Abstract
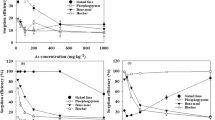
Pb, one of the constituents of ammunition, was identified as a contaminant in an ammunition destruction site. The present study aimed to assess Pb adsorption in the horizons of an uncontaminated representative soil profile of the region where the ammunition destruction site is located. Batch test experiments were performed to determine Pb adsorption in soil horizons, using solutions with natural and modified pH. The ISOFIT software was used to select the isotherm model that best fit Pb adsorption in soil horizons. The results showed that the Langmuir model is the best fit, because it presented the lowest corrected Akaike information criterion value. In addition, the graphical analysis indicated a Langmuir-type isotherm. The Langmuir isotherm parameter (Q0) indicated lower Pb adsorption capacity in the surface soil layers when compared with that in the deeper layers. The change in the initial solution pH influenced Pb adsorption, mainly in superficial horizons. Thus, the risk of soil Pb contamination might be more pronounced in the surface soil layers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed IM, Helal AA, El Aziz NA, Gamal R, Shaker NO, Helal AA (2015) Influence of some organic ligands on the adsorption of lead by agricultural soil. Arab J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.03.012
Alloway BJ (2005) Bioavailability of elements in soil. In: Selinus O, Alloway B, Centeno JA, Finkelman RB, Fuge R, Lindh U, Smedley P (eds) Essentials of medical geology—impacts of the natural environment on public health. Elsevier Academic Press, Burlington, pp 347–372
Ampleman G, Thiboutot S, Gagnon A, Marois A, Martel R, Lefebvre R (1998) Study of the impacts of OB/OD activity on soils and ground water at the destruction area in CFAD Dundurn. DREV R-9827. Defense Research Development Canada (DRDC-Valcartier). http://www.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a359042.pdf. Accessed 6 May 2017
Appel C, Ma L (2002) Concentration, pH, and surface charge effects on cadmium and lead sorption in three tropical soils. J Environ Qual 31:581–589
Appel C, Ma LQ, Rhue RD, Kennelley E (2003) Point of zero charge determination in soils and minerals via traditional methods and detection of electroacoustic mobility. Geoderma 113:77–93
Bolster CH, Hornberger GM (2007) On the use of linearized Langmuir equations. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:1796–1806
Bradl HB (2004) Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soils and soils constituents. J Colloid Interface Sci 277:1–18
Brum T (2010) Técnicas de remediação ambiental de áreas contaminadas por explosivos. Dissertation, Instituto Militar de Engenharia
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model selection and multimodel inference: a practical information–theoretic approach. Springer, New York
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2004) Multimodel inference: understanding AIC and BIC in model selection. Sociol Methods Res 33:261–304
Cantrell KJ, Serne RJ, Last GV (2002) Applicability of the linear sorption isotherm model to represent contaminant transport processes in site-wide performance assessments. Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. Technical reports, PNNL-14576. http://www.pnl.gov/main/publications/external/technical_reports/PNNL-14576.pdf. Accessed 6 May 2017
Donagemma GK, Campos DVB, Calderano SB, Teixeira WG, Viana JHM (2011) Manual de métodos de análise de solos. Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária, Rio de Janeiro. https://www.embrapa.br/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/990374/manual-de-metodos-de-analise-de-solo Accessed 18 Mar 2018
Fontes MPF, Alleoni LRF (2006) Electrochemical attributes and availability of nutrients, toxic elements, and heavy metals in tropical soils. Sci Agric 63:589–608
Giles CH, MacEwan TH, Nakhwa SN, Smith D (1960) Studies in adsorption, part XI. A system of classification of solution adsorption isotherms and its use in diagnosis and adsorptive mechanism and measurements of specific area of solids. Chem Soc J 1:3973–3993
Guedes JN (2009) Diagnóstico e estudo da variabilidade espacial da contaminação por metais pesados em solos e águas superficiais de área de destruição de munição. Dissertation, Universidade Federal Rural do Rio de Janeiro
Guedes JN, Amaral Sobrinho NMB, Ceddia MB, Vilella ALO, Tolón-Becerra A, Lastra-Bravo XB (2012) Concentration and spatial distribution of lead in soil used for ammunition destruction. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89:775–781
Gustafsson JP (2016) Visual MINTEQ, ver. 3.1. KTH, SEED, Stockholm, Sweden. https://vminteq.lwr.kth.se/. Accessed 6 Jun 2017
Ji GL, Li HY (1997) Electrostatic adsorption of cations. In: Yu TR (ed) Chemistry of variable charge soils. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 64–111
