Abstract
Background
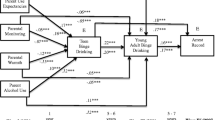
This study aimed to investigate whether parental monitoring skills mediate the effect of hazardous parental alcohol consumption on adolescents’ lifetime alcohol use.
Methods
This three wave longitudinal study was conducted with 884 families (n = 1,768 participants) to evaluate the effectiveness of a family-based drug prevention program for adolescents and parents across 12 Brazilian cities. We used structural equation mediation modeling to analyze the effect of hazardous parental alcohol consumption at baseline on adolescents’ lifetime alcohol use at 12-month follow-up, mediated by parental monitoring skills latent dimension at 6-month follow-up.
Results
We found a significant indirect effect of parents’ hazardous alcohol use on adolescents’ alcohol use through parental monitoring (OR:1.18, 95%CI:1.02;1.36).
Conclusion
Our finding underscores the importance of comprehensive preventive family alcohol approaches targeting adolescent alcohol use, which should consider both parental drinking behavior and monitoring practices.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Whiteford HA, Degenhardt L, Rehm J, Baxter AJ, Ferrari AJ, Erskine HE et al (2013) Global burden of disease attributable to mental and substance use disorders: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. The Lancet [Internet]. 382(9904):1575–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61611-6
Hall WD, Patton G, Stockings E, Weier M, Lynskey M, Morley KI et al (2016) Why young people’s substance use matters for global health. Lancet Psychiatry [Internet]. 3(3):265–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(16)00013-4
Rossow I, Keating P, Felix L, McCambridge J (2016) Does parental drinking influence children’s drinking? A systematic review of prospective cohort studies. Addiction [Internet]. 111(2):204–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.13097
Bandura A (1977) Social Learning Theory [Internet]. United States: Pearson Education (US); 256 p. https://academic.oup.com/joc/article/28/3/12-29/4371624
Latendresse SJ, Rose RJ, Viken RJ, Pulkkinen L, Kaprio J, Dick DM (2008) Parenting mechanisms in Links between Parents’ and adolescents’ Alcohol Use behaviors. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32(2):322–330
Mahedy L, MacArthur GJ, Hammerton G, Edwards AC, Kendler KS, Macleod J et al (2018) The effect of parental drinking on alcohol use in young adults: the mediating role of parental monitoring and peer deviance. Addiction 113(11):2041–2050
Ryan SM, Jorm AF, Lubman DI (2010) Parenting Factors Associated with Reduced Adolescent Alcohol Use: A Systematic Review of Longitudinal Studies. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry [Internet]. 44(9):774–83. http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/https://doi.org/10.1080/00048674.2010.501759
Yap MBH, Cheong TWK, Zaravinos-Tsakos F, Lubman DI, Jorm AF (2017) Modifiable parenting factors associated with adolescent alcohol misuse: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Addiction [Internet]. 112(7):1142–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.13785
Coombes L, Allen D, Marsh M, Foxcroft D (2009) The strengthening families Programme (SFP) 10-14 and substance misuse in Barnsley: the perspectives of facilitators and families. Child Abuse Review: J Br Association Study Prev Child Abuse Negl 18(1):41–59
Lima CT, Freire ACC, Silva APB, Teixeira RM, Farrell M, Prince M (2005) Concurrent and construct validity of the audit in an urban Brazilian sample. Alcohol and Alcoholism [Internet]. 40(6):584–9. http://academic.oup.com/alcalc/article/40/6/584/126118/CONCURRENT-AND-CONSTRUCT-VALIDITY-OF-THE-AUDIT-IN
ABEP, Brazilian Association of Research Companies. Critério Brasil 2015 e atualização da distribuição de classes para 2016. [Internet]. ABEP (2016) www.abep.org/criterio-brasil
Brown TA (2006) Confirmatory Factor Analysis for Applied Research, Second Edition. New York: The Guilford Press; 462 p
Asparouhov T, Muthén B (2006) Multilevel modeling of complex survey data. In: Proceedings of the Joint Statistical Meeting. Seattle; pp. 2718–26
Valente JY, Cogo-Moreira H, Sanchez ZM (2018) Predicting latent classes of drug use among adolescents through parental alcohol use and parental style: a longitudinal study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol [Internet]. 0(0):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-018-1645-4
Valente JY, Cogo-Moreira H, Sanchez ZM (2020) Evaluating the effects of parenting styles dimensions on adolescent drug use: secondary analysis of #Tamojunto randomized controlled trial. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 29(7)
Carver H, Elliott L, Kennedy C, Hanley J (2017) Parent–child connectedness and communication in relation to alcohol, tobacco and drug use in adolescence: An integrative review of the literature. Drugs: Education, Prevention and Policy [Internet]. 24(2):119–33. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/https://doi.org/10.1080/09687637.2016.1221060
van der Zwaluw CS, Scholte RHJ, Vermulst AA, Buitelaar JK, Verkes RJ, Engels RCME (2008) Parental problem drinking, parenting, and adolescent alcohol use. J Behav Med [Internet]. 31(3):189–200. http://link.springer.com/https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-007-9146-z
Alati R, Najman JM, Kinner SA, Mamun AA, Williams GM, O’Callaghan M et al (2005) Early predictors of adult drinking: a birth cohort study. Am J Epidemiol 162(11):1098–1107
LaFreniere S, Newman LG, Graham MW (2021) J. Parental support and monitoring influences on adolescent alcohol use: a peer selection mediation model. Ment Health Addict Res. 6(2)
Pedersen GA, Smallegange E, Coetzee A, Hartog K, Turner J, Jordans MJD et al (2019) A Systematic Review of the Evidence for Family and Parenting Interventions in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Child and Youth Mental Health Outcomes. J Child Fam Stud [Internet]. 28(8):2036–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-019-01399-4
Acknowledgements
We thank all the SARCs, field researchers, the MMFDH team, and especially the families who participated in the study.
Funding
The Ministry of Women, Family and Human Rights (MMFDH) supported this study through grant number TED 02/2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dra. Juliana Y. Valente conceptualized and designed the study, conducted the data analyses, and drafted the initial manuscript. Dra. Patricia Galvão, Msc. Miguel Henrique Santos, Dra. Fabiane Gurbert reviewed and revised the manuscript. Dra. Zila Sanchez is responsible for the grant acquisition and data collection and approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Y. Valente, J., de Oliveira Galvão, P.P., da Silva dos Santos, M.H. et al. The role of monitoring skills in mediating the association between parent’s hazardous alcohol consumption and adolescents’ drinking. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-024-02682-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-024-02682-6