Abstract
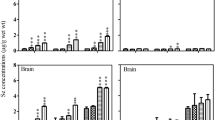
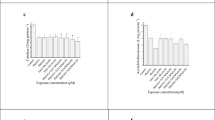
Aquatic organisms are considered excellent biomarkers of mercury (Hg) occurrence in the environment. Selenium (Se) acts in antagonism to this metal, stimulating its elimination, and reducing its toxicity. In this paper, tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) were chronically acclimated in sub-lethal Hg2+, Hg2+ + Se4+ and Hg2+ + Se6+ concentrations. Distribution and bioaccumulation of both elements were evaluated in fish tissues. The kidney was the main target of the Hg and Se uptake, and the presence of Hg induced the Se hepatic elimination. The Hg bioaccumulation in the gill, spleen and heart were higher in the presence of Se6+ than in the presence of Se4+.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi H, Malm O, Branches FJP (1995) Human exposure to mercury due to gold mining in the Tapajós river basin, Amazon, Brazil: speciation of mercury in human hair, blood and urine. Water, Air and Soil Poll 80:85–94. doi:10.1007/BF01189656
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Helath Association, Washington, DC
Beyrouty P, Chan HM (2006) Co-consumption of selenium and vitamin E altered the reproductive and developmental toxicity of methylmercury in rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 28:49–58. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2005.11.002
Cabañero AI, Madrid Y, Cámara C (2006) Selenium long-term administration and its effect on mercury toxicity. J Agr Food Chem 54:4461–4468. doi:10.1021/jf0603230
Chen C, Qu L, Zhao J, Liu S, Deng G, Li B, Zhang P, Chai Z (2006) Accumulation of mercury, selenium and their binding proteins in porcine kidney and liver from mercury-exposed areas with the investigation of their redox responses. Sci Total Environ 366:627–637. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2005.12.021
França JG, Paiva MJTR, Lombardi JV, Carvalho S, Seriani R (2007) Chronic mercury chloride toxicity combined with selenium, by means of hematological study in tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Bioikos 21:11–19
Gailer J (2007) Arsenic-selenium and mercury-selenium bonds in biology. Coordin Chem Rev 251:234–254. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.07.018
Hansen JC, Kristensen P, Al-Masri SN (1981) Mercury/selenium interaction. Nord Vet Med 33:57–64
Kim JH, Birks E, Heisinger JF (1977) Protective action of selenium against mercury in northern creek chubs. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 17:132–136. doi:10.1007/BF01685539
Montgomery DC (2001) Design and analysis of experiments, 5th edn. John Wiley, New York
Patel B, Chandy JP, Patel S (1988) Do selenium and glutathione inhibit the toxic effects of mercury in marine lamellibranchs? Sci Total Environ 76:147–165. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(88)90104-0
Pelgrom MGJ, Lamers LPM, Lock RAC, Balm PHM (1995) Interactions between copper and cadmium modify metal organ distribution in mature tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Environ Pollut 90:415–423. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(95)00022-J
Pelletier E (1986) Modification de la bioaccumulation du selenium chez Mytilus edulis en presence du mercure organique et inorganique. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 43:203–210
Quevauviller P, Vercoutere K, Muntau H, Griepink B (1993) Certified reference material (CRM414) for the quality control of trace element analysis in plankton. Fresen J Anal Chem 345:12–17. doi:10.1007/BF00323319
Su L, Wang M, Yin A, Wang H, Chen L, Sun L, Ruan D (2008) The interaction of selenium and mercury in the accumulations and oxidative stress of rat tissues. Ecotox Environ Safe 70:483–489. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.05.018
Wang W, Wong RSK, Wang J, Yen Y (2004) Influences of different selenium species on the uptake and assimilation of Hg(II) and methylmercury by diatoms and green mussels. Aquat Toxicol 68:39–50. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2004.02.003
Acknowledgments
Our gratitude to FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do estado de São Paulo), by the grant obtained in the Project no: 00/14460-3 and CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico) for the scholarship to Gabriel G. A. Carvalho (Process no: 110751/2005-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carvalho, G.G.A., de França, J.G., Dias, D.C. et al. Selenite and Selenate Effects on Mercury (Hg2+) Uptake and Distribution in Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus L., Assessed by Chronic Bioassay. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82, 300–304 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9617-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9617-0