Abstract
Key message
An uncharacterized gene, ZmAPRG, isolated by map-based cloning, enhances acid phosphatase activity and phosphate concentration in maize leaf during phosphate starvation.
Abstract
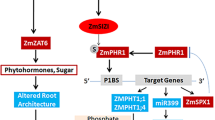
Acid phosphatase (APase) plays important roles in the absorption and utilization of phosphate (Pi) during maize growth. The information on genes regulating the acid phosphatase activity (APA) in maize leaves remains obscured. In a previous study, we delimited the quantitative trait locus, QTL-AP9 for APA to a region of about 546 kb. Here, we demonstrate that the GRMZM2G041022 located in the 546 kb region is a novel acid phosphatase-regulating gene (ZmAPRG). Its overexpression significantly increased the APA and Pi concentration in maize and rice leaves. Subcellular localization of ZmAPRG showed that it was anchored on the plasma and nuclear membrane. The transcriptome analysis of maize ZmAPRG overexpressing lines (ZmAPRG OE) revealed 1287 up-regulated and 392 down-regulated genes. Among these, we found APase, protein phosphatase, and phosphate transporter genes, which are known to be implicated in the metabolism and utilization of Pi. We inferred the ZmAPRG functions as an upstream regulation node, directly or indirectly regulating APases, protein phosphatases, and phosphate transporter genes involved in Pi metabolism and utilization in maize. These findings will pave the way for elucidating the mechanism of APase regulation, absorption and utilization of Pi, and would facilitate maize breeding for efficient use of fertilizers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelson PH (1999) A potential phosphate crisis. Science 283:2015
Ai P, Sun SJ, Fan X, Xin W, Guo Q, Yu L, Shen Q, Wu P, Miller AJ, Xu G (2009) Two rice phosphate transporters, OsPht1;2 and OsPht1;6, have different functions and kinetic properties in uptake and translocation. Plant J 57:798–809
Baldwin JC, Karthikeyan AS, Raghothama KG (2001) LEPS2, a phosphorus starvation-induced novel acid phosphatase from tomato. Plant Physiol 125:728–737
Baldwin JC, Karthikeyan AS, Cao A, Raghothama KG (2008) Biochemical and molecular analysis of LePS2;1: a phosphate starvation induced protein phosphatase gene from tomato. Planta 228:273–280
Bucher M (2007) Functional biology of plant phosphate uptake at root and mycorrhiza interfaces. New Phytol 173:11–26
Carman GM, Han GS (2006) Roles of phosphatidate phosphatase enzymes in lipid metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci 31:694–699
Chen J, Xu L, Cai Y, Xu J (2008) QTL mapping of phosphorus efficiency and relative biologic characteristic in maize (Zea mays L.) at two sites. Plant Soil 313:251–266
Cheng Y, Zhou W, El Sheery NI, Peters C, Li M, Wang X, Huang J (2011) Characterization of the Arabidopsis glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase (GDPD) family reveals a role of the plastid-localized AtGDPD1 in maintaining cellular phosphate homeostasis under phosphate starvation. Plant J 66:781–795
Clark RB, Brown JC (1974) Differential phosphorus uptake by phosphorus-stressed corn inbreds 1. Crop Sci 14:505–508
Del Vecchio H (2012) Biochemical and Molecular characterization of AtPAP25, a novel cell wall-localized purple acid phosphatase isozyme upregulated by phosphate-starved Arabidopsis thaliana. Dissertation, Queen's University
Dionisio G, Madsen CK, Holm PB (2011) Cloning and characterization of purple acid phosphatase phytases from wheat, barley, maize, and rice. Plant Physiol 156:1087–1100
Duff SMG, Sarath G, Plaxton WC (1994) The role of acid phosphatases in plant phosphorus metabolism. Physiol Plant 90:791–800
Elliott G, Läuchli Andre (1986) Evaluation of an acid phosphatase assay for detection of phosphorus deficiency in leaves of maize (Zea mays L.). J Plant Nutr 9:1469–1477
Ferreira JA, Zwinderman AH (2006) On the Benjamini–Hochberg method. Ann Stat 34:1827–1849
Gao W, Lu L, Qiu W, Wang C, Shou H (2017) OsPAP26 encodes a major purple acid phosphatase and regulates phosphate remobilization in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 58:885
Gaume A, Mächler F, León CD, Narro L, Frossard E (2001) Low-P tolerance by maize (Zea mays L.) genotypes: significance of root growth, and organic acids and acid phosphatase root exudation. Plant Soil 228:253–264
