Abstract
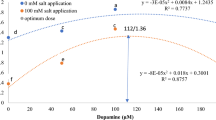
We studied the antioxidant responses of macrophyte Vallisnerria natans seedlings to combined ammonia (0, 0.21, and 0.85 mg L−1) and microcystin-LR (MC-LR) (0, 10, and 50 μg L−1) for 7 days. Results showed that superoxide dismutase, catalase (CAT), peroxidase, and glutathione were significantly induced by the mixtures of ammonia and MC-LR, and there were significant interactions between ammonia and MC-LR. Specially, CAT increased about fivefold at ammonia 0.85 mg L−1 and MC-LR 50 μg L−1 on day 3. Malondialdehyde fluctuated with both ammonia and MC-LR, and significant interactions were detected between the two stressors. Changes in all the measured variables were time-dependent.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asada K (1999) The water–water cycle in chloroplasts: scavenging of active oxygens and dissipation of excess photons. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 50:601–639
Blokhina O, Virolainen E, Fagerstedt KV (2003) Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: a review. Ann Bot 91:179–194
Bowler C, Montagu MV, Inze D (1992) Superoxide dismutase and stress tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 43:83–116
Cao T, Xie P, Li ZQ, Ni LY, Zhang M, Xu J (2009) Physiological stress of high NH4 + concentration in water column on the submersed macrophyte Vallisneria Natans L. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82:296–299
Casanova MT, Burch MD, Brock MA, Bond PM (1999) Does toxic Microcystis aeruginosa affect aquatic plant establishment. Environ Toxicol 14:97–109
Codd GA (1995) Cyanobacterial toxins: occurrence, properties and biological significance. Water Sci Technol 32:149–156
Dittmann E, Wiegand C (2006) Cyanobacterial toxins—occurrence, biosynthesis and impact on human affairs. Mol Nutrit Food Res 50:7–17
Doyotte A, Cossu C, Jacquin MC, Babut M, Vasseur P (1997) Antioxidant enzymes, glutathione and lipid peroxidation as relevant biomarkers of experimental or field exposure in the gills and the digestive gland of the freshwater bivalve Unio tumidus. Aquat Toxicol 39:93–110
Duy TN, Lam PK, Shaw GR, Connell DW (2000) Toxicology and risk assessment of freshwater cyanobacterial (blue-green algal) toxins in water. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 163:113–185
Emerson KR, Russo RC, Lund RE, Thurston RV (1975) Aqueous ammonia equilibrium calculations: effect of pH and temperature. J Fish Res Board Can 32:379–383
Hilt S, Gross EM, Hupfer M, Morscheid H, Mählmann J, Melzer A, Poltz J, Sandrock S, Scharf E-M, Schneider S, Van de Weyer K (2006) Restoration of submerged vegetation in shallow eutrophic lakes—guideline and state of the art in Germany. Limnologica 36:155–171
Jiang JL, Gu XY, Song R, Wang XR, Yang LY (2011) Microcystin-LR induced oxidative stress and ultrastructural alterations in mesophyll cells of submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. J Hazard Mater 190:188–196
Mackintosh C, Beattie KA, Klumpp S, Cohen P, Codd GA (1990) Cyanobacterial microcystin-LR is a potent and specific inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1 and phosphatase-2A from both mammals and higher-plants. FEBS Lett 264:187–192
Nimptsch J, Pflugmacher S (2007) Ammonia triggers the promotion of oxidative stress in the aquatic macrophyte Myriophyllum mattogrossense. Chemosphere 66:708–714
Ortiz-Rodríguez R, Wiegand C (2010) Age related acute effects of microcystin-LR on Daphnia magna biotransformation and oxidative stress. Toxicon 56:1342–1349
Pandey S, Parvez S, Sayeed I, Haque R, BinHafeez B, Raisuddin S (2003) Biomarkers of oxidative stress: a comparative study of river Yamuna fish Wallago attu. Sci Total Environ 309:105–115
Pearce SK, Woodin SJ, van der Wal R (2003) Physiological and growth responses of the montane bryophyte Racomitrium lanuginosum to atmospheric nitrogen deposition. New Phytol 160:145–155
Pflugmacher S (2004) Promotion of oxidative stress in the aquatic macrophyte Ceratophyllum demersum during biotransformation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin-LR. Aquat Toxicol 70:169–178
Pflugmacher S, Codd GA, Steinberg CEW (1997) Effects of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin-LR on detoxication enzymes in aquatic plants. Environ Toxicol 14:111–115
Pflugmacher S, Aulhorn M, Grimm B (2007) Influence of a cyanobacterial crude extract containing microcystin-LR on the physiology and antioxidative defence systems of different spinach variants. New Phytol 175:482–489
Rudolph H, Voigt JU (1986) Effects of NH3–N and NO3–N on growth and metabolism of Sphagnum magellanicum. Physiol Plant 66:339–343
Stüven J, Pflugmacher S (2007) Antioxidative stress response of Lepidium sativum due to exposure to cyanobacterial secondary metabolites. Toxicon 50:85–93
Takenaka S, Otsu R (1999) Effects of l-cysteine and reduced glutathione on the toxicities of microcystin-LR: the effect for acute liver failure and inhibition of protein phosphatase activity. Aquat Toxicol 48:65–68
Wang C, Zhang SH (2008) Metabolic adaptations to ammonia-induced oxidative stress in leaves of the submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans (Lour.) Hara. Aquat Toxicol 87:88–98
Wiegand C, Pflugmacher S (2005) Ecotoxicological effects of selected cyanobacterial secondary metabolites. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 203:201–218
Xiao KY, Yu D, Wu ZH (2007) Differential effects of water depth and sediment type on clonal growth of the submersed macrophyte Vallisneria natans. Hydrobiologia 589:265–272
Yin LY, Huang JQ, Li DH, Liu YD (2005) Microcystin-RR uptake and its effects on the growth of submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans (L.) Hara. Environ Toxicol 20:308–313
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the State Key Fundamental Research and Development Program of China (2008CB418102), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK2011073).
Conflict of interest
We declare that there is no potential.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, J., Li, J., Zhang, J. et al. Time-Dependent Oxidative Stress Responses of Submerged Macrophyte Vallisneria natans Seedlings Exposed to Ammonia in Combination with Microcystin Under Laboratory Conditions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89, 67–72 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0633-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0633-8