Lee SZ, Chang L, Yang HH, Chen CM, Liu MC (1998) Adsorption characteristics of lead onto soils. J Hazard Mater 63:37–49
Ma LQ, Hardison DW Jr, Harris WG, Cao X, Zhou Q (2007) Effects of soil property and soil amendment on weathering of abraded metallic Pb in shooting ranges. Water Air Soil Pollut 178:297–307
Martínez-Villegas N, Flores-Vélez LM, Domínguez O (2004) Sorption of lead in soil as a function of pH: a study case in México. Chemosphere 57:1537–1542
Matott LS (2007) ISOFIT documentation and user’s guide version 1.2. State University of New York at Buffalo. http://www.eng.buffalo.edu/~lsmatott/IsoFit/IsoFitMain.html. Accessed 5 May 2017
Matott LS, Rabideau AJ (2008) ISOFIT—a program for fitting sorption isotherms to experimental data. Environ Model Softw 23:670–676
Naidu R, Kookana RS, Sumner ME, Harter RD, Tiller KG (1997) Cadmium sorption and transport in variable charge soils: a review. J Environ Qual 26:602–617
National Institute of Standards and Technology-NIST (2002) Standard Reference Materials-SRM 2709, 2710 and 2711 Addendum Issue Date: 18 January
Rodrigues ACD (2010) Utilização de Brachiaria decumbens na fitoestabilização de solos contaminados por metais pesados provenientes da destruição de munição. Dissertation, Universidade Federal Rural do Rio de Janeiro
Santos HG, Jacomine PKT, Anjos LHC, Oliveira VA, Lumbreras JF, Coelho MR, Almeida JA, Cunha TJF, Oliveira JB (2013) Sistema brasileiro de classificação de solos. Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária, Rio de Janeiro
Shafqat MN, Pierzynski GM (2014) The Freundlich adsorption isotherm constants and prediction of phosphorus bioavailability as affected by different phosphorus sources in two Kansas soils. Chemosphere 99:72–80
Silva AAD (2010) Estudo da contaminação por metais pesados em área de destruição de munição. Dissertation, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro
Silva FAS, Azevedo CAV (2016) The Assistat Software Version 7.7 and its use in the analysis of experimental data. Afr J Agric Res 11:3733–3740
Silva AAD, Brum T, Barbosa MC, Marques MES (2014) Investigation of a military site for destruction of ammunitions by open detonation with emphasis on Pb and Cu contamination. In: Paper presented at XVII Congresso Brasileiro de Mecânica dos Solos e Engenharia Geotécnica (COBRAMSEG), ABMS (Brazilian Society of Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering), Goiânia, GO, Brazil, 9–13 Sept 2014
Silveira MLA, Alleoni LRF, Guilherme LRG (2003) Biosolids and heavy metals in soils. Sci agric 60:793–806
Soares MR, Casagrande JC (2009) Adsorção e Modelos. In: Ribeiro MR, Nascimento CWA, Cantalice JRB, Ribeiro Filho MR (eds) Tópicos em Ciência do Solo. SBCS, Viçosa, pp 71–201
USDA – United States Department of Agriculture (1998) Soil Quality Indicators: pH. Washington, DC. https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs142p2_052208.pdf. Accessed 6 May 2017
USEPA – United States Environmental Protection Agency (1992) Batch-type procedures for estimating soil adsorption of chemicals. Washington, DC. https://nepis.epa.gov/Exe/ZyPDF.cgi/100018S4.PDF?Dockey=100018S4.PDF. Accessed 6 May 2017
USEPA – United States Environmental Protection Agency (1999) Understanding variation in partition coefficient, kd, values. Volume I: the kd model, methods of measurement, and application of chemical reaction codes. Washington, DC. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-05/documents/402-r-99-004a.pdf. Accessed 6 May 2017
USEPA – United States Environmental Protection Agency (2007) Method 3051 A—microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils, and oils. Washington, DC. https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-12/documents/3051a.pdf. Accessed 6 May 2017
van Raij B, Peech M (1972) Electrochemical properties of some Oxisols and Alfisols of the tropics. Soil Sci Soc Am J 36:587–593
Wilkinson J, Watt D (2006) Review of demilitarization and disposal techniques for munitions and related materials. Munitions Safety Information Analysis Centre (MSIAC), NATO Headquarters, Brussels, Belgium. http://www.rasrinitiative.org/pdfs/MSIAC-2006.pdf. Accessed 6 May 2017
Xavier RBL (2012) Impacto da atividade de destruição de munição na vegetação circundante—estudo de caso para metais pesados. Dissertation, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Rio de Janeiro State Research Foundation (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro - FAPERJ - Grant No. E-26/111.451/2014) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, S.A., de Lucena Tavares, S.R. & Barbosa, M.C. Pb Adsorption on Soil Typical to an Ammunition Destruction Site. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101, 365–371 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2403-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2403-8