George TS, Gregory PJ, Hocking P, Richardson AE (2008) Variation in root-associated phosphatase activities in wheat contributes to the utilization of organic P substrates in vitro, but does not explain differences in the P-nutrition of plants when grown in soils. Environ Exp Bot 64:239–249
Hammond J, Broadley M, White PJ (2004) Genetic responses to phosphorus deficiency. Ann Bot 94:323–332
Hanks SK, Hunter T (1995) Protein kinases 6. The eukaryotic protein kinase superfamily: kinase (catalytic) domain structure and classification. FASEB J 9:576–596
Howarth RW, Sharpley A, Dan W (2002) Sources of nutrient pollution to coastal waters in the United States: implications for achieving coastal water quality goals. Estuaries 25:656–676
Hunter Tony (1995) Protein kinases and phosphatases: the Yin and Yang of protein phosphorylation and signaling. Cell 80:225
Ito S, Nozoye T, Sasaki E, Imai M, Shiwa Y, Shibata-Hatta M, Ishige T, Fukui K, Ito K, Nakanishi H (2015) Strigolactone regulates anthocyanin accumulation, acid phosphatases production and plant growth under low phosphate condition in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 10:e0119724
Iyamuremye F, Dick RP, Baham J (1996) Organic amendments and phosphorus dynamics: II. Distribution of soil phosphorus fractions. Soil Sci 161:436–443
Kuang R, Chan KH, Yeung E, Lim BL (2009) Molecular and biochemical characterization of AtPAP15, a purple acid phosphatase with phytase activity, in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 151:199
Lei M, Liu Y, Zhang B, Zhao Y, Wang X, Zhou Y, Raghothama KG, Liu D (2011a) Genetic and genomic evidence that sucrose is a global regulator of plant responses to phosphate starvation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 156:1116–1130
Lei M, Zhu C, Liu Y, Karthikeyan AS, Bressan RA, Raghothama KG, Liu D (2011b) Ethylene signalling is involved in regulation of phosphate starvation-induced gene expression and production of acid phosphatases and anthocyanin in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 189:1084
Li K, Xu C, Zhang K, Yang A, Zhang J (2010a) Proteomic analysis of roots growth and metabolic changes under phosphorus deficit in maize (Zea mays L.) plants. Proteomics 7:1501–1512
Li M, Guo X, Zhang M, Wang X, Zhang G, Tian Y, Wang Z (2010b) Mapping QTLs for grain yield and yield components under high and low phosphorus treatments in maize (Zea mays L.). Plant Sci 178:454–462
Li Z, Gao Q, Liu Y, He C, Zhang X, Zhang J (2011) Overexpression of transcription factor ZmPTF1 improves low phosphate tolerance of maize by regulating carbon metabolism and root growth. Planta 233:1129–1143
Liu C, Su J, Stephen GUK, Wang H, Song A, Chen F, Zhu Y, Chen S, Jiang J (2018) Overexpression of phosphate transporter gene CmPht1;2 facilitated pi uptake and alternated the metabolic profiles of chrysanthemum under phosphate deficiency. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00686
Lu L, Qiu W, Gao W, Tyerman SD, Shou H, Wang C (2016) OsPAP10c, a novel secreted acid phosphatase in rice, plays an important role in the utilization of external organic phosphorus. Plant Cell Environ 39:2247–2259
Ma W, Ma L, Li J, Wang F, Sisák I, Zhang F (2011) Phosphorus flows and use efficiencies in production and consumption of wheat, rice, and maize in China. Chemosphere 84:814–821
Mehra P, Pandey BK, Giri J (2017) Improvement in phosphate acquisition and utilization by a secretory purple acid phosphatase (OsPAP21b) in rice. Plant Biotechnol J 15:1054–1067
Moss B (2008) Water pollution by agriculture. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 363:659–666
Muchhal US, Pardo JM, Raghothama KG (1996) Phosphate transporters from the higher plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:10519–10523
Naismith RW, Johnson MW, Thomas WI (1974) Genetic control of relative Calcium, phosphorus, and manganese accumulation on chromosome 9 in Maize. Crop Sci 14:845–849
Nanamori M, Shinano T, Wasaki J, Yamamura T, Rao IM, Osaki M (2004) Low phosphorus tolerance mechanisms: phosphorus recycling and photosynthate partitioning in the tropical forage grass, Brachiaria hybrid cultivar Mulato compared with rice. Plant Cell Physiol 45:460–469
Nielsen NE, Barber SA (1978) Differences among genotypes of corn in the kinetics of P uptake. Agron J 70:695–698
Pandey BK, Mehra P, Verma L, Bhadouria J, Giri J (2017) OsHAD1, a haloacid dehalogenase-like APase enhances phosphate accumulation. Plant Physiol 174:00571.02017
