Abstract
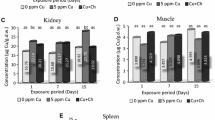
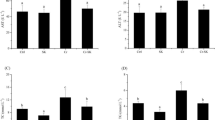
Discovering cost effective strategies to reduce cadmium (Cd) uptake is of great concern for consumer food safety in the aquaculture industry. This study investigated the protective effects of calcium (Ca) on Cd uptake in co-cultured silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) and triangle sail mussel (Hyriopsis cumingii). The results show that Ca—depending on its applied concentration—caused a significant decrease in the Cd uptake into muscle (by 48 %–72 %), gills (by 51 %–57 %), liver (by 52 %–81 %) and kidney (by 54 %–81 %) of silver carp (p < 0.001), as well as foot (by 8 %–32 %) and visceral mass (by 40 %–47 %) of triangle sail mussels (p < 0.05). The results indicate that Ca treatment is an effective means of reducing Cd accumulation in aquaculture. Since Ca is often used to increase the quality of pearls produced by triangle sail mussel, the quality of co-cultured edible fish might improve as a consequence of the potentially reduced Cd uptake.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Tawwab M, Mousa MAA, Ahmad MH, Sakr SFM (2007) The use of calcium pre-exposure as a protective agent against environmental copper toxicity for juvenile Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) Aquaculture 264:236–246
Baldisserotto B, Kamunde C, Matsuo A, Wood C (2004) A protective effect of dietary calcium against acute waterborne cadmium uptake in rainbow trout. Aquat Toxicol 67:57–73
Banaee M, Mehrpak M, Haghi BN, Noori A (2015) Amelioration of cadmium-induced changes in biochemical parameters of the muscle of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) by vitamin C and chitosan. Inter J Aquat Biol 2:271–362
Bonga S, Lock R, Fu H, Pratap H (1989) Effect of waterborne and dietary cadmium on plasma ions of the teleost Oreochromis mossambicus in relation to water calcium levels. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 18:568–575
Carroll JJ, Ellis SJ, Oliver WS (1979) Influences of hardness constituents on the acute toxicity of cadmium to brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 22:575–581
Chen DQ, Xiong F, Wang K, Chang Y (2009) Status of research on Yangtze fish biology and fisheries. Environ Biol Fish 85:337–357
Franklin NM, Glover CN, Nicol JA, Wood CM (2005) Calcium/cadmium interactions at uptake surfaces in rainbow trout: waterborne versus dietary routes of exposure. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:2954–2964
Fu J, Hu X, Tao XC, Yu HX, Zhang XW (2013) Risk and toxicity assessments of heavy metals in sediments and fishes from the Yangtze River and Taihu Lake, China. Chemosphere 93:1887–1895
Ge XP (2013) Current status and development trend of large freshwater fish industry in China. Fish Guide Rich 14:17–21
Ghosh L, Adhikari S (2006) Accumulation of heavy metals in freshwater fish-an assessment of toxic interactions with calcium. Am J Food Tech 1:139–148
Han Y, Chen G, Chen YH, Shen ZG (2015) Cadmium toxicity and alleviating effects of exogenous salicylic acid in Iris hexagona. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 95:802–976
Hansen JA, Welsh PG, Lipton J, Cacela D, Dailey AD (2002) Relative sensitivity of bull trout (Salvelinus confluentus) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) to acute exposures of cadmium and zinc. Environ Toxicol Chem 21:67–75
Hollis L, Muench L, Playle RC (1997) Influence of dissolved organic matter on copper binding, and calcium on cadmium binding, by gills of rainbow trout. J Fish Biol 50:703–720
Hollis L, McGeer JC, McDald DG, Wood CM (2000) Protective effects of calcium against chronic waterborne cadmium exposure to juvenile rainbow trout. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:2725–2734
Li J, Li YS (2009) Aquaculture in China—freshwater pearl culture. World Aquacult 40:60–62
Liu Y C, Gao L, Li Z G, Liu SQ, Huang KL, Li J (2010) Analysis on heavy metals pollution status and reasons in Xiangjiang River and discussion on its countermeasures. Environ Protect Sci 36:26–29
Marasinghe Wadige CPM, Maher WA, Taylor AM, Krikowa F (2014) Exposure-dose-response relationships of the freshwater bivalve Hyridella australis to cadmium spiked sediments. Aquat Toxicol 152:361–371
Meinelt T, Playle RC, Pietrock M, Burnison BK, Wienke A, Steinberg CEW (2001) Interaction of cadmium toxicity in embryos and larvae of zebrafish (Danio rerio) with calcium and humic substances. Aquat Toxicol 54:205–215
Qiu JW, Xie ZC, Wang WX (2005) Effects of calcium on the uptake and elimination of cadmium and zinc in Asiatic clams. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48:278–287
SMOHC (2012) National food safety standard for pollutants limits of food (GB 2762–2012) Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China
Song YF, Luo Z, Chen QL, Liu X, Liu CX, Zheng JL (2013) Protective effects of calcium pre-exposure against waterborne cadmium toxicity in Synechogobius hasta. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 65:105–121
Squadrone S, Bruioli E, Monaco G, Koya MK, Prearo M, Gennero S, Dominici A, Abete MC (2016) Human exposure to metals due to consumption of fish from an artificial lake basin close to an active mining area in Katanga (D.R. Congo). Sci Total. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.02.167 (in press)
Wicklund A, Runn P (1988) Calcium effects on cadmium uptake, redistribution, and elimination in minnows, Phoxinus phoxinus, acclimated to different calcium concentrations. Aquat Toxicol 13:109–122
Yan LL, Zhang GF, Liu QG, Li JL (2009) Optimization of culturing the freshwater pearl mussels, Hyriopsis cumingii with filter feeding Chinese carps (bighead carp and silver carp) by orthogonal array design. Aquaculture 292:60–66
Yi YJ, Wang ZY, Zhang K, Yu GA, Duan XH (2008) Sediment pollution and its effect on fish through food chain in the Yangtze River. Int J Sediment Res 23:338–347
Zeng LY, Li WL, Li Y (2012) Analysis and evaluation on heavy metals of fishes in Changsha section of Xiangjiang River. Light Ind Sci Tech 9:94–95
Zhang T, Zhang Y, Li DL, Xiao Ty, Li J (2013) Exposure of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) to environmentally relevant levels of cadmium: hematology, muscle physiology, and implications for stock enhancement in the Xiangjiang River (Hunan, China). Sci China Ser C 56: 66–72
Zhang W, Zhang YH, Zhang L, Lin Q (2016) Bioaccumulation of metals in tissues of seahorse colleted from coastal China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96:281–288
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Andrew Harbicht and Matthew Yates, Concordia University, for their critical reading and editing. This study was supported by the Special Fund for Agro-Scientific Research in the Public Interest (No. 201503108) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31100282).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Pi, J., Wang, J. et al. Protective Effects of Calcium on Cadmium Accumulation in Co-Cultured Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) and Triangle Sail Mussel (Hyriopsis cumingii). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 97, 826–831 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1952-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1952-y