Abstract
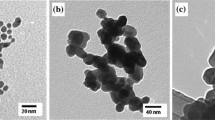
Effects of benzoic acid (BA) on physicochemical properties and ecotoxicities of CuO nanoparticles (CuONPs) in model aqueous media were studied. The CuONPs had larger hydrodynamic sizes and higher surface zeta potentials during 96 h of settling in the presence of BA than when the BA were not present. BA interaction with CuONPs is shown to promote dissolved Cu release from CuONPs in a dose-dependent manner. The contribution of free Cu2+-ions to growth inhibition toxicity of the CuONP suspensions at a toxicologically relevant concentration for the green alga Scenedesmus obliquus was around 22 %, indicating that dissolved fraction was not the major source of toxicity of CuONPs. The toxicity of CuONPs increased as the BA concentration increased. BA significantly altered total antioxidant capacity of CuONPs-exposed algal cells. The mechanism of the BA effect on the CuONPs toxicity may be mainly associated with degree of agglomeration, dissolved Cu, and particle-induced oxidative stress.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calabrese EJ (2008) Hormesis: why it is important to toxicology and toxicologists. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1451–1474
Chang X, Vikesland PJ (2009) Effects of carboxylic acids on nC60 aggregate formation. Environ Pollut 157:1072–1080
Chen Y, Miao Y, Huang L, Li J, Sun H, Zhao Y, Yang J, Zhou W (2014) Antioxidant activities of saponins extracted from Radix Trichosanthis: an in vivo and in vitro evaluation. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:86
Griffitt RJ, Luo J, Gao J, Bonzongo JC, Barber DS (2008) Effects of particle composition and species on toxicity of metallic nanomaterials in aquatic organisms. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1972–1978
Jiang X, Herricks T, Xia Y (2002) CuO nanowires can be synthesized by heating copper substrates in air. Nano Lett 2:1333–1338
Kahru A, Dubourguier HC (2010) From ecotoxicology to nanoecotoxicology. Toxicology 269:105–119
Karlsson HL, Cronholm P, Gustafsson J, Möller L (2008) Copper oxide nanoparticles are highly toxic: a comparison between metal oxide nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Chem Res Toxicol 21:1726–1732
Lowry GV, Gregory KB, Apte SC, Lead JR (2012) Transformations of nanomaterials in the environment. Environ Sci Technol 46:6893–6899
Mortimer M, Kasemets K, Vodovnik M, Marinsek-Logar R, Kahru A (2011) Exposure to CuO nanoparticles changes the fatty acid composition of protozoa Tetrahymena thermophila. Environ Sci Technol 45:6617–6624
OECD (2006) Freshwater alga and cyanobacteria, growth inhibition test, Nr. 201; OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Paris. http://www.oecd.org
Pan B, Xing B (2008) Adsorption mechanisms of organic chemicals on carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 42:9005–9013
Quik JT, Lynch I, Van Hoecke K, Miermans CJ, De Schamphelaere KA, Janssen CR, Dawson KA, Stuart MA, Van De Meent D (2010) Effect of natural organic matter on cerium dioxide nanoparticles settling in model fresh water. Chemosphere 81:711–715
Strobel BW (2001) Influence of vegetation on low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids in soil solution—a review. Geoderma 99:169–198
Thomas CR, George S, Horst AM, Ji Z, Miller RJ, Peralta-Videa JR, Xia T, Pokhrel S, Mädler L, Gardea-Torresdey JL, Holden PA, Keller AA, Lenihan HS, Nel AE, Zink JI (2011) Nanomaterials in the environment: from materials to high-throughput screening to organisms. ACS Nano 5:13–20
Wang Z, Li J, Zhao J, Xing B (2011) Toxicity and internalization of CuO nanoparticles to prokaryotic alga Microcystis aeruginosa as affected by dissolved organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 45:6032–6040
Wang Z, Chen JW, Li X, Shao JP, Peijnenburg WJGM (2012) Aquatic toxicity of nanosilver colloids to different trophic organisms: contributions of particles and free silver ion. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:2408–2413
Wang Z, Quik JT, Song L, Van Den Brandhof EJ, Wouterse M, Peijnenburg WJGM (2015a) Humic substances alleviate the aquatic toxicity of polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silver nanoparticles to organisms of different trophic levels. Environ Toxicol Chem 34:1239–1245
Wang Z, Wang S, Chen M, Xu D, Tang L, Wang D (2015b) Elucidating adsorption mechanisms of phthalate estersupon carbon nanotubes/graphene and natural organic acid competitive effects in waterby DFT and MD calculations. Bull Korean Chem Soc 36:1631–1636
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21407080) and the Foundation Research Project of Jiangsu Province (BK20140987 and BK20150891). We also thank the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent (2014r020 and 2015r011) and the open fund by Laboratory/Equipment Management Office (15KF052 and 15KF053) of Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Zhuang Wang and Hao Fang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Fang, H. & Wang, S. Benzoic Acid Interactions Affect Aquatic Properties and Toxicity of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 97, 159–165 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1804-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1804-9