Porebski S, Bailey LG, Baum BR (1997) Modification of a CTAB DNA extraction protocol for plants containing high polysaccharide and polyphenol components. Plant Mol Biol Rep 15:8–15
Qiu H, Mei X, Liu C, Wang J, Wang G, Wang X, Liu Z, Cai Y (2013) Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci for acid phosphatase activity in maize leaf under low phosphorus stress. Mol Breed 32:629–639
Qiu H, Liu C, Yu T, Mei X, Wang G, Wang J, Cai Y (2014) Identification of QTL for acid phosphatase activity in root and rhizosphere soil of maize under low phosphorus stress. Euphytica 197:133–143
Rubio V (1999) A type 5 acid phosphatase gene from Arabidopsis thaliana is induced by phosphate starvation and by some other types of phosphate mobilising/oxidative stress conditions. Plant J 19:579–589
Rutherford S, Moore I (2002) The Arabidopsis Rab GTPase family: another enigma variation. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:518–528
Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Shane MW, Stigter K, Fedosejevs ET, Plaxton WC (2014) Senescence-inducible cell wall and intracellular purple acid phosphatases: implications for phosphorus remobilization in Hakea prostrata (Proteaceae) and Arabidopsis thaliana (Brassicaceae). J Exp Bot 65:6097–6106
Silva ÁED, Gabelman WH (1992) Screening maize inbred lines for tolerance to low-P stress condition. Plant Soil 146:181–187
Song JY, Kaeppler SM (2001) Induction of maize acid phosphatase activities under phosphorus starvation. Plant Soil 237:109–115
Song H, Yin Z, Chao M, Ning L, Zhang D, Deyue YU (2014) Functional properties and expression quantitative trait loci for phosphate transporter GmPT1 in soybean. Plant Cell Environ 37:462–472
Suen PK, Zhang S, Sun SS (2015) Molecular characterization of a tomato purple acid phosphatase during seed germination and seedling growth under phosphate stress. Plant Cell Rep 34:981–992
Tabatabai MA, Bremner JM (1969) Use of p -nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol Biochem 1:301–307
Tian J, Wang C, Zhang Q, He X, Whelan J, Shou H (2012) Overexpression of OsPAP10a, a root-associated acid phosphatase, increased extracellular organic phosphorus utilization in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 54:631–639
Tran HT, Hurley BA, Plaxton WC (2010a) Feeding hungry plants: the role of purple acid phosphatases in phosphate nutrition. Plant Sci 179:14–27
Tran HT, Qian W, Hurley BA, She YM, Wang D, Plaxton WC (2010b) Biochemical and molecular characterization of AtPAP12 and AtPAP26: the predominant purple acid phosphatase isozymes secreted by phosphate-starved Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Environ 33:1789–1803
Trinidad TJ, Gamuyao R, Chin JH, Dalid C, Haefele S, Heuer S (2009) Candidate genes in the major rice QTL for phosphate uptake Pup1. Philipp J Crop Sci 34:94
Turner BL, Baxter R, Whitton BA (2002) Seasonal phosphatase activity in three characteristic soils of the English uplands polluted by long-term atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Environ Pollut 120:313–317
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allan DL (2003) Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol 157:423–447
Wang L, Liu D (2011) The Arabidopsis purple acid phosphatase AtPAP10 is predominantly associated with the root surface and plays an important role in plant tolerance to phosphate limitation. Plant Physiol 157:1283–1299
Wang X, Wang Y, Tian J, Lim BL, Yan X, Liao H (2009) Overexpressing AtPAP15 enhances phosphorus efficiency in soybean. Plant Physiol 151:233–240
Wang C, Huang W, Ying Y, Li S, Secco D, Tyerman S, Whelan J, Shou H (2012a) Functional characterization of the rice SPX-MFS family reveals a key role of OsSPX-MFS1 in controlling phosphate homeostasis in leaves. New Phytol 196:139–148
Wang L, Dong J, Gao Z, Liu D (2012b) The Arabidopsis gene HYPERSENSITIVE TO PHOSPHATE STARVATION 3 encodes ethylene overproduction 1. Plant Cell Physiol 53:1093–1105
Wang X, Bai J, Liu H, Sun Y, Shi X, Ren Z (2013) Overexpression of a maize transcription factor ZmPHR1 improves shoot inorganic phosphate content and growth of Arabidopsis under low-phosphate conditions. Plant Mol Biol Rep 31:665–677
