and preconcentration of some metal ions at trace levels in water and food samples. Talanta 146:435–441
Habila M, Yilmaz E, Alothman ZA, Soylak M (2016) Combination of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction and multivariate optimization for separation-enrichment of traces lead by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. J Ind Eng Chem 37:306–311
Kahe H, Chamsaz M, Rounaghi GH (2016) A microextraction method based on ligand less ion-pair formation for measuring the cadmium cation in real samples by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Anal Methods 9:2887–2895
Karadas C, Kara D (2017) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic drop for preconcentration and determination of trace amounts of copper by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem 220:242–248
Karimi M, Dadfarnia S, Shabani AMH, Tamaddon F, Azadi D (2015) Deep eutectic liquid organic salt as a new solvent for liquid-phase microextraction and its application in ligandless extraction and preconcentraion of lead and cadmium in edible oils. Talanta 144:648–654
Khezeli T, Daneshfar A, Sahraei RS (2015) Emulsification liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent: An extraction method for the determination of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and seven polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples. J Chromatogr A 1425:25–33
Kocot K, Zawisza B, Sitko R (2012) Dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction using diethyldithiocarbamate as a chelating agent and the dried-spot technique for the determination of Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Se and Pb by energy-dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta B 73:79–83
Lamei N, Ezoddin M, Abdi K (2017) Air assisted emulsification liquid–liquid microextraction based on deep eutectic solvent for preconcentration of methadone in water and biological samples. Talanta 165:176–181
Loh SH, Sanagi MM, WanIbrahim WA, NoorHasan M (2013) Multi-walled carbon nanotube-impregnated agarose film microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in green tea beverage. Talanta 106:200–205
Louriño-Cabana B, Lesven L, Charriau A, Billon G, Ouddane B, Boughriet A (2011) Potential risks of metal toxicity in contaminated sediments of Deûle river in Northern France. J Hazard Mater 186:2129–2137
Mirzaei M, Behzad M, Abadi M, Beizaei N (2011) A Simultaneous separation/preconcentration of ultra trace heavy metals in industrial wastewaters by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction based on solidification of floating organic drop prior to determination by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 186:1739–1743
Seeger TS, Rosa FC, Bizzi CA, Dressler VL, Flores EMM, Duarte FA (2015) Feasibility of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for extraction and preconcentration of Cu and Fe in red and white wine and determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta Part B 105:136–140
Sorouraddin SM, Farajzadeh MA, Okhravi T (2017) Cyclohexylamine as extraction solvent and chelating agent in extraction and preconcentration of some heavy metals in aqueous samples based on heat-induced homogeneous liquid–liquid extraction. Talanta 175:359–365
Tan T, Zhang M, Wan Y, Qiu H (2016) Utilization of deep eutectic solvents as novel mobile phase additives for improving the separation of bioactive quaternary alkaloids. Talanta 14:85–90
Tokalıoglu S, Papak A, Kartal S (2017) Separation/preconcentration of trace Pb (II) and Cd (II) with 2-mercaptobenzothiazole impregnated Amberlite XAD-1180 resin and their determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Arab J Chem 10:19–23
Yao L, Wang X, Liu H, Lin C, Pang L, Yang J, Zeng Q (2017) Optimization of ultrasound-assisted magnetic retrieval-linked ionic liquid dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of cadmium and lead in water samples by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. J Ind Eng Chem 56:321–326
Yoke JT III, Weiss JF, Tollin G (1963) Reactions of triethyl amine with copper(I) and copper(II) halides. Inorg Chem 2:1210–1216
Zhang Q, De Oliveira Vigier K, Royer S, Jérôme F (2012) Deep eutectic solvents: syntheses, properties and applications. Chem Soc Rev 41:7108–7146
Acknowledgements
Support of this investigation by the research council of faculty of pharmacy, Tehran University of medical sciences and the research council of Payame Noor University is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ezoddin, M., Lamei, N., Siami, F. et al. Deep Eutectic Solvent Based Air Assisted Ligandless Emulsification Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for Preconcentration of Some Heavy Metals in Biological and Environmental Samples. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101, 814–819 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2456-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2456-8