Wang L, Lu S, Zhang Y, Li Z, Du X, Liu D (2014) Comparative genetic analysis of Arabidopsis purple acid phosphatases AtPAP10, AtPAP12, and AtPAP26 provides new insights into their roles in plant adaptation to phosphate deprivation. J Integr Plant Biol 56:299–314
Wasaki J, Maruyama H, Tanaka M, Yamamura T, Dateki H, Shinano T, Ito S, Osaki M (2010) Overexpression of the LASAP2 gene for secretory acid phosphatase in white lupin improves the phosphorus uptake and growth of tobacco plants. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 55:107–113
Wissuwa M, Wegner J, Ae N, Yano M (2002) Substitution mapping of Pup1: a major QTL increasing phosphorus uptake of rice from a phosphorus-deficient soil. Theor Appl Genet 105:890–897
Yirgalem C, Naga GM, Rivero R (2010) Phosphorus run-off assessment in a watershed. J Environ Monit JEM 13:66–73
Yuan H, Liu D (2008) Signaling components involved in plant responses to phosphate starvation. J Integr Plant Biol 50:849–859
Zelazny E, Borst JW, Muylaert M, Batoko H, Hemminga MA, Chaumont F (2007) FRET imaging in living maize cells reveals that plasma membrane aquaporins interact to regulate their subcellular localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:12359–12364
Zhang D, Song H, Cheng H, Hao D, Wang H, Kan G, Jin H, Yu D (2014a) The acid phosphatase-encoding gene GmACP1 contributes to Soybean tolerance to low-phosphorus stress. PLoS Genet 10:e1004061
Zhang F, Wu XN, Zhou HM, Wang DF, Jiang TT, Sun YF, Cao Y, Pei WX, Sun SB, Xu GH (2014b) Overexpression of rice phosphate transporter gene OsPT6 enhances phosphate uptake and accumulation in transgenic rice plants. Plant Soil 384:259–270
Zhang Y, Thomas CL, Xiang J, Long Y, Wang X, Zou J, Luo Z, Ding G, Cai H, Graham NS (2016) QTL meta-analysis of root traits in Brassica napus under contrasting phosphorus supply in two growth systems. Sci Rep 6:33113
Zhang Y, Anis GB, Wang R, Wu W, Yu N, Shen X, Zhan X, Cheng S, Cao L (2018) Genetic dissection of QTL against phosphate deficiency in the hybrid rice ‘Xieyou9308’. Plant Growth Regul 84:123–133
Zhu J, Kaeppler SM, Lynch JP (2005a) Mapping of QTL controlling root hair length in maize (Zea mays L.) under phosphorus deficiency. Plant Soil 270:299–310
Zhu J, Kaeppler SM, Lynch JP (2005b) Mapping of QTLs for lateral root branching and length in maize (Zea mays L.) under differential phosphorus supply. Theor Appl Genet 111:688–695
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371700) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2018C052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration
The experiments comply with the current laws of the country.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Matthias Wissuwa.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Coding sequence blast result of Expansin A20 between 082 and Ye107. Fig. S2 Promoter sequence blast result of VQ family gene between 082 and Ye107. Fig. S3 Coding sequence blast result of GRMZM2G122476 between 082 and Ye107. Fig. S4 Coding sequence blast result of Zinc finger family gene between 082 and Ye107. Fig. S5 Coding sequence blast result of ZmAPRG between 082 and Ye107. Fig. S6 Expression patterns of candidate genes in Ye107 and the NIL. Fig. S7 Promoter sequence blast result of ZmAPRG between 082 and Ye107. Fig. S8 Prediction of transmembrane helices in ZmAPRG of 082 and Ye107 (DOCX 707 kb)
Table S1
Primer sequences for preliminary candidate genes. Table S2 Primer sequences for the qRT-PCR. Table S3 Primer sequences for the ZmAPRG.Table S4 Biomass of Y107 and NIL plants hydroponically supplied with HP and LP condition (DOCX 21 kb)
Table S5
Gene information of 2443 up-regulated genes (DOCX 439 kb)
Table S6
Gene information of 1400 down-regulated genes (DOCX 277 kb)
Table S7
Enriched Go term analysis for the 1287 up-regulated genes (DOCX 29 kb)
Table S8
Enriched Go term analysis for the 392 down-regulated genes (DOCX 18 kb)
Table S9
Gene information of 1287 up-regulated genes involved in enriched Go term (DOCX 236 kb)
Table S10
Gene information of 392 down-regulated genes involved in enriched Go term (DOCX 95 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, T., Liu, C., Lu, X. et al. ZmAPRG, an uncharacterized gene, enhances acid phosphatase activity and Pi concentration in maize leaf during phosphate starvation. Theor Appl Genet 132, 1035–1048 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3257-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